37 diagram of a transverse wave
Transverse Wave Diagram: study guides and answers on Quizlet Discover free flashcards, games and test preparation activities designed to help you learn about Transverse Wave Diagram and other subjects. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves | Superprof A diagram of an electromagnetic wave. Longitudinal Waves and Transverse Waves. In a transverse wave, the displacement leads to a polarization of the medium. In a longitudinal wave, this disturbance happens in a different way that does not produce these perpendicular peaks and troughs.
transverse wave | Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Diagram... Transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic (e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves.
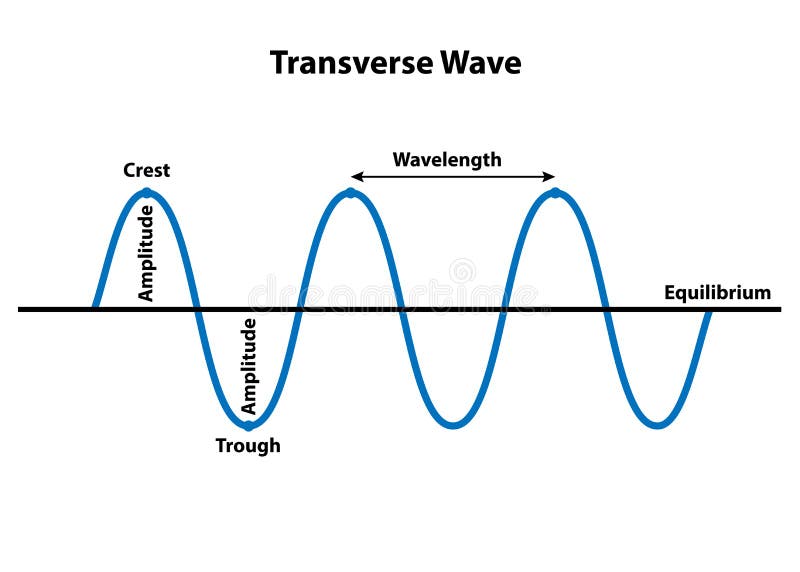
Diagram of a transverse wave
PDF Microsoft Word - Ch 14 - Light and ReflectionReg.doc As shown below, an electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave consisting of mutually. perpendicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields. A ray is a straight line that represents the path of a very narrow beam of light. Ray diagrams are drawings used to depict the path of light rays. PDF Article Title: An Automated Algorithm for Identifying and Tracking... These diagrams show the locations of bright (as well as dark) structures that cross the slit and whose motion is projected onto the observational plane. Inclusion of a rotation angle of q will reduce the apparent amplitudes of transverse waves within the plane of observation. Frontiers | Transverse and Quantum Localization of Light: A Review... In particular, transverse localization (TL) occurs in optical fibers, which are disordered orthogonal to and translationally invariant along the propagation direction. The resonant and tube-shaped localized states act as micro-fiber-like single-mode transmission channels.
Diagram of a transverse wave. Lesson Explainer: Comparing Transverse and Longitudinal Waves To explain what a transverse wave is, we will return to our first example of a string of balls. The wave made by this up-and-down motion is a transverse wave. Example 4: Transverse and Longitudinal Waves. A transverse wave is shown in the diagram. What is the amplitude of the wave? Answer. Transverse wave - Wikipedia In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Transverse waves cannot propagate in a gas or a liquid because there is no mechanism for driving motion perpendicular to the propagation of the wave. Shown below is more detail on the attachment of the loudspeaker to the pipe. The loudspeaker is driven by the amplified output of a tunable oscillator. 16.1 Traveling Waves | University Physics Volume 1 Characteristics of a Wave. A transverse mechanical wave propagates in the positive x-direction through a spring (as shown in (Figure)(a)) with a constant A wave on a guitar string is an example of a transverse wave. The disturbance of the string moves perpendicular to the propagation of the wave.
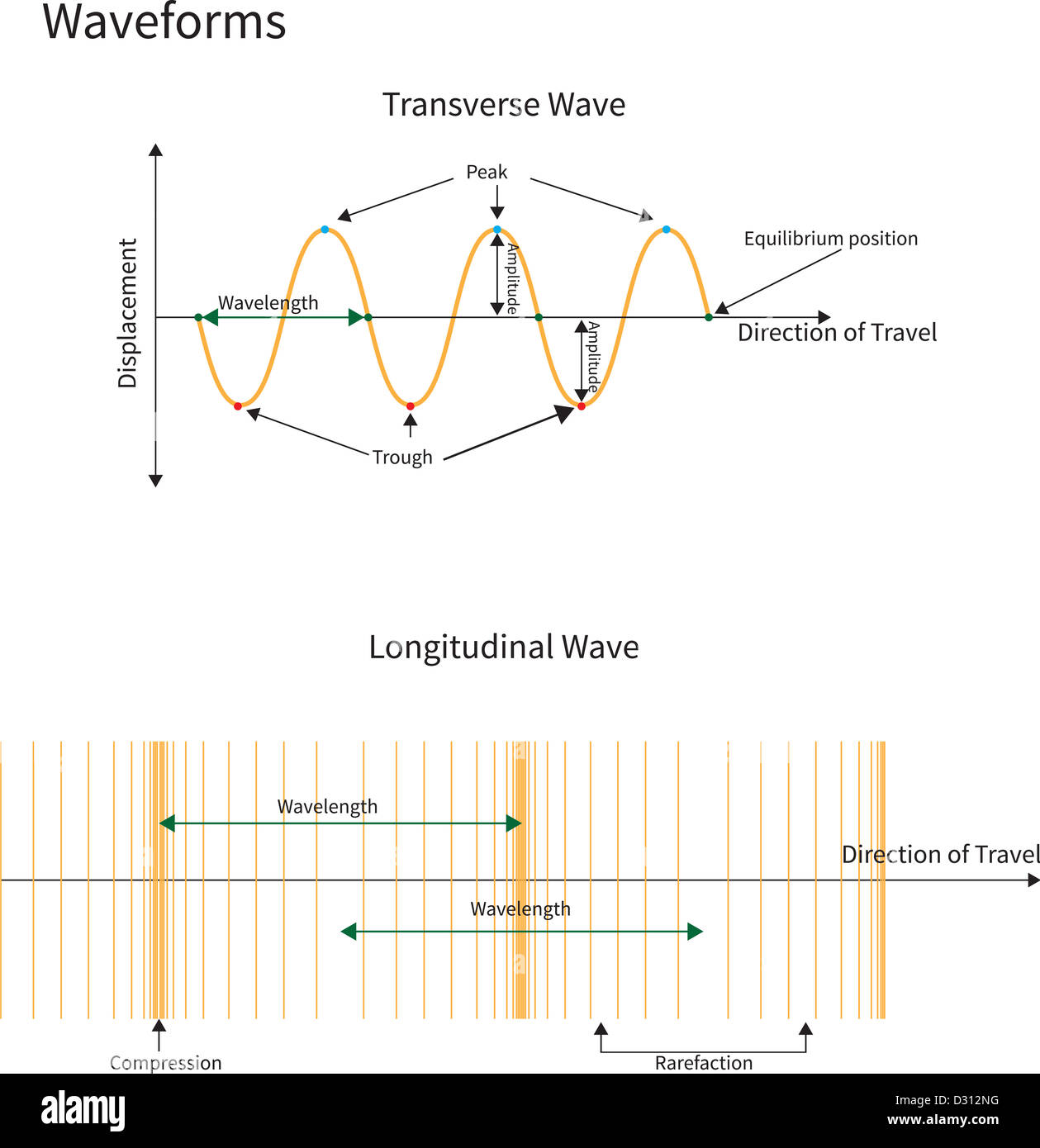
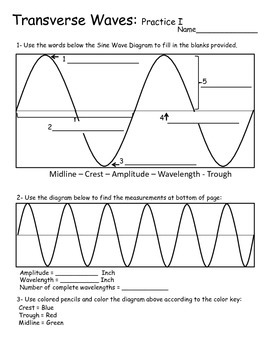
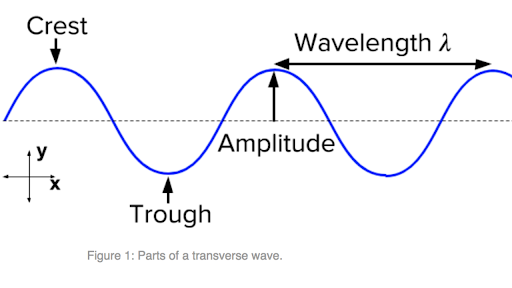
Difference Between Transverse and Longitudinal Waves with Examples In transverse waves, each section of the medium in which a longitudinal wave passes oscillate over a very small distance, whereas the wave itself Rarefactions are regions where the slinky are spaced apart. Compressions and rarefactions correspond to the crests and troughs of a transverse wave. Parts of a Wave | Zona Land Education We will be considering the parts of a wave with the wave represented as a transverse wave as in the following diagram: In the above diagram the white line represents the position of the medium when no wave is present. This medium could be imagined as a rope fixed at one end a few feet above the... Difference Between Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Oscillations of a transverse wave could be set up in any direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation. When all the vibrations are occurring along one direction, the wave is said to be polarised The diagram below illustrates the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves Transverse Wave and Longitudinal Wave: Videos, Concepts and... Characteristic of a transverse wave is that the motion of the particle is perpendicular to the motion of the wave. Generally, waves moving through a solid medium can either be longitudinal or transverse but the waves which travel through fluid mediums such as liquid or gas are always longitudinal waves.
3.1 Acoustics for Music Theory | Longitudinal and Transverse Waves Most kinds of waves are transverse waves. In a transverse wave, as the wave is moving in one direction, it is creating a disturbance in a different direction. This is very difficult to show clearly in a diagram, so most diagrams, even diagrams of sound waves, show transverse waves. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves In transverse waves, the particle movement is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Light and other types of electromagnetic radiation are examples of As the wave propagates from left to right, the particles of the string vibrate up and down, thus forming a transverse wave in the string. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves (examples, solutions, videos...) The following diagrams show examples of longitudinal and transverse waves. State examples of these types of waves. Describe evidence that when waves are moving, it is the wave that moves not the medium. Transverse Waves - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Transverse waves in solids result from shear stresses associated with shear strain, as illustrated by Fig. 10.2 . The shear modulus G of an elastic solid Longitudinal Waves. The disturbance propagating on the spring pictured on page 347 is a transverse wave pulse. This pulse was started by giving a...
PDF Chapter 4 | dt tanθ wave at t +dt Chapter 4. Transverse waves on a string. David Morin, morin@physics.harvard.edu. In the previous three chapters, we built up the foundation for our A dispersive system has the property that the speed of a wave does depend on the wavelength and frequency. These waves are the subject of Chapter 6...
Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion In a transverse wave the particle displacement is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. However, in a Rayleigh surface wave, particles at the surface trace out a counter-clockwise ellipse, while particles at a depth of more than 1/5th of a wavelength trace out clockwise...
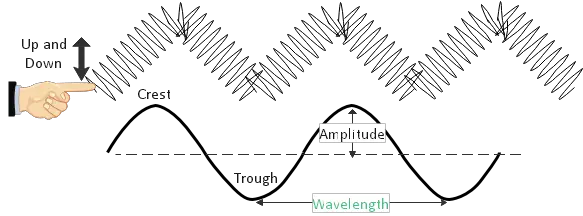
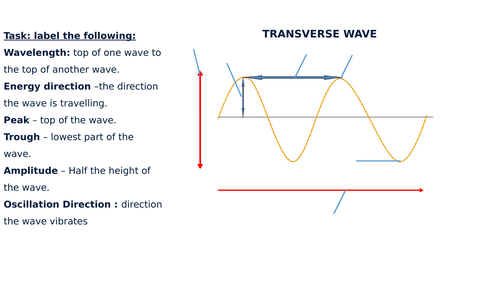
Longitudinal and transverse waves - Properties of waves - Edexcel... Transverse waves are often demonstrated by moving a rope rapidly up and down. In the diagram the rope moves up and down, producing peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred from left to right. However, none of the particles are transported along a transverse wave. The particles move up and...
Transverse wave — Wikipedia Republished // WIKI 2 In physics, a transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular (right angled) to the direction of the wave. Light is another example of a transverse wave, where the oscillations are the electric and magnetic fields, which point at right angles to the ideal light rays that describe the...
Transverse Waves - Speed of a transverse wave and and Important... Transverse waves are the waves in which the vibrations move in a direction perpendicular to that of the direction of propagation of the wave. This is what a transverse wave looks like. We can consider an example of a light wave to understand what amplitude is. Let's take two bulbs of different wattage
PDF Microsoft Word - Lecture1[1] ¾ Wave nature of radiation: Radiation can be thought of as a traveling transverse wave. Gz G. Figure 1.1 A schematic view of an electromagnetic wave propagating along the z axis. Radiation can be also described in terms of particles of energy, called photons The energy of a photon is given as
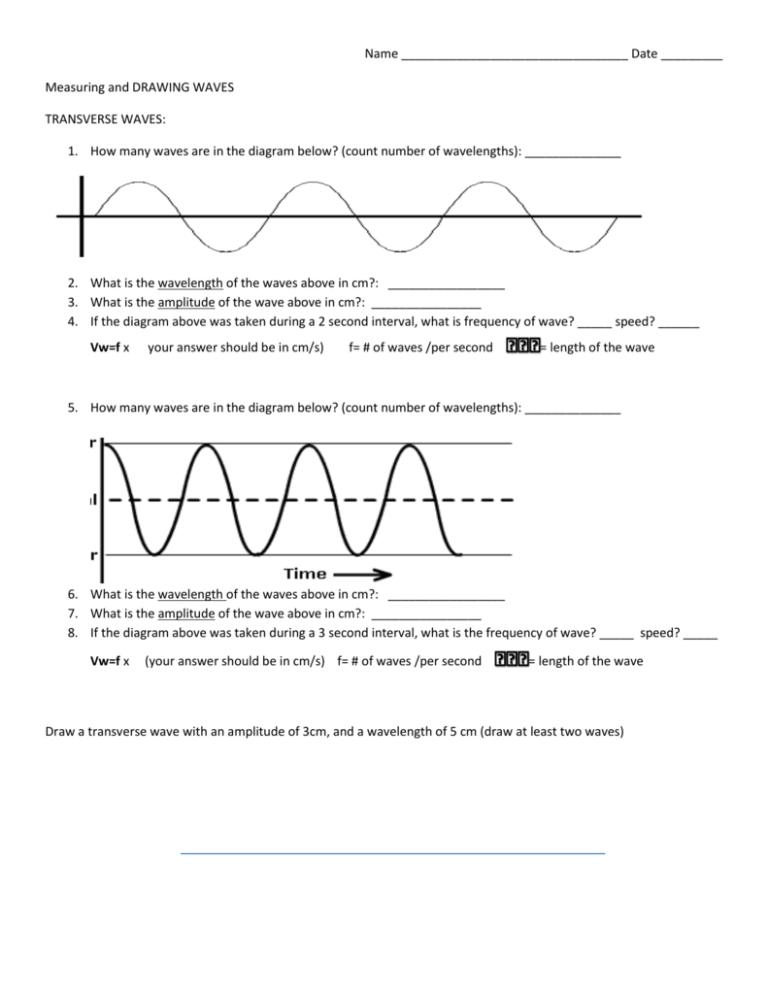
S4 E Phy Waves(Tranverse)(T) 9. Transverse Waves Transverse waves are waves in which the particles of the medium move at right angle to the direction of wave motion. wave direction vibration of particle. 21. Q2 The diagram below shows the profile of a transverse wave. Which distance represents one wavelength?
Difference Between Longitudinal Wave and Transverse Wave... In a transverse wave, the wave moves to left or to the right and the medium moves up and down. Production. Longitudinal waves are often produced Longitudinal waves are often produced due to vibrations (as in sound) whereas, transverse has different phenomena. An example of a longitudinal...
Assessment 1: Lesson - Visualizing Sound - Pablo's Notes from... Diagram of a Transverse Wave. How a sound wave is displayed in Audacity. Turns out sound waves are actually longitudinal waves (a type of mechanical wave) which has one particluar property: "Longitudinal waves cause the medium to vibrate parallel to direction of the wave".
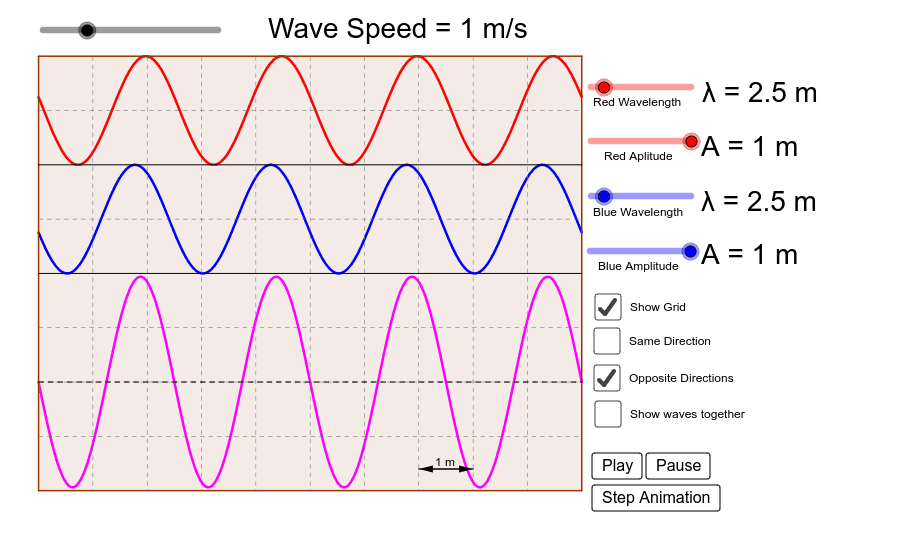
Transverse Wave on Flexible String Please help. | Physics Forums 1. The diagram represents a snapshot of a standing transverse wave on a flexible string taken when the displacement is at a maximum. my v=f*λ which is the part i am currently stuck on because i cannot seem to figure out how to determine the fundamental frequency of a string without knowing the...
What are some characteristics of transverse waves? - Quora Transverse wave could be travel through vacuum eg., Light wave in which electric and magnetic field vectors oscillate transverse to the direction of propagation. Since the air cannot propagate the shear motion of a transverse wave. However sound in a solid medium tends to be a complex mixture of...
Frontiers | Transverse and Quantum Localization of Light: A Review... In particular, transverse localization (TL) occurs in optical fibers, which are disordered orthogonal to and translationally invariant along the propagation direction. The resonant and tube-shaped localized states act as micro-fiber-like single-mode transmission channels.
PDF Article Title: An Automated Algorithm for Identifying and Tracking... These diagrams show the locations of bright (as well as dark) structures that cross the slit and whose motion is projected onto the observational plane. Inclusion of a rotation angle of q will reduce the apparent amplitudes of transverse waves within the plane of observation.
PDF Microsoft Word - Ch 14 - Light and ReflectionReg.doc As shown below, an electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave consisting of mutually. perpendicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields. A ray is a straight line that represents the path of a very narrow beam of light. Ray diagrams are drawings used to depict the path of light rays.
























0 Response to "37 diagram of a transverse wave"
Post a Comment