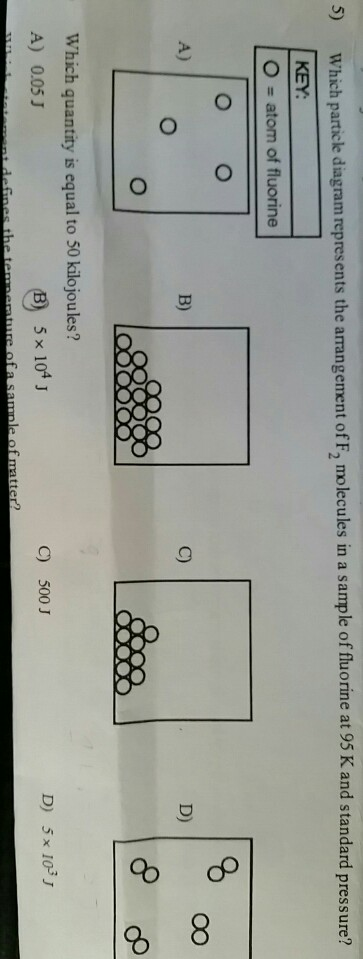
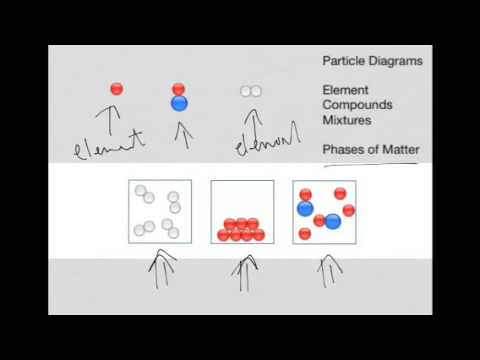
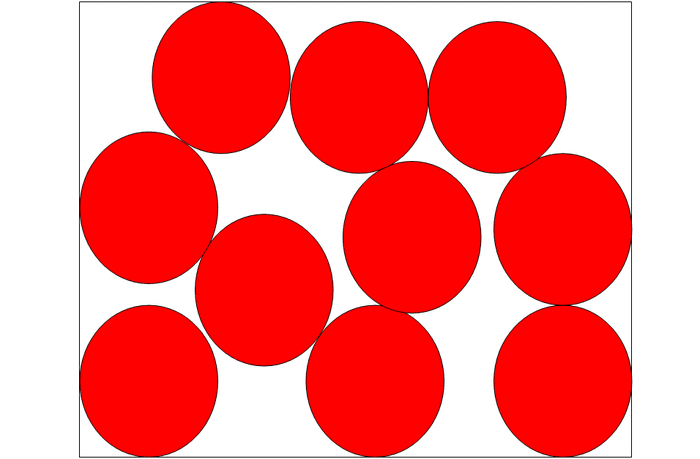
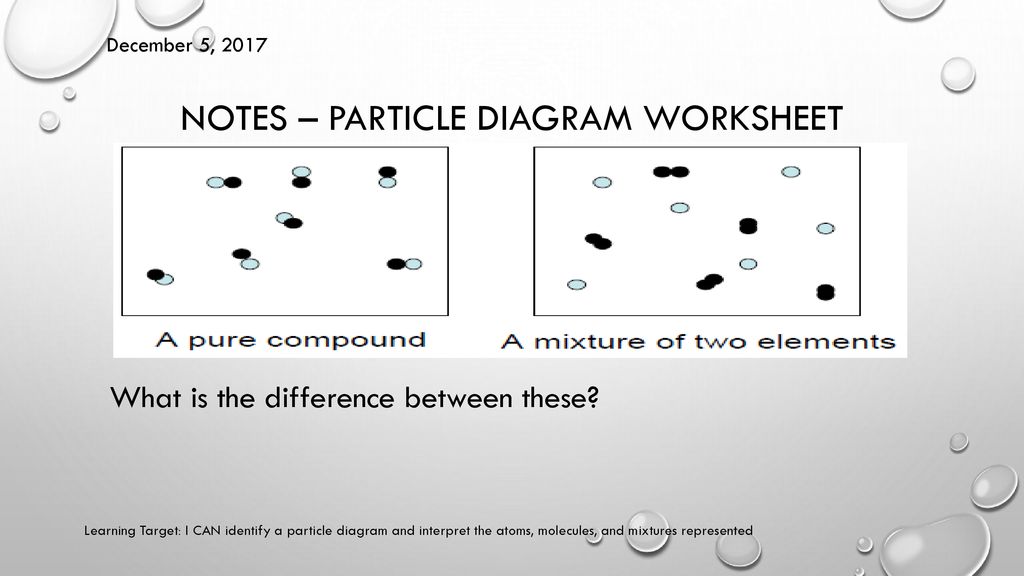
40 which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram
33: Particle Physics - Physics LibreTexts 33: Particle Physics. Particle physics (or high energy physics) studies the nature of the particles that constitute matter (particles with mass) and radiation (massless particles). Although the word "particle" can refer to various types of very small objects (e.g., protons, gas particles, or even household dust), "particle physics" usually ... Matter - Wikipedia Sometimes in the field of physics "matter" is simply equated with particles that exhibit rest mass (i.e., that cannot travel at the speed of light), such as quarks and leptons. However, in both physics and chemistry, matter exhibits both wave -like and particle -like properties, the so-called wave-particle duality. Definition Based on atoms
Classification Particle Worksheet Of Diagram Matter [612ZS8] Matter is made up of tiny particles (Atoms & Molecules)2. 4 Phase Diagrams. The Atomic Model of Matter Key More than 2000 thousand years ago, A Greek philosopher namedDemocritus led a group of scientists now known as 'atomists'. Classification. plying the particle size analysis to a textural triangle (Figure 1).
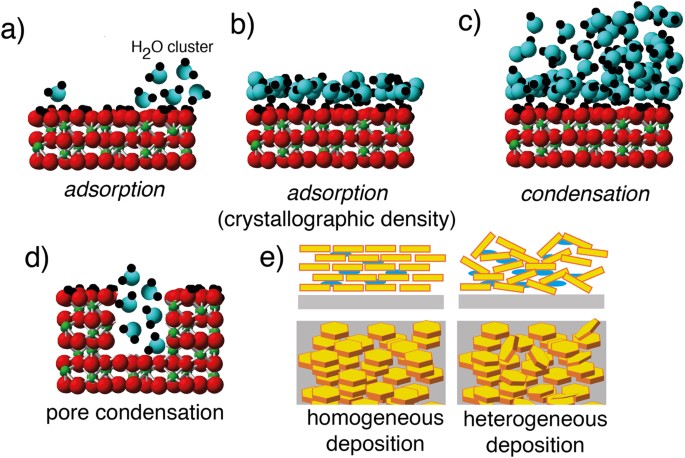
Which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram
2013 MCAS Sample Student Work - Massachusetts ... Particle models of four different types of matter are shown in the diagram below. Identify which of the four models best represents a pure compound. Explain your answer and give a specific example of a compound. 7.3: Penrose Diagrams and Causality - Physics LibreTexts Despite the distortion, the diagram shows lightlike surfaces as 45-degree diagonals. Spacelike and timelike geodesics, however, are distorted, as shown by the curves in the diagram. Figure 7.3. 1 - Penrose diagram for flat spacetime. The distortion becomes greater as we move away from the center of the diagram, and becomes infinite near the edges. Which best represents the reaction of calcium and zinc ... Given the particle diagram which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram; The perceptual disorder in which a person has lost the ability to recognize familiar faces is: Which of the following was a goal of Prohibition? A. increase of innovation B. increase of immigrant influence C. high moral identity for
Which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram. Particulate Matter (PM) Basics - US EPA PM stands for particulate matter (also called particle pollution): the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye. Others are so small they can only be detected using an electron microscope. A beginner's guide to Feynman diagrams | BBC Science Focus ... On the diagrams, matter particles are represented by straight lines and photons as wiggly lines. (There are other types of line when the use of the diagram is expanded beyond simple QED.) There is not a clear convention on which axis is time and space. The Structure of an Atom: Model, Diagram, Examples - Embibe The proton is present in the nucleus of an atom. Charge on Neutrons The particles of an atom without any charge are called neutrons, and it resides in the nucleus of an atom. The mass of the neutron is almost equal to the mass of the proton. It is usually represented by \ ( {\rm {n}}\) or \ ( { {\rm {n}}^ {\rm {0}}}\). The Structure of an Atom: Model, Diagram, Important Notes The smallest particle of an atom that has a negative charge on it is called electrons. It revolves around the nucleus in a circular path in an atom and is represented by \ ( { {\rm {e}}^ - }\). In the \ (1897\), the electron was discovered by J.J Thomson through his cathode ray experiment. Characteristics of Electrons
Phase Diagrams - Chemistry LibreTexts The green line divides the solid and liquid phases and represents melting (solid to liquid) and freezing (liquid to solid). The blue divides the liquid and gas phases, represents vaporization (liquid to gas) and condensation (gas to liquid). There are also two important points on the diagram, the triple point and the critical point. Matter: Definition & the Five States of Matter - Live Science For example, in January 2021, research published in the journal PNAS revealed that during the transformation between the state of liquid and solid, glass becomes a new state of matter referred to... Feynman diagram - Wikipedia The particles are represented by the lines of the diagram, which can be squiggly or straight, with an arrow or without, depending on the type of particle. A point where lines connect to other lines is a vertex, and this is where the particles meet and interact: by emitting or absorbing new particles, deflecting one another, or changing type. Electric Force Fields and the Significance of ... - Study.com Scientists use diagrams to represent the electric force field surrounding a charged particle. When the field lines point away from the particle, the diagram represents a positive charge.
5.3: Light, Particles, and Waves - Chemistry LibreTexts The electromagnetic spectrum is conventionally divided into various parts as depicted in the diagram below, in which the four logarithmic scales correlate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation with its frequency in herz (units of s -1) and the energy per photon, expressed both in joules and electron-volts. Chapter 4 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions - CHE 105/110 ... The first part to be discovered was the electron, a tiny subatomic particle with a negative charge. It is often represented as e −, with the right superscript showing the negative charge. Later, two larger particles were discovered. The proton is a more massive (but still tiny) subatomic particle with a positive charge, represented as p +. 3.2: Elements and Compounds - Biology ... - Biology LibreTexts The answer is chemical bonds. A chemical bond is a force that holds together the atoms of molecules. Bonds in molecules involve atoms sharing electrons. New chemical bonds form when substances react with one another. Figure 3.2. 4: Water Molecule. A water molecule always has this composition, one atom of oxygen, and two atoms of hydrogen. Review Making Chemistry Visible with Doug Ragan | Chemical ... Many chemistry teachers use models and diagrams to help students describe how matter behaves at the particle level. On April 14, 2022, Doug Ragan explained how he uses colored magnets in his classroom to represent things such as subatomic particles, states of matter, balancing chemical equations, types of bonding, molecular geometry and much more. View a recording of his presentation and ...
How To Draw Element Diagrams - U Wiring These diagrams can represent elements and compounds as well as their molecular composition by the types of balls and how they are connected. A particle diagram is a box in which coloured balls are draw to represent atoms or molecules. 11 Na Sodium Electron Shell Structure Schoolmykids Matter Worksheets Element Chemistry Electron Configuration Element Compound […]
Phases of Matter - NASA Phases of Matter All matter is made from atoms. Every substance (oxygen, lead, silver, neon ...) has a unique number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Oxygen, for example, has 8 protons, 8 neutrons, and 8 electrons. Hydrogen has 1 proton and 1 electron. Individual atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules.
3 Types of Soil Particles Sized From Biggest to ... - Hunker Only one type of soil particle can be seen by the naked eye, and that's a sand particle. If you have to get out a microscope to see it, it's either silt or clay, and there you have it: The three types of soil particles, from largest to smallest, are sand, silt, and clay.
Atoms Molecules Compounds And Elements Worksheet This set of printable worksheets and bulletin board printouts really help students learn the difference between elements and compounds.. Unit - 2: Matter/Atoms, Elements, Molecules, Compounds, and Periodic Table. In this unit, students will develop the critical scientific concept concerning the ....
Wave Motion: Types, Definition, Classification ... Matter Waves. The wa ve motion that is associated with the motion of particles like electrons, protons, etc. are termed matter waves. Standing Wave Motion. A standing wave or stationary wave is a special type of wave which oscillates within a confined space. The crest and trough of a standing wave do not move in space.
Chemistry Practice Exam Quiz! - ProProfs A. An element and a mixture B. An element and a compound C. A solution and a mixture D. A mixture and a compound 2. Given the simple representations for atoms of two elements: Which particle diagram represents molecules of only one compound in the gaseous phase? A. B. C. D. 3. Which process is a chemical change? A. Melting of ice B.
Types of tissue: Structure and function | Kenhub Epithelial cells nuclei (histological slide) Epithelial tissue is a highly cellular tissue that overlies body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands.In addition, specialized epithelial cells function as receptors for special senses (smell, taste, hearing, and vision).Epithelial cells are numerous, exist in close apposition to each other, and form specialized junctions to create a barrier ...
Intro To Waves Homework - ProProfs Quiz Questions and Answers 1. Describe how a wave is different than a pulse. 2. Compare the direction in which particles of the medium vibrate for a longitudinal wave compared to a transverse wave. Reference the diagram in question #9 in your discussion. 3. Waves are created by a vibration. A. True B. False 4.
Phase Change: Evaporation, Condensation ... - Study.com But, matter on Earth exists mostly in three distinct phases: gas, liquid and solid. A phase is a distinctive form of a substance, and matter can change among the phases.
Chemistry: The States of Matter - dummies Figure 1: Solid, liquid, and gaseous states of matter. Liquids When an ice cube melts, it becomes a liquid. Unlike solids, liquids have no definite shape, but they do have a definite volume, just like solids do.
Which best represents the reaction of calcium and zinc ... Given the particle diagram which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram; The perceptual disorder in which a person has lost the ability to recognize familiar faces is: Which of the following was a goal of Prohibition? A. increase of innovation B. increase of immigrant influence C. high moral identity for
7.3: Penrose Diagrams and Causality - Physics LibreTexts Despite the distortion, the diagram shows lightlike surfaces as 45-degree diagonals. Spacelike and timelike geodesics, however, are distorted, as shown by the curves in the diagram. Figure 7.3. 1 - Penrose diagram for flat spacetime. The distortion becomes greater as we move away from the center of the diagram, and becomes infinite near the edges.
2013 MCAS Sample Student Work - Massachusetts ... Particle models of four different types of matter are shown in the diagram below. Identify which of the four models best represents a pure compound. Explain your answer and give a specific example of a compound.












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phase-changes-56a12ddd3df78cf772682e07.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TC_606106-heterogeneous-and-homogeneous-mixtures1-5ac4f1a9642dca0036847e52.png)
0 Response to "40 which type of matter is represented by the particle diagram"
Post a Comment