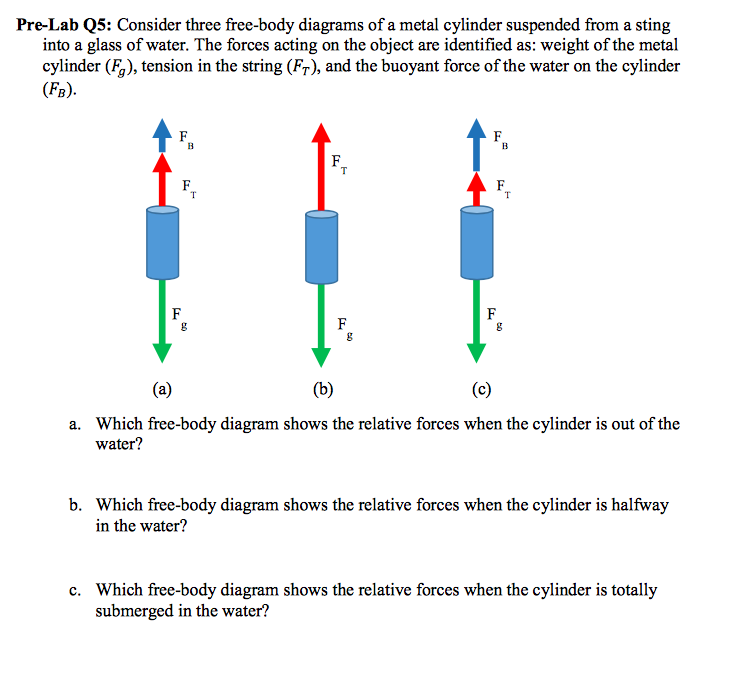
36 buoyant force free body diagram
A submerged object suspended by a string. b. A floating object. Draw to scale. Buoyant Force: The force that acts on the object keeping it floating above ...1 answer · Top answer: Part (a): Consider an object of mass MM is submerged completely in the fluid and it is suspended by a massless string. The free-body diagram of the object ...
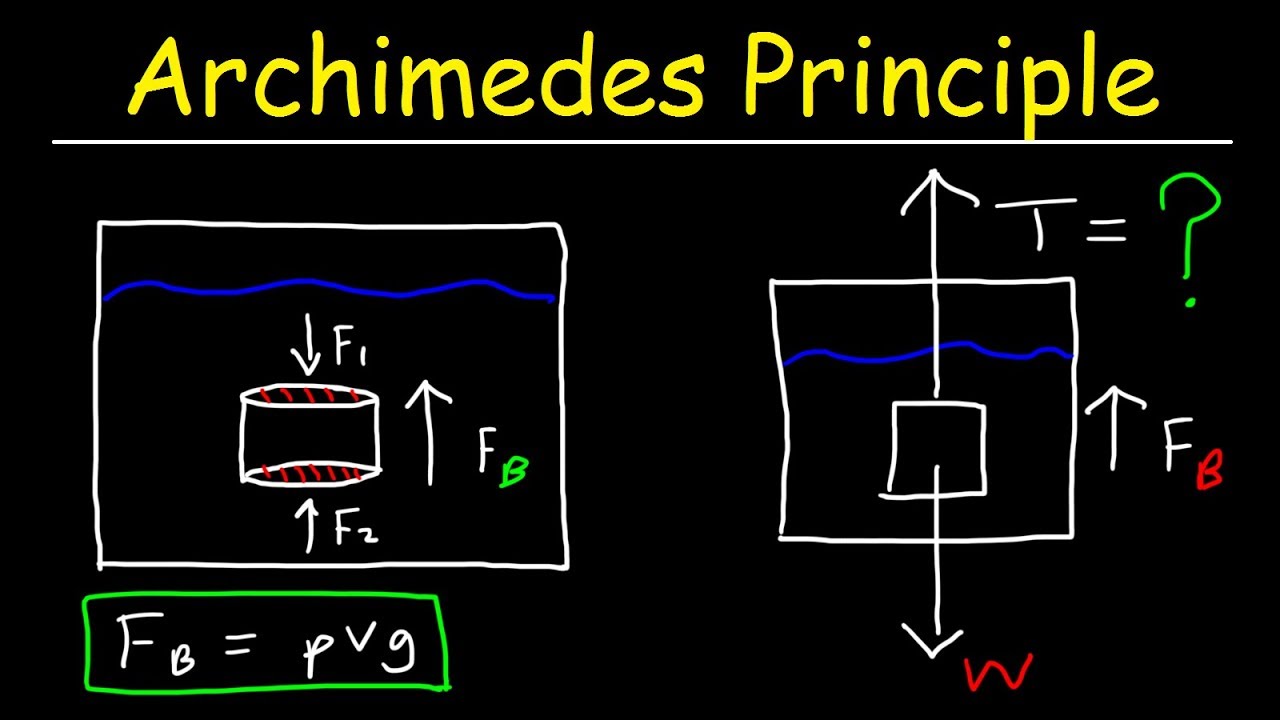
In physics and engineering a free body diagram force diagram or fbd is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces movements and resulting reactions on a body in a given condition. In this case the raft and the chests are in a fluid and the force due to the pressure of a fluid is called the buoyant force.
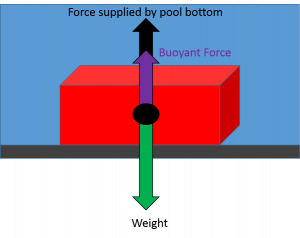
same free body diagram as the fish? Are the forces exerted by the water on the fish any different from the forces exerted on the water that took ... A floating object experiences a buoyant force due only to the submerged portion of the object F buoyant m f= V submergedrg. 3/3/13 3 “Light” versus Regular Coke Why does one sink but the
Buoyant force free body diagram
Often a Free Body Diagram is useful or necessary to solve a problem that involves forces. Follow these steps, and you’ll solve any problem with little difficulty. 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object (see below for what is a good FBD). 2. Break the forces up into components. 3.
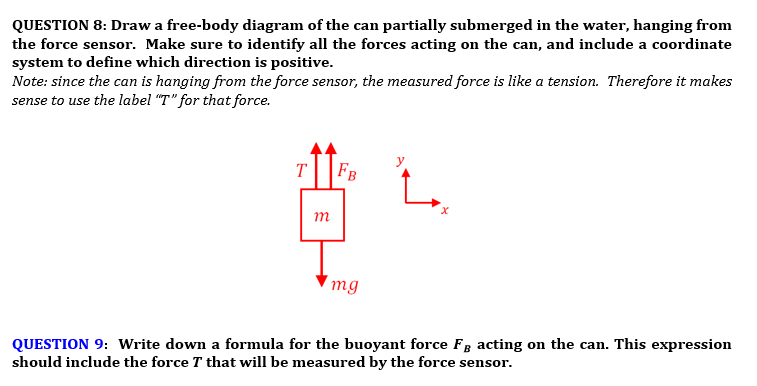
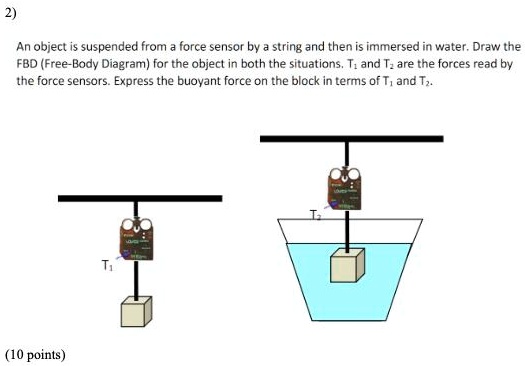
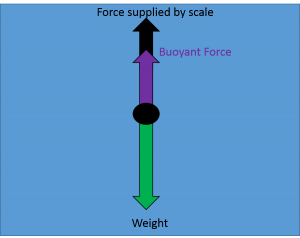
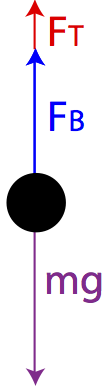
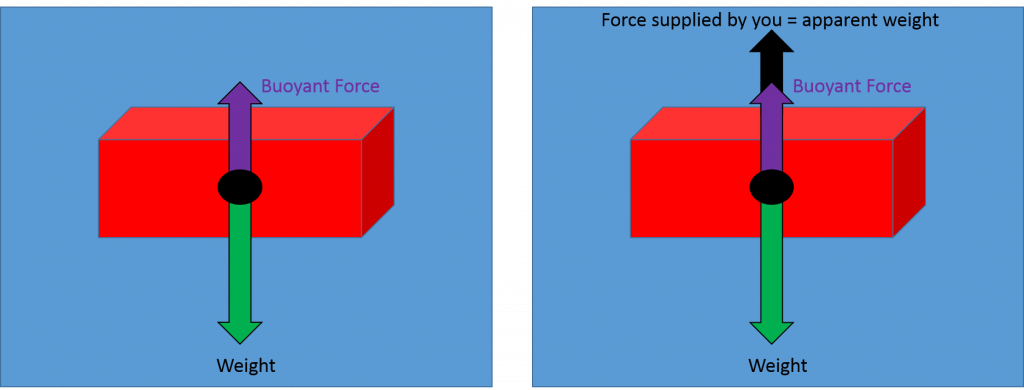
Well, that's correct, but your free body diagram technically has 3 forces acting on the object: its weight down (30N), The buoyant force up (F_b), and tension in the scale's cord acting up (20N). So your FBD equation using Newtyon 1 is from which 20 + F_b -30 = 0, that is, F_b = 10N up, whuch is what you got, but don't take shortcuts.
This question helped distinguish between a misuse of the term ''buoyant force'' and a misunderstanding of the forces exerted on a submerged object. Performance ...
Buoyant force free body diagram.
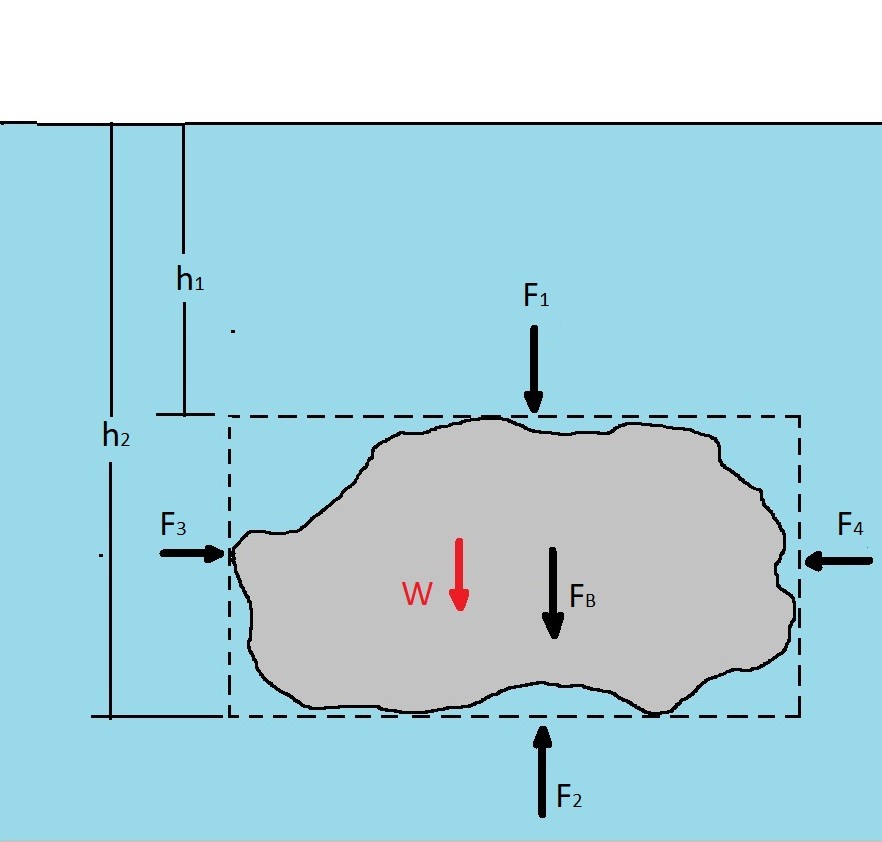
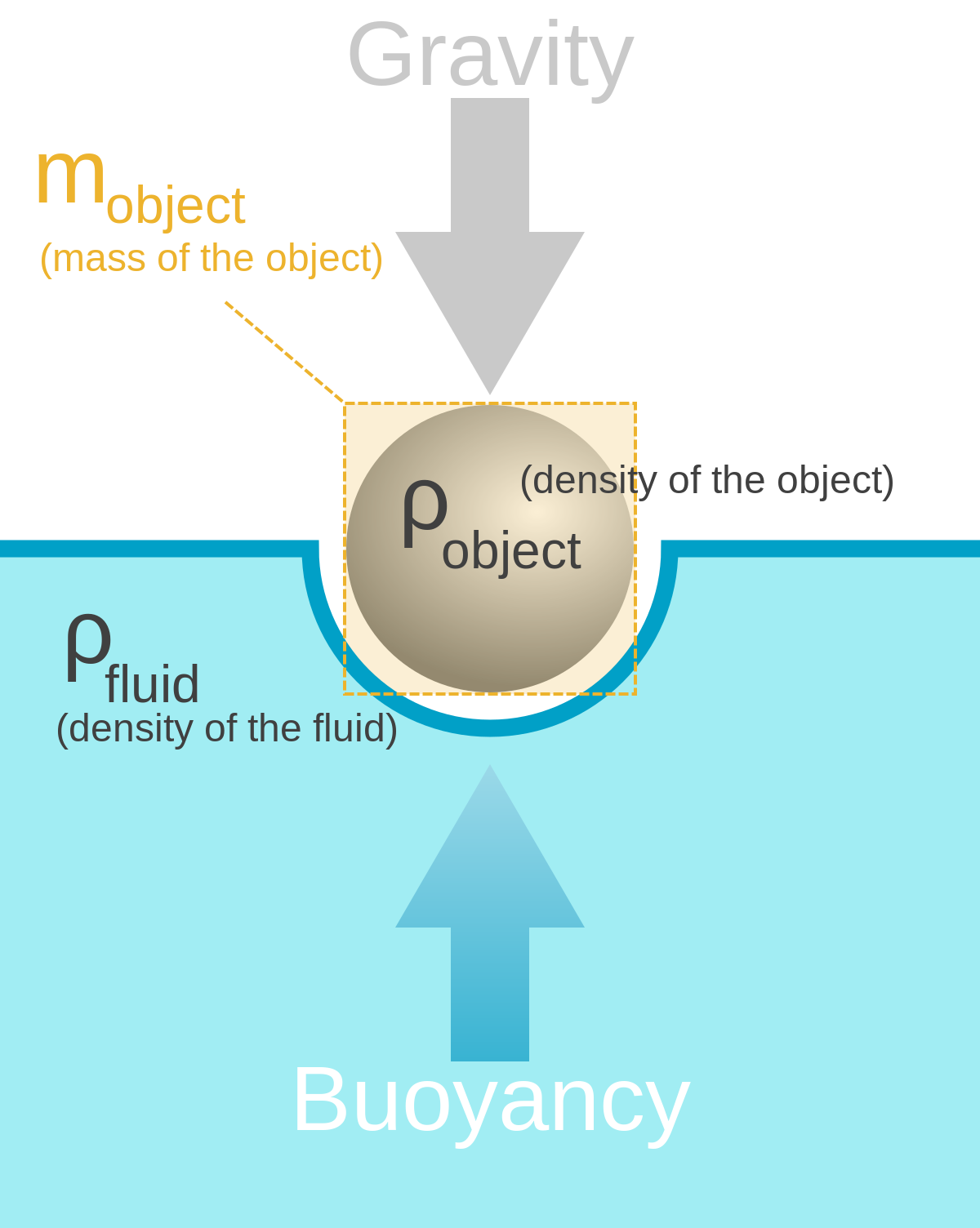
forces free-body-diagram density fluid-statics buoyancy. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited Oct 22 '18 at 20:21. ... Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, ...
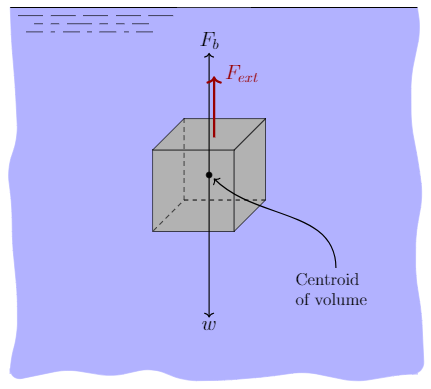
(a) On the block’s free-body diagram, we draw a downward force of gravity, applied by the Earth. We also draw an upward force of tension (applied by the string), and, because the block displaces some fluid, an upward buoyant force (applied by the fluid). The block is in equilibrium, so there must be no net force acting on the block.
Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass after it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. Which force is measured with the spring scale? Apply Newton’s second law to your free body diagram in Pre-Lab Question 2 to derive a general equation for the buoyant force. Show your work.
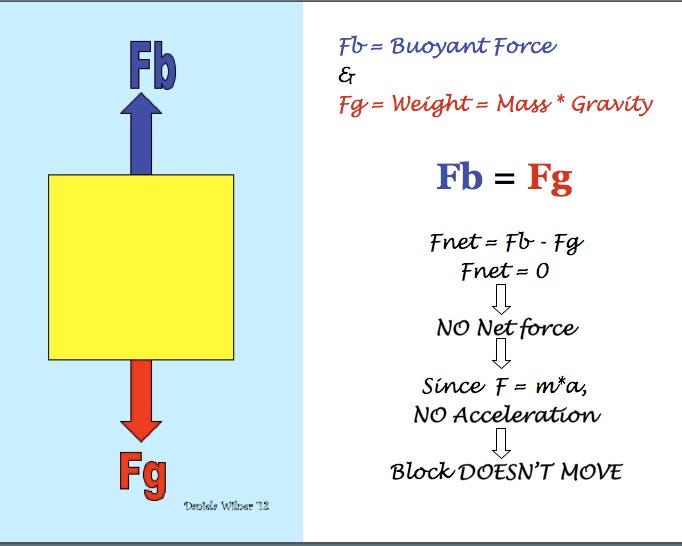
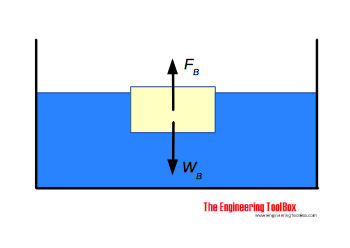
B) In the diagram you made, draw the forces that are acting on the block (i.e. a Free-Body Diagram). Next to your diagram, apply Newton’s 2nd Law and then solve algebraically for the buoyant force. You should conclude that F B = W. If this is not your conclusion then go back and check your work. If you still do not get this result
So why do fluids exert an upward buoyant force on submerged objects? ... so we should first draw a free body diagram (i.e. force diagram) for the balloon.
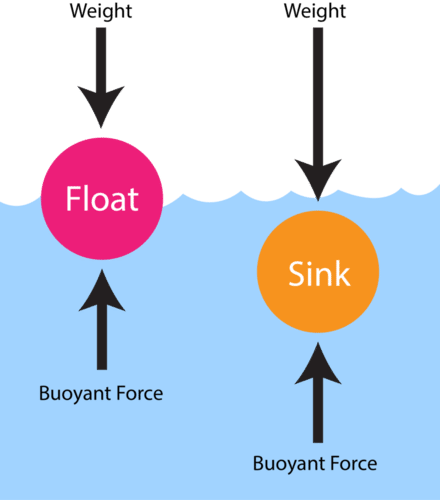
Density, Buoyancy And Free Body Diagrams Updated: 7-Jan-16 Page 4 of 4 11. The red block in the “Same Volume” floats in water. The blue block sinks in water. Using your data from the chart above and your knowledge of buoyant forces and weights, what volume of the blue block would float above the water line if the blue block was placed on
Buoyant force free body diagram. This second weight called the apparent weight differs from the first due to the buoyant force. Why isnt normal force included on the free body diagram. It pushes out from the surfaces and keeps them from falling into each other. The upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid whether fully ...
Sketch the free-body diagram of the blocks in Figure 9.2 as they float in the container of water. Note that each block is in equilibrium – what does that imply ...
21 Nov 2020 — For now, know that the buoyant force is written as Fb and acts mostly on objects in fluids in the opposite direction as gravity. The normal ...

















0 Response to "36 buoyant force free body diagram"
Post a Comment