38 electron transport chain diagram labeled
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The electron transport chain is a crucial step in oxidative phosphorylation in which electrons are transferred from electron carriers, into the proteins of the electron transport chain which then deposit the electrons onto oxygen atoms and consequently transport protons across the mitochondrial membrane.This excess of protons drives the protein complex ATP ...
In the diagram below, the red arrows show the flow of energy through the electron-transport chain. Follow the flow of electrons through the electron-transport chain, and label the components of the chain. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Label the steps of electron transport leading to oxidative phosphorylation where ATP is.
The electron transport chain can be observed in the most basic of organisms. Any eukaryote (cell with organelles), has mitochondria and therefore uses this exact same method to produce ATP. Even plants, which are often considered so different than animals, rely on the same process of oxidative phosphorylation.
Electron transport chain diagram labeled
Labeled electron transport linked metabolism scheme. Educational diagram with cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients process in explanation infographics. electron transport chain ,
An electron transport chain is a series of enzymes and coenzymes that globally perform two actions simultaneously: it transfers electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors during successive redox reactions, and ensures the pumping of protons or other cations through a biological membrane.
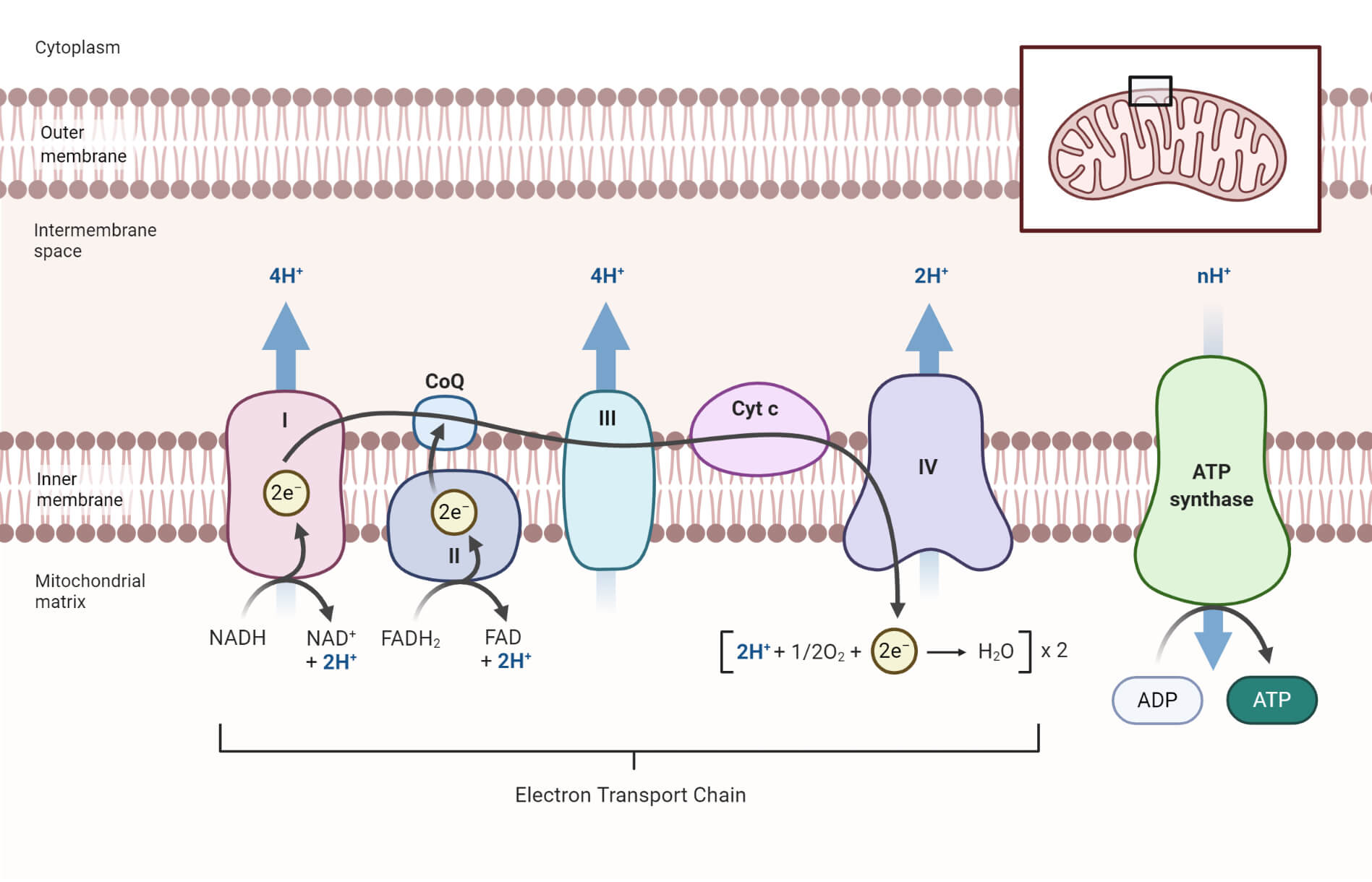
Electron Transfer Chain. This process takes place on the inner mitochondrial membrane which is folded to cristae. This provides a large surface area for the electron transfer chain to take place. The carriers FAD and NAD bring the hydrogen and it separates to H+ and electrons (e-). The electrons pass from carrier to carrier and loose energy.
Electron transport chain diagram labeled.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which energy from electron transport chain (respiratory chain) is used to make ATP, and is the culmination of energy yielding metabolism in aerobic organisms. Oxidative phosphorylation involves the reduction of O 2 to H 2 O with electrons donated by NADH and FADH 2, and equally occurs in light or ...
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes and electron carrier molecules within the inner membrane of mitochondria that generate ATP for energy. Electrons are passed along the chain from protein complex to protein complex until they are donated to oxygen. During the passage of electrons, protons are pumped out of the ...
The chemiosmotic theory explains the functioning of electron transport chains. According to this theory, the transfer of electrons down an electron transport system through a series of oxidation-reduction reactions releases energy (Figure 18.3 D. 1 ). This energy allows certain carriers in the chain to transport hydrogen ions (H + or protons ...
For Higher Human Biology, discover how and where energy is made in the cell and the chemical reactions involved.
STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONSUse the diagram to answer the following questions. The diagram below summarizes the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis in aerobic respiration. Label the substances that are transported along the arrows labeled a-din the spaces provided. Label the reactants or products that are represented by e-gin the spaces ...
Download scientific diagram | Schematic diagram of the electron transport chain (ETC) of mitochondria. Complex (C) I, II, III, IV, and V represent each complex in the ETC chain. The ETC uses NADH and FADH2 to make ATP. These reducing equivalents for ETC are generated during glycolysis, fatty ...
Cellular respiration diagram labeled. Atp electron transport chain glycolysis krebs cycle mitochondrion use. Free rubric builder and assessment tools. Glycolysis, the bridge (transition) reaction, the krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. The total energy yield is 36 to 38 molecules of atp. Definition, structure & function (with diagram).
PSI, PSII, ATP Synthase, & electron transport chain. Label everything in diagram 6. A: Photons enter and go to the chlorophyll; water also enters and goes to the chlorophyll. A: Electrons in the chlorophyll are excited to a higher energy level & the energy is transferring further into the reaction.
July 27, 2020 - Note: Electrons from FADH2 enter the electron transport chain at the fourth protein complex, succinate-Q reductase. This protein complex contains succinate dehydrogenase which was responsible for generating FADH2 from the reaction converting succinate into fumarate.
Label the reactants and the products. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? Label the location on the cell diagram (Where in the cell does the Krebs (Citric Acid) cycle occur? Label the location on the cell diagram (Where in the cell does the electron transport chain occur?
April 22, 2016 - If you were to zoom into the area that is labeled electron transport chain proteins (that I told you to note) you would see something like this.
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway and is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins found on ...
April 8, 2012 - This is shown by the diagram below. Complex I-IV each play a role in transporting electrons( hence the name electron transport chain), and establishing the proton gradient. The exact mechanism of each Complex can be overwhelming so I will save that for a future post.
Electron transport is a series of chemical reactions that resembles a bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the endpoint of the chain where oxygen is the final electron acceptor and water is produced. There are four complexes composed of proteins, labeled ...
Electron Transport Chain is a series of compounds where it makes use of electrons from electron carrier to develop a chemical gradient. It could be used to power oxidative phosphorylation. The molecules present in the chain comprises enzymes that are protein complex or proteins, peptides and much more.
(A) Electron micrograph of a human cell section showing three mitochondria. (B) Scheme of the protein complexes that form the ETS, showing the mitochondrial membranes in blue and red; NADH dehydrogenase in light green; succinate dehydrogenase in dark green; the complex formed by acyl-CoA ...
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
The electron transport chain is an aggregation of four of these complexes (labeled I through IV), together with associated mobile electron carriers. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and the plasma membrane of prokaryotes.
MATCH THE LETTER IN THE DIAGRAM WITH THE LABEL: (You can use them MORE THAN ONCE or NOT AT ALL) _____ Place where glycolysis happens _____ Place where enzymes for the Electron Transport Chain are located _____ Place that fills with H+ ions as electrons move down the Electron Transport Chain _____ Place where ADP and P join to make ATP
We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Glycolysis Electron Transport Chain Diagram.We hope this picture Glycolysis Electron Transport Chain Diagram can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Glycolysis Electron Transport Chain Diagram from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet.
August 31, 2017 - Hentei. porno thumbs - watch best sex thumbs with cute blondes, brunets.
Electronegativity is “the tendency to acquire electrons.” As you move along the electron transport chain, each electron carrier has a greater electronegativity than the one before it. You can see this in the diagram to the left. Inside Complex I you can see the electron carriers FMN and ...
The electron transport chain is the final step of cellular respiration where 34 ATP molecules are produced.
Having considered in general terms how a mitochondrion uses electron transport to create an electrochemical proton gradient, we need to examine the mechanisms that underlie this membrane-based energy-conversion process. In doing so, we also accomplish a larger purpose.
Overview of oxidative phosphorylation. The electron transport chain forms a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which drives the synthesis of ATP via chemiosmosis.
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane within mitochondria to form a gradient of protons that drives the creation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is used by the cell as the energy for metabolic processes for cellular functions.
The diagram below summarizes the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis in aerobic respiration. Label the substances that are transported along the arrows labeled a—d in the spaces provided. Label the reactants or products that are represented by e—g in the spaces provided. FAD MITOCHONDRIAL MATRIX ATP synthase ATP NADH Inner mitochondrial
in the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to the next in a series of electron transfers called __ __ reactions electron carrier At the end of the chain of electron carriers is the final __ __ which is a molecule that takes up electrons and does not pass them on.
Figure 8.26. A simplified illustration of the mitochondrion electric transport chain. Hydrogen pumps are labeled 1 (NADH dehydrogenase), 2 (cytochrome ... complex), and 3 (cytochrome c oxidase complex). Electron carriers are labeled Q (Coenzyme Q) and C (cytochrome c).
Electron Transport Chain The electron transport chain uses the high-energy electrons produced by the Krebs cycle to move hydrogen ions from one side of the inner membrane to the other. Label the diagram with the following terms: electron, hydrogen ion, and inner membrane. Intermembrane space 2 H20 FADH2 2 NADH FAD 2 NAD* 4 H+ 02 Matrix
The electron transport chain has two essential functions in the cell: Regeneration of electron carriers: Reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 pass their electrons to the chain, turning them back into NAD + and FAD. This function is vital because the oxidized forms are reused in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) during cellular respiration.
Transfer of electrons between carriers in the electron transport chain in the membrane of the cristae is coupled to proton pumping AND In chemiosmosis protons diffuse through ATP synthase to generate ATP AND Oxygen is needed to bind with the free protons to maintain the hydrogen gradient, resulting ...
We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Diagram Of Simple Electron Transport Chain.We hope this picture Diagram Of Simple Electron Transport Chain can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Diagram Of Simple Electron Transport Chain from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet.
Oxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. In the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient. In chemiosmosis, the energy stored in the ...
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
The electron transport chain (ETC; respiratory chain) is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across a membrane.The electron transport chain is built up of peptides, enzymes, and other ...
Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article provides a simple explanation of this pathway.
Sequence of events in the electron transport chain The following diagram shows the sequence of events that occurs in the electron transport chain NAD Q Cyt b FeS Cyt c 1 Cyt c Cyt a Cu 1/2 O 2 Cyt a 3 Cu Isocitrate Malate β-hydroxy acyl CoA β-hydroxy butyrate Succinate Acyl CoA Choline Flavoprotein (FAD) FeS Flavoprotein (FMN), FeS 2 H+ O=
Electron transport is a series of redox reactions that resemble a relay race or bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the endpoint of the chain where the electrons reduce molecular oxygen, producing water. There are four complexes composed of proteins, labeled ...
December 2, 2020 - The electron transport chain is an aggregation of four of these complexes (labeled I through IV), together with associated mobile electron carriers. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and the plasma membrane of prokaryotes.

0 Response to "38 electron transport chain diagram labeled"
Post a Comment