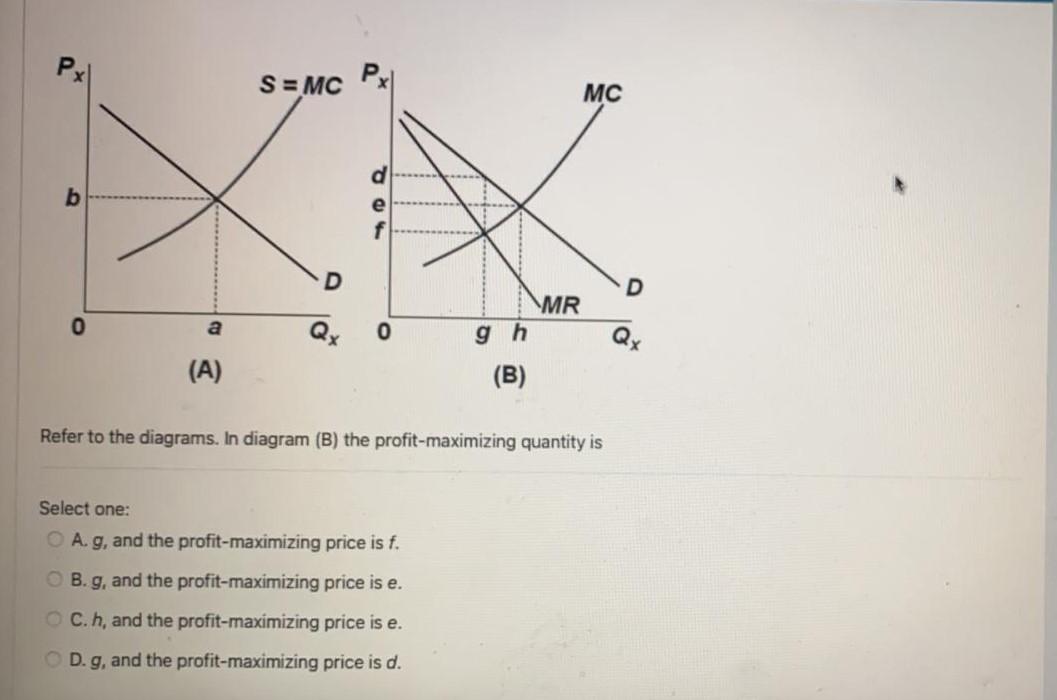
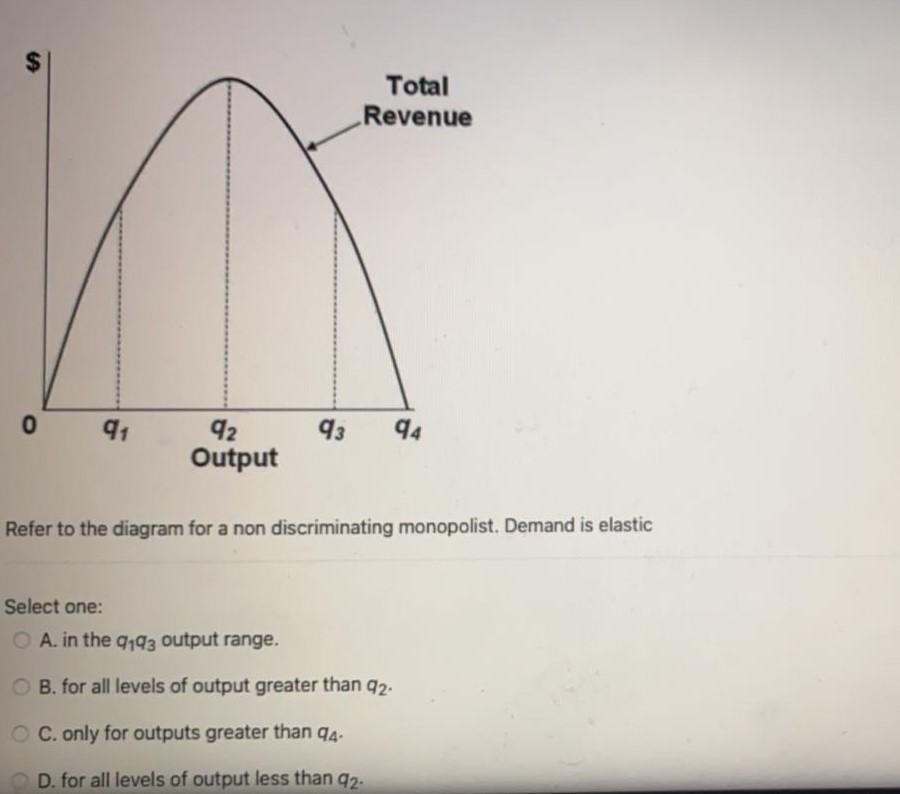
37 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will
A nondiscriminating profit maximizing monopolist A will ... A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: A. will never produce in the output range where marginal revenue is positive. B. will never produce in the output range where demand is inelastic. C. will never produce in the output range where demand is elastic. 41 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output R economic profits will be zero. True 22. A pure monopolist is producing an output such that ATC = $4, P = $5, MC = $2, and MR =. $3. This firm is realizing: an economic profit that could be increased by producing more output. 23.Refer to the diagram.
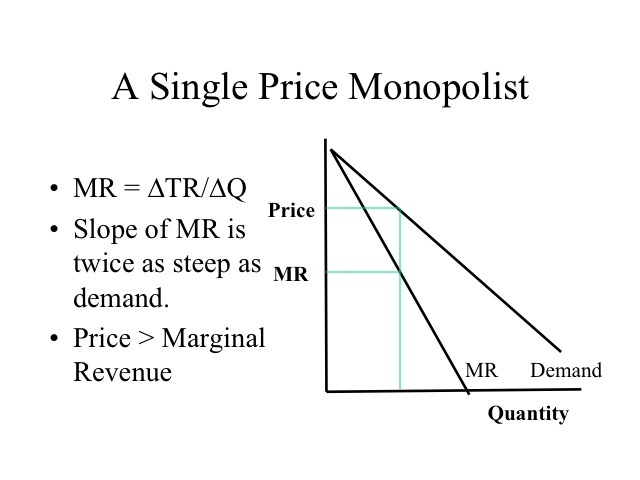
Hw 9 Chap 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's total profit will be $82. Refer to the graph, which shows a total revenue curve for a monopolist. The firm's marginal revenue curve must be downsloping. Answer the question on the basis of the provided demand and cost data for a pure monopolist.

Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will
PDF Answers to End-of-chapter Questions than with nondiscriminating monopoly; others, a lower price. Good features: greater output and improved allocative efficiency. Bad feature: More income is transferred from consumers to the monopolist. 24-7 Assume a pure monopolist and a purely competitive firm have the same unit costs. Contrast the Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At ... Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by ____. ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Kaywee. principles-of-economics; Chapter 12- Monopolies Flashcards | Quizlet Pure monopoly refers to a.) any market in which the demand curve for the firm is downsloping. b.) a standardized product being produced by many firms. c.) a single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. d.) a large number of firms producing a differentiated product.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will. Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 53. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q1. B. q2. C. q3. D. q4. 54. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A. always produce at output q2. B. always produce more than q2. C. never produce an output larger than q2. Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. This ... Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by ____. asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Dorothy Solved 11. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating ... Expert Answer 100% (2 ratings) A non-discriminating monopolist will charge the same price to all consumers. Profits are maximized at the leve … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Total Revenue 0 q1 92 Output 93 94 Previous question Next question Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating monopolist achieves For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be
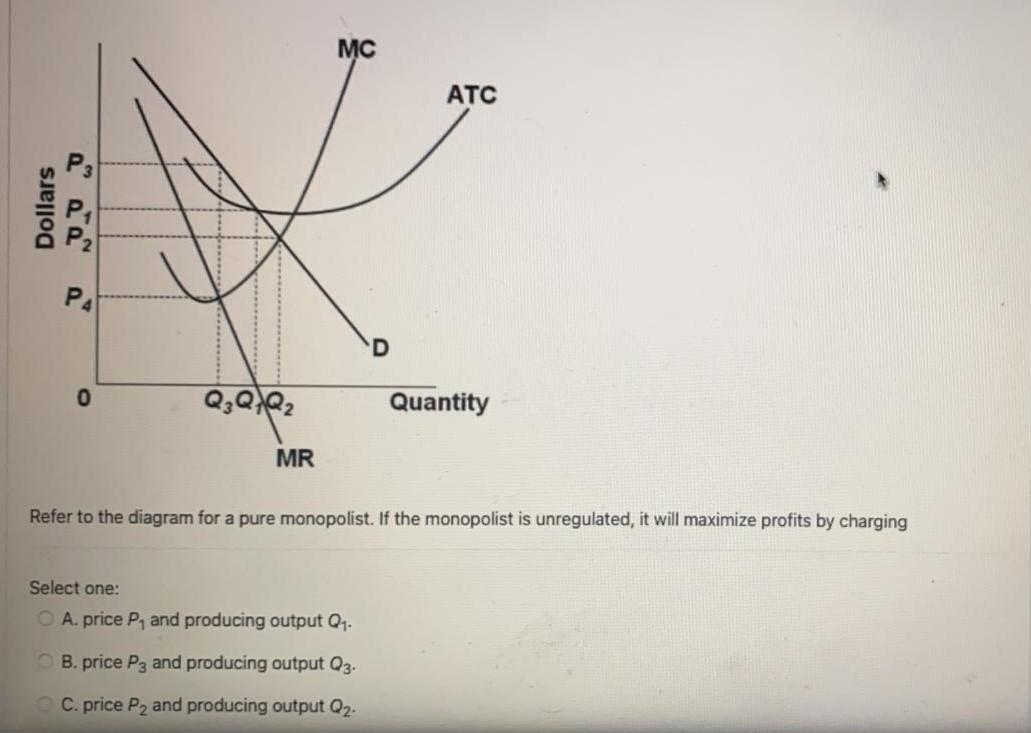
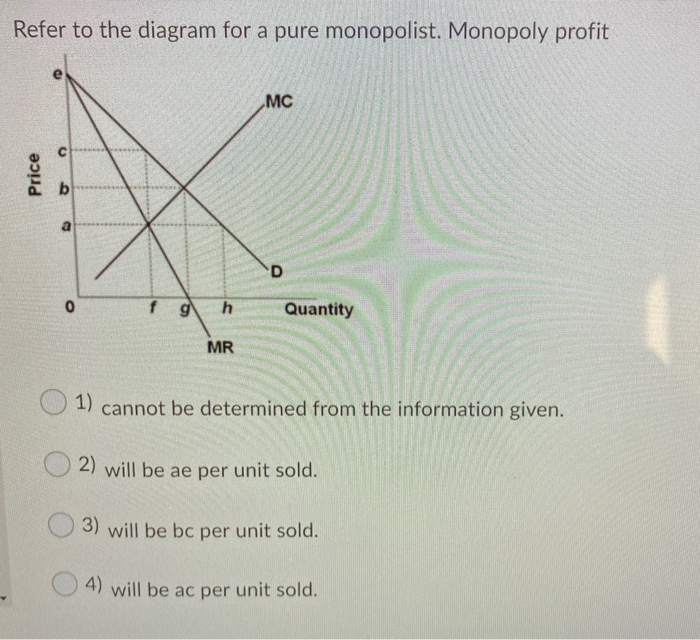
Use the following diagram of a pure monopolist to answer ... Use the following diagram of a pure monopolist to answer the next question. Refer to the diagram. Which of the following is a correct statement? a. Maximum profits are obtained by selling at price $ a b. Maximum profits are obtained by producing output c. The firm's per-unit profits are $ c - $ a d. Demand is elastic at price $ c g ch12.docx - Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms ... For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because when a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. Refer to the diagram for a non discriminating monopolist. Demand is elastic for all levels of output less than q 2 . Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com by drcollinsapeconomics , Apr. 2014 Subjects: Morgan Hughes Click to Rate "Hated It" Click to Rate "Didn't Like It" Click to Rate "Liked It" Click to Rate "Really Liked It" Click to Rate "Loved It" Favorite Add to folder [?] Flag Flashcards Memorize Test Games Tweet Related Essays Card Range To Study through Click or Press Spacebar to Begin » At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will; For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because; Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic: Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic
Question 6 Correct Mark 150 out of 150 Flag ... - Course Hero Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: Select one: a. always produce at output q 2 b. always produce more than q 2 c. never produce an output larger than q 2 d. never produce an output larger than q 1 Feedback The correct answer is: never produce an output larger than q 2 . . . . . 8 Microeconomics Exam 2 Chapter 12 - Subjecto.com 5. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: C. never produce an output larger than q 2. 6. Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should: D. charge a higher ... Solved value: 1.00 points Total Revenue 42 Output ... - Chegg The profit seeking monopolist will Never produce an output larger than Q2 In a monopoly the marginal revenue will be lower than… View the full answer Transcribed image text : value: 1.00 points Total Revenue 42 Output 3 94 Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly ... If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where p = atc, then Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic: Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic The deadweight loss associated with a monopoly occurs because the monopolist
Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At ... Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by ____. asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Dorothy
Microeconomics Exam 2 Chapter 12 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: C. never produce an output larger than q 2. 6. Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should:
A p Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will A. always produce at output q2. B. always produce more than q2. C. never produce an output larger than q2. D. never produce an output larger than q1. C. never produce an output larger than q2. 8.
ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Pure monopoly refers to: Click card to see definition 👆 A single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. Click again to see term 👆 1/66 Previous ← Next → Flip Space
A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: - ScieMce A. will never produce in the output range where marginal revenue is positive. B. will never produce in the output range where demand is inelastic. C. will never produce in the output range where demand is elastic. D. may produce where demand is either elastic or inelastic, depending on the level of production costs. principles-of-economics
Chapter 12- Monopolies Flashcards | Quizlet Pure monopoly refers to a.) any market in which the demand curve for the firm is downsloping. b.) a standardized product being produced by many firms. c.) a single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. d.) a large number of firms producing a differentiated product.
Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At ... Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by ____. ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Kaywee. principles-of-economics;
PDF Answers to End-of-chapter Questions than with nondiscriminating monopoly; others, a lower price. Good features: greater output and improved allocative efficiency. Bad feature: More income is transferred from consumers to the monopolist. 24-7 Assume a pure monopolist and a purely competitive firm have the same unit costs. Contrast the



















0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will"
Post a Comment