39 free body diagram centripetal force
Free-Body Exercises: Circular Motion Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on the rock, and in each case, indicate the centripetal force. Please note that the rock is not in equilibrium if it is moving in a circle. The centripetal force depends on angular velocity and there may not be any indication of exactly how big that force should ...
Once more the F norm must provide sufficient force to produce the required inward or centripetal net force. Earlier in Lesson 2, the use of Newton's second law and free-body diagrams to solve circular motion diagrams was illustrated. It was emphasized at that time that any given physical situation could be analyzed in terms of the individual ...
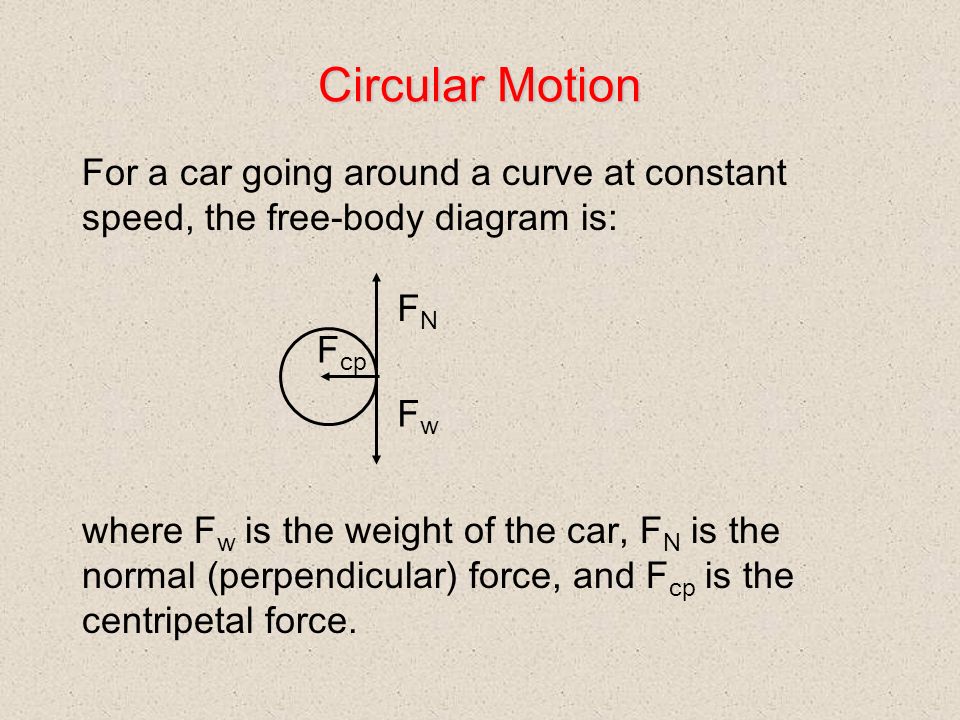
(Figure) shows a free-body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle is ideal for the speed and radius, then the net external force equals the necessary centripetal force. The only two external forces acting on the car are its weight and the normal force of the road
Free body diagram centripetal force
Which free-body diagram in Figure 5.11 correctly shows the force(s) acting on the Earth (E) as it orbits the Sun, when the Earth is at the position shown, to the right of the Sun? is the gravitational force exerted on the Earth by the Sun, while stands for centripetal force. The correct free-body diagram is diagram 3, which
Free Body Diagram Centripetal force. physics help centripetal force free body diagrams part 7 free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website centripetal force and free body diagram 1 the problem statement all variables and given known data a draw a free body diagram for mass mb while in motion fig 2a identify the centripetal
Answer (1 of 6): In order to be able to understand this, first let us understand the meaning of centripetal force. Whenever an object moves on a circular path, it is undergoing a continuous change in direction. This change in direction is to brought by the action of a force acting on it. More s...
Free body diagram centripetal force.
A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it. FBDs are very helpful in engineering and physics problem solving. Part 1 Creating a Basic FBD Download Article 1 Identify the body/object you want to make an FBD of.
Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram A 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. The loop has a radius of 16 m, and the car's velocity at the top is 12 m/s.
When a free body diagram of a ball being swung in a circle is drawn ( example ), only tension and weight are drawn on it. I understand that the centripetal force equals tension plus weight at the top of the circle, and tension minus weight at the bottom of it, but there must also always be an equal centrifugal force because of Newton's 3rd Law.
In the free-body diagram below, what is the balancing force in the question mark? centripetal-force. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited May 6 '17 at 15:00. blackened. asked May 6 '17 at 13:56. blackened blackened. 275 3 3 silver badges 10 10 bronze badges $\endgroup$ 3
Browse other questions tagged newtonian-mechanics reference-frames free-body-diagram centripetal-force centrifugal-force or ask your own question. Featured on Meta New responsive Activity page. Reducing the weight of our footer. Linked. 14. Physical meaning of the Coriolis force ...
Free Body Diagram Centripetal Force This is sometimes referred to as the centripetal force requirement. However, your body, being in motion, tends to continue in motion while the car is skidding to a stop. . ice slides out of the freezer and a mechanical arm exerts a force to accelerate it across the icy, friction free surface.
Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N +(- mg) F N
The forces at the bottom are shown here in a free-body diagram. The two forces at the bottom are co-linear, with the upward tension force T being larger than the downward weight, mg, by the required centripetal force. In your experiment, you will compare the measured tension force with one calculated based on the motion. Figure 1.
http://www.physicshelp.caGO AHEAD and click on this site...it wont hurt.Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website
http://www.physicseh.com/Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website.
I prefer NOT to use the phrase "centripetal force" because it makes you think there is a magical force that appears when an object is experiencing uniform circular motion. There is no such thing, and, in my opinion, you should never put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram.
We can draw the free body diagram of bob at a as shown in figure 1.43. The force acting on the bob is it's weight mg and tension T of the string. Tenstion T is resolved in two components T cos θ and T sin θ as shown in figure 1.43. we can write the equation of motion. T cos θ = mg T sin θ = mv2/r.
Note that centripetal force is the name given to the resultant force: it is not a separate force in the free-body diagram. The centripetal acceleration has to be provided by some other force (tension, friction, normal force) in order for circular motion to occur. 10 •
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
The centripetal force needed to turn the car (mv 2 /r) depends on the speed of the car ... A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep ...
A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting.
examples of free body diagrams with an opportunity to practice, examples of situations in which diagrams have been drawn incorrectly (and corrections for them), a &nal segment that draws ... Centripetal force is an important concept, and one that is often confusing for students. Because of both
This test covers Newton's Laws of Motion, forces, coefficients of friction, free-body diagrams, and centripetal force. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. A locomotive engine of unknown mass pulls a series of railroad cars of varying mass: the first car has mass m, the second car has mass 2m, and the last car has mass 3m.
Centripetal force and acceleration: In a free body diagram, centripetal force should never be mentioned by name (it should be called "tension" "friction" etc), and should not be shown at all if it is only the component of a force or forces. In a free body diagram in an inertial frame, centripetal acceleration should be shown by a different sort ...
15.11.2021 · newtonian-mechanics forces free-body-diagram centripetal-force centrifugal-force. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited Nov 15 at 17:09. Vince Vickler. 25 4 4 bronze badges. asked Nov 15 at 8:44. COOKIE COOKIE. 83 4 4 bronze badges $\endgroup$ Add a comment | 4 Answers Active Oldest Votes. 11 $\begingroup$ The force of gravity acts …
One method to determine the centripetal force acting on a mass is to utilize free body diagrams and force summation equations. Let us consider a mass traveling in a vertical circle attached to a string. Drawing a free body diagram of this mass when it's at the lowest point of its circular path gives us the following.
Redbelly98 said: Centripetal force is a net force on the car, it is caused by one or more of the other forces that have been mentioned. but i thought the sum of all the forces has to equal the net force (ie, centripetal force) - how come on my diagram those force vectors dont add up to the centripetal force vector? Share: Share.
As always, the place to start is with a free-body diagram, which just has two forces, the tension and the weight. It's simplest to choose a coordinate system that is horizontal and vertical, because the centripetal acceleration will be horizontal, and there is no vertical acceleration.
The correct free-body diagram is diagram 3, which shows only the force of gravity applied by the Sun on the Earth. The word "centripetal" means "directed toward the center." When an object experiences uniform circular motion, the object has a centripetal acceleration directed toward the center of the circle.
the centripetal force. F sp mg, ( 5 ) where m is the total mass of the load including the hanger. This force is equal to the centripetal force for holding the bob at the same radius when it is rotating. Figure 3. Free-body diagrams for (a) dynamic and (b) static measurements. Figure 2. Centripetal force apparatus. Shaft Sliding arm Counter

0 Response to "39 free body diagram centripetal force"
Post a Comment