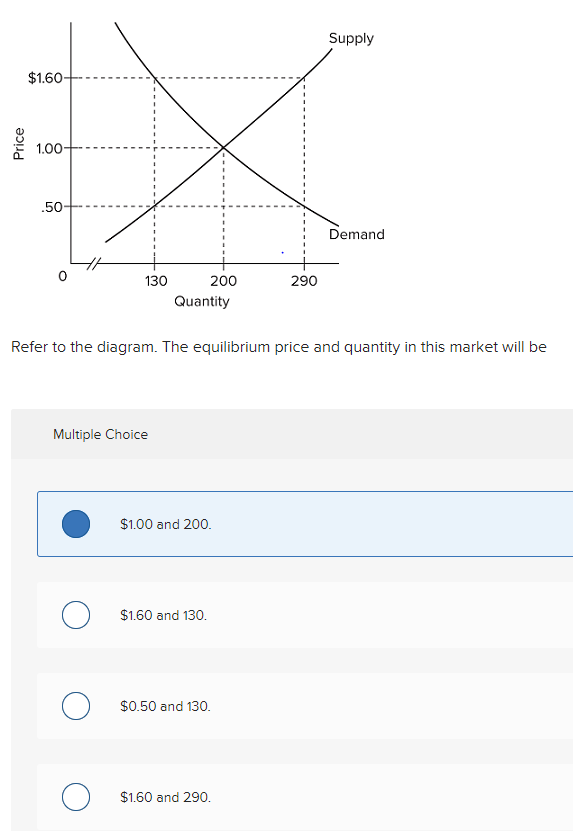
37 refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be
Economists use the term "demand" to refer to what? ... Refer to the above diagram. ... The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 90. Refer to the above diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if price was: A. ...
Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: $1.00 and 200.

Refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be
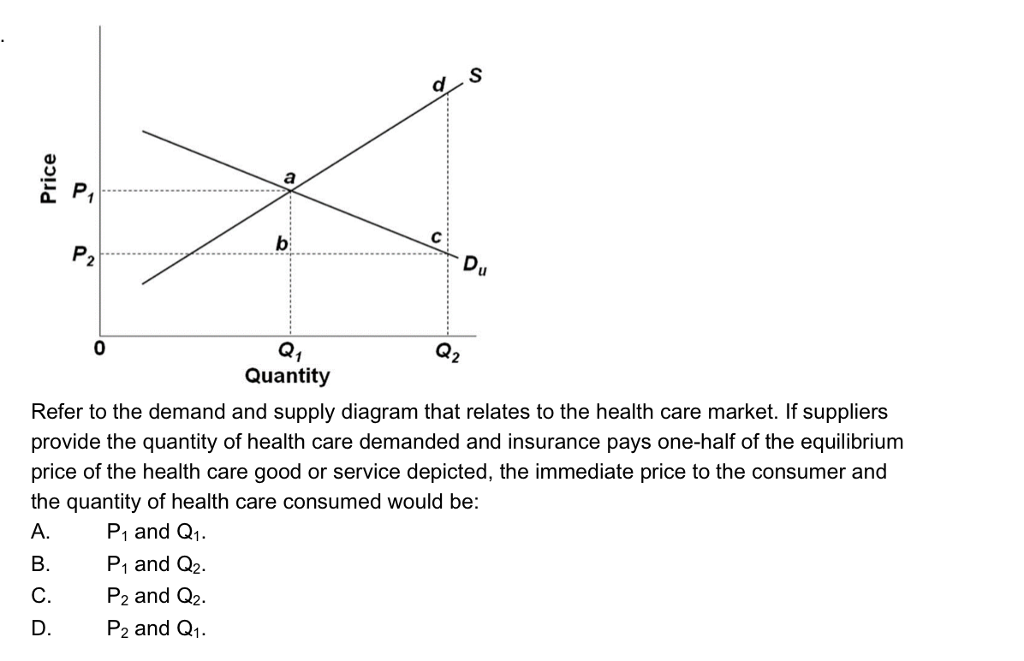
The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: *{$1.00 and 200.} $1.60 and 130. $0.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. Refer to the diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if the price was: $1.10, that is, $1.60 minus $.50. *{$1.60.} $1.00. $0.50. Refer to the diagram. A shortage of 160 units would be encountered if price was: Money market equilibrium occurs at the interest rate at which the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied. All other things unchanged, a shift in money demand or supply will lead to a change in the equilibrium interest rate and therefore to changes in the level of real GDP and the price level. (a) and the new quantity sold with the price ceiling. c) Calculate the consumer surplus and producer surplus at the initial equilibrium price and quantity from part (a). d) Calculate the new consumer surplus and producer surplus with the price ceiling of $2.25 per gallon (part b).
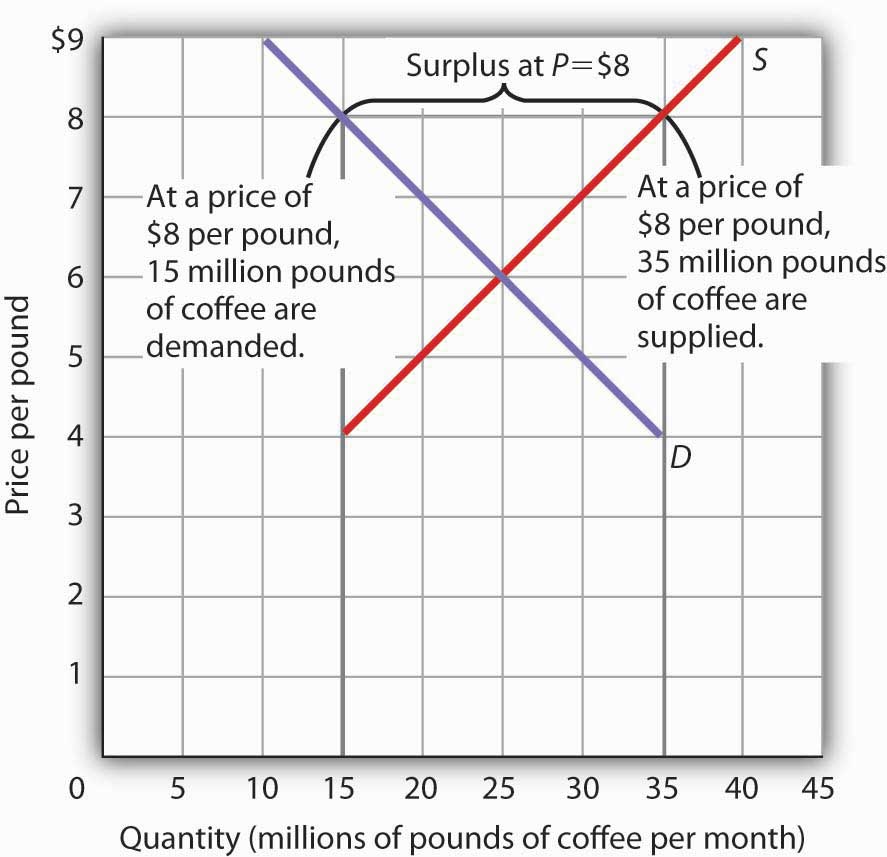
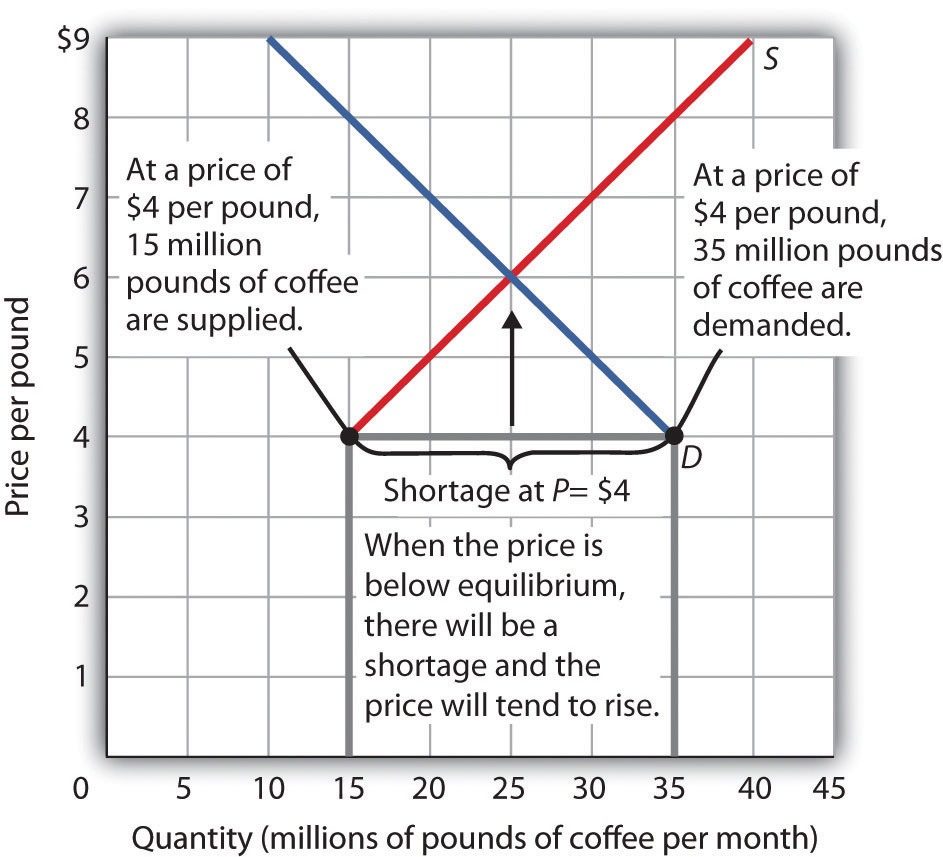
Refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be. The market for coffee is in equilibrium. Unless the demand or supply curve shifts, there will be no tendency for price to change. The equilibrium price in any market is the price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price in the market for coffee is thus $6 per pound. 71. Refer to the above diagram for the milk market. In this market, the equilibrium price is ____ and equilibrium quantity is ___. A. $1.50 per gallon; 28 million gallons B. $1.50 per gallon; 30 million gallons C. $28 per gallon; 150 million gallons D. $1.00 per gallon; 35 million gallons 72. Refer to the above diagram for the milk market. D. price and equilibrium quantity must both decline. A Refer to the diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. 137) Refer to the diagram below for the market for corn. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market are: 137) A) $2 and 11,000 bushels. B) $2 and 4,000 bushels. C) $3 and 8,000 bushels. D) $4 and 10,000 bushels. Answer: C
The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: ... Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for ... At any other price, the quantity demanded does not equal the quantity supplied, so the market is not in equilibrium at that price. It should be clear, ... 13 Refer to the above diagram The equilibrium price and quantity in this market from ECON 202S at Old Dominion University. ... 13 Refer to the above diagram The equilibrium price and quantity in this market. ... The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $0.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 14 ... Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130.
Refer to the above diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If the initial demand and supply curves are D0 and S0, equilibrium price and quantity will be: The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. . If government levies a per unit excise tax of on suppliers of this product, equilibrium price and quantity will be: Refer to the diagram below, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive ... The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: The equilibrium price and | Chegg.com. Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $0.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. If there is a surplus of a product, its price: A. is below the equilibrium level. B. is above the equilibrium level. D. will rise in the near future.
Refer to the diagram below for the market for corn.The equilibrium price and quantity in this market are: 11eacf22_e8e8_3150_aab5_bde45835eb7b_TB6686_00 A)$4 and 10,000 bushels. B)$3 and 8,000 bushels. C)$2 and 4,000 bushels. D)$2 and 11,000 bushels.
Refer to the above diagram. The Equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: If two products are complementary goods, how will a decrease in the price of one affect the other?
The equilibrium price and quantity in this market are: A) $4 and 10,000 bushels. B) $3 and 8,000 bushels. C) $2 and 4,000 bushels. D) $2 and 11,000 bushels. 139. Refer to the above diagram illustrating the market for corn. If the price in this market were to be fixed at $4 per bushel, the part of the line marked A would represent a:
Refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 ... C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290.
Chapter 03 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: 03-04 Relate how supply and demand interact to determine market equilibrium. Topic: 03-17 Market Supply 158. Refer to the diagram below for the market for corn. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market are: A. $4 and 10,000 bushels. B. $3 and 8,000 bushels. C. $2 and 4,000 bushels.
Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: (Pic29) $1.00 and 200. $1.60 and 130. $0.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. $1.00 and 200. A market is in equilibrium: provided there is no surplus of the product. at all prices above that shown by the intersection of the supply and demand curves.
The price of product X is reduced from $100 to $90 and, as a result, the quantity demanded increases from 50 to 60 units. Therefore demand for X in this price range: A. has declined. B. is of unit elasticity.
The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: ... Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for ...
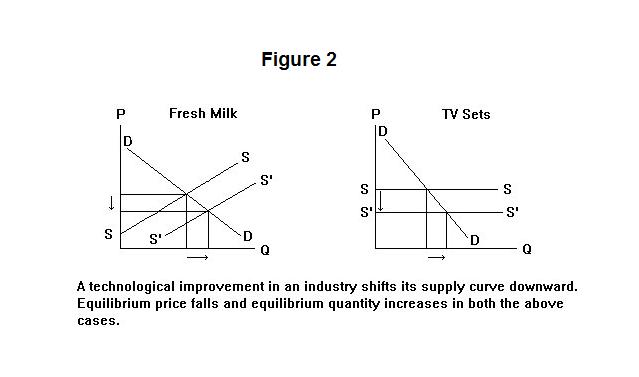
a) A lower equilibrium quantity and a higher equilibrium price. b) A lower equilibrium quantity and a lower equilibrium price. c) A higher equilibrium quantity and a higher equilibrium price. d) A higher equilibrium quantity and a lower equilibrium price. The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 15.
The equilibrium price in any market is the price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price in the market for coffee is thus $6 per pound. The equilibrium quantity is the quantity demanded and supplied at the equilibrium price. At a price above the equilibrium, there is a natural tendency for the price to fall.
When looking for the market equilibrium (sometimes called the unregulated market equilibrium), we want to select the quantity where demand = supply or where marginal private benefit = marginal private cost. Diagrammatically, this will happen where MPB intersects MPC. The quantity where this occurs will always maximize market surplus.
The equilibrium price is the price at which _____ and the equilibrium quantity is the _____. A ... ; quantity at which demand is less than supply. Login. ... refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be. asked Dec 12, ...
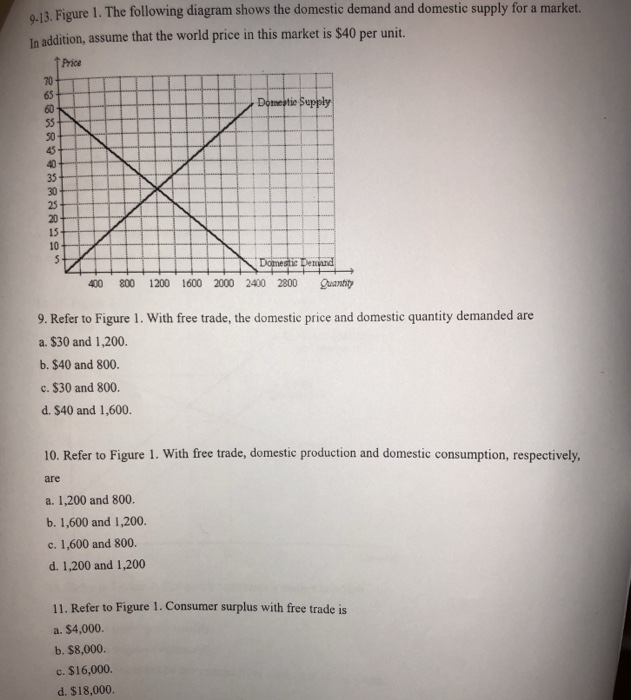
Refer to the above data. If the price in this market was $4: A. The market would clear; quantity demanded would equal quantity supplied B. Buyers would want to purchase more wheat than is currently being supplied C. Farmers would not be able to sell all their wheat D. There would be a shortage of wheat
27. A market for a product is in equilibrium when: A) Product price equals demand B) The supply curve remains fixed C) Quantity supplied equals quantity demanded D) Supply is equal to the price 28. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity for milk in this market are: A) $1.50 and 28 million gallons B) $1.50 and 30 million ...
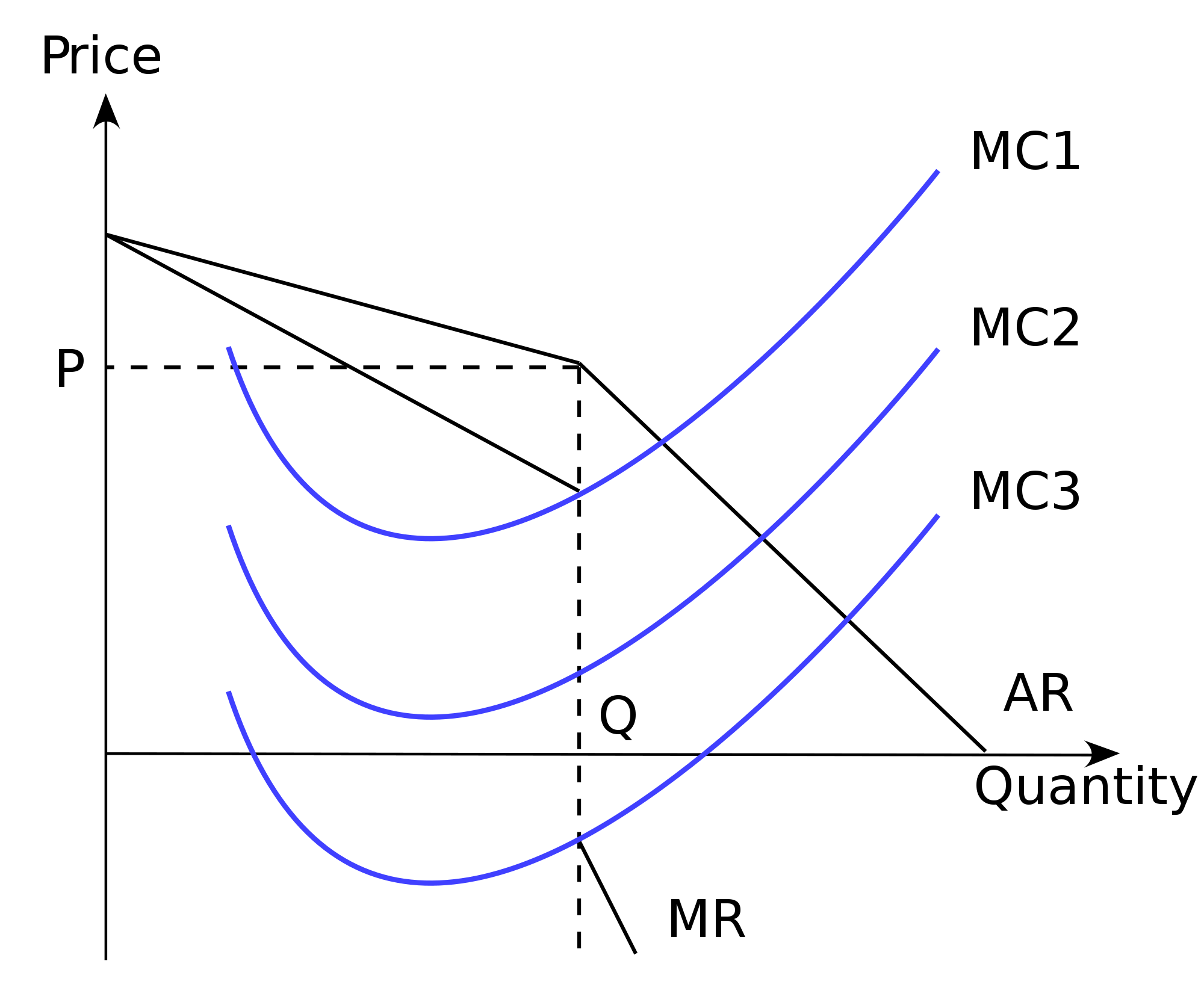
At equilibrium level of output OX, price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the MR curve from below. The firm enjoys normal profits. Now, suppose demand increases from DD to D 1 D 1 and the industry is in equilibrium at point E 1 which determines the price OP 1 The new price OP 1 is less than the new market price i.e ...
Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 7. R-2 F03090. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. equilibrium. B. a shortage of 50 units. C. a surplus of 50 units. ...
15. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A) $1.00 and 200. B) $1.60 and 130. C) $.50 and 130. D) $1.60 and 290. 16. Refer to the above diagram. A surplus would be encountered if price was in the following range: A) $0.01 - $0.50. B) $0.51 - $1.00. C) Exactly $1.00.
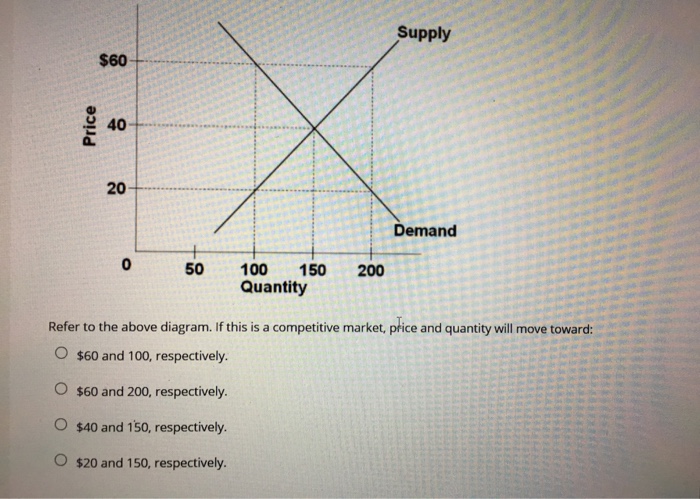
According to the figures in the given table, Market Equilibrium quantity is 150 and the Market equilibrium price is 15. It is the point where QD = QS, of the given figures. Demand and Supply Curves. This is the way how economist use demand and supply curves to prove the market equilibrium.
(a) and the new quantity sold with the price ceiling. c) Calculate the consumer surplus and producer surplus at the initial equilibrium price and quantity from part (a). d) Calculate the new consumer surplus and producer surplus with the price ceiling of $2.25 per gallon (part b).
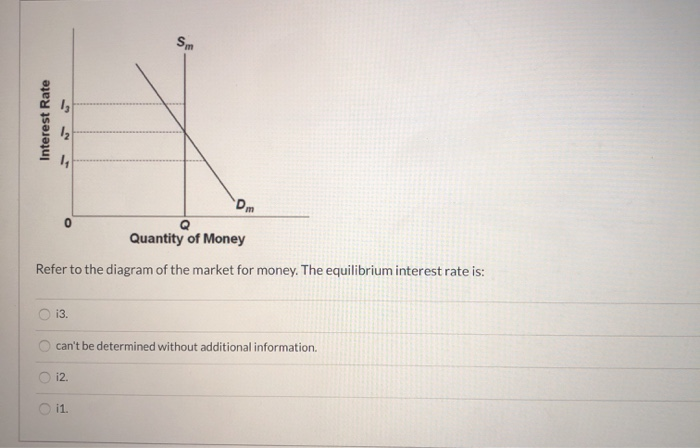
Money market equilibrium occurs at the interest rate at which the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied. All other things unchanged, a shift in money demand or supply will lead to a change in the equilibrium interest rate and therefore to changes in the level of real GDP and the price level.
The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: *{$1.00 and 200.} $1.60 and 130. $0.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. Refer to the diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if the price was: $1.10, that is, $1.60 minus $.50. *{$1.60.} $1.00. $0.50. Refer to the diagram. A shortage of 160 units would be encountered if price was:



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)










/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)




0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be"
Post a Comment