41 phase diagram of water pdf
Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Pure Sugar Temperature (°C) 0 20 40 60 80 100 Co =Composition (wt% sugar) L (liquid solution i.e., syrup) Solubility Limit L (liquid) + S (solid 20 sugar) 40 60 80 100 Pure Water Adapted from Fig. 9.1, Callister 7e. Chapter 9 - 3 • Components : Normally, Here you can download 'ammonium sulfate water phase diagram' in PDF … Phase diagrams (video) States of matter Khan Academy Phase Diagrams for the Sodium and Potassium Benzoate For example, the water phase diagram has a triple point corresponding to the single temperature and pressure at which solid, liquid, and gaseous water can ...
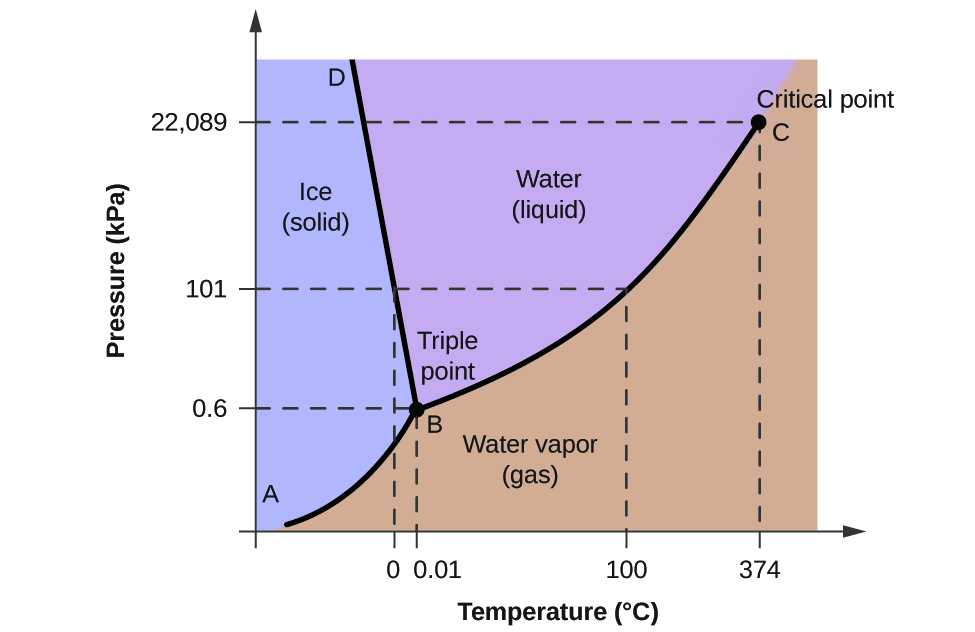
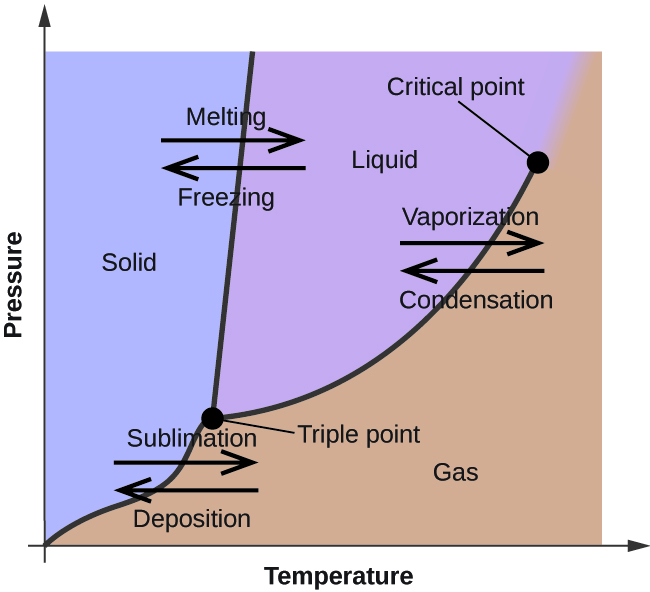
Phase Change in Water 1. Water Triple Point Figure 1: Pressure - Temperature Phase Diagram for Water (Peruzzi et al, 2006) The triple point of water is a unique physical state in which all the three phases (solid, liquid and vapour) coexist at thermodynamic equilibrium. It is assigned a numerical value

Phase diagram of water pdf
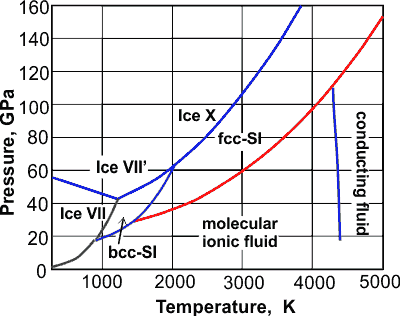
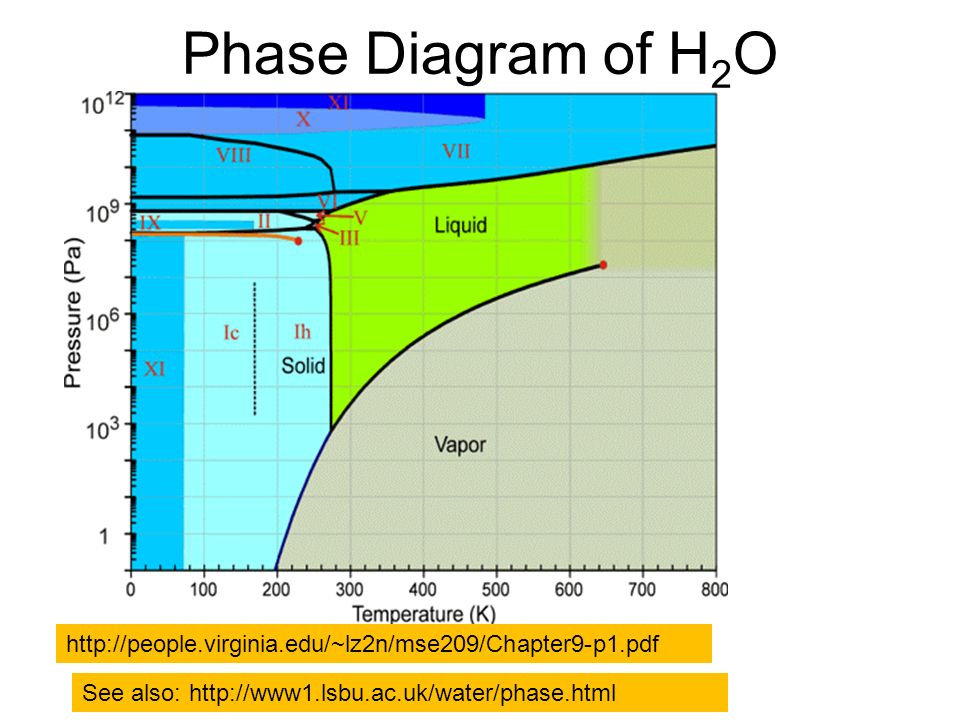
The phase diagram of water is complex,b ,f having a number of triple points and one, or possibly two, critical points. Many of the crystalline forms may remain metastable in much of the low-temperature phase space at lower pressures. A thermodynamic model of water and The phase diagram for the water-surfactant (A-C) binary solution is more complex and is characterized by a UCST behavior at low temperatures and a closed loop immiscibility island at high temperatures; i.e., it phase separates both upon cooling and upon heating. The closed loop is due to the breaking of hydrogen bonds upon heating and Phase diagram questions. 14:440:407 ch9 Question 9.1 Consider the sugar-water phase diagram of Figure 9.1. (a) How much sugar will dissolve in 1500 g water at 90°C (194°F)? (b) If the saturated liquid solution in part (a) is cooled to 20°C (68°F), some of the sugar will precipitate out as a solid. What will be the composition of the ...
Phase diagram of water pdf. Phase diagram worksheet part b phase diagram for water Learning Objectives To understand the basics of a one-component phase diagram as a function of temperature and pressure in a closed system. To be able to identify the triple point, the critical point, and four regions: solid, liquid, gas, and a supercritical fluid. the water phase diagram so significantly. The mentioned liquids evaporate at comparable or lower temperatures than water. Therefore, the discussed effect cannot be observed. The density of liquids at the liquid−vapor interface (Figure 4) provides important information regarding their phase In water's diagram, the slope of the line between the solid and liquid states is negative rather than positive. The reason is that water is an unusual substance in that its solid state is less dense than the liquid state. Ice floats in liquid water. Therefore, a pressure change has the opposite effect on those two phases. e phase behavior of water co n ned by graphene sheets is summarized in the phase diagram of Fig. 5. at this phase diagram is very di erent from the phase diagram of b ulk water may not be surprising.
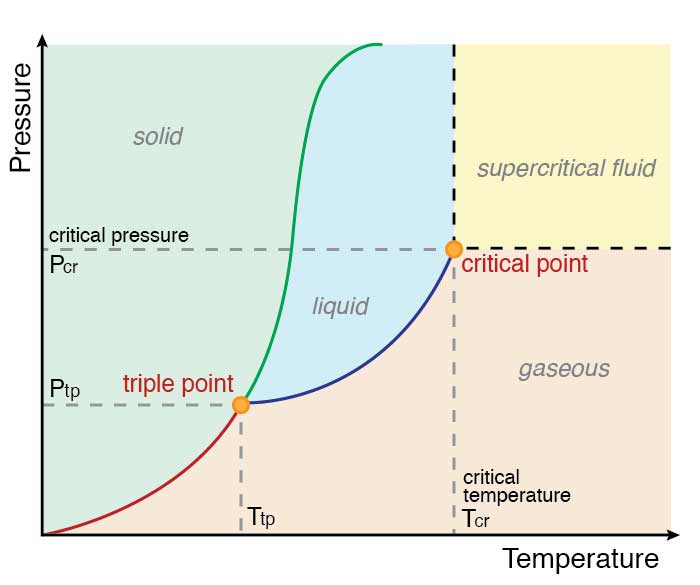
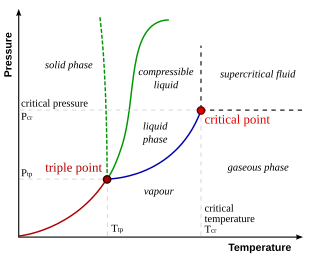
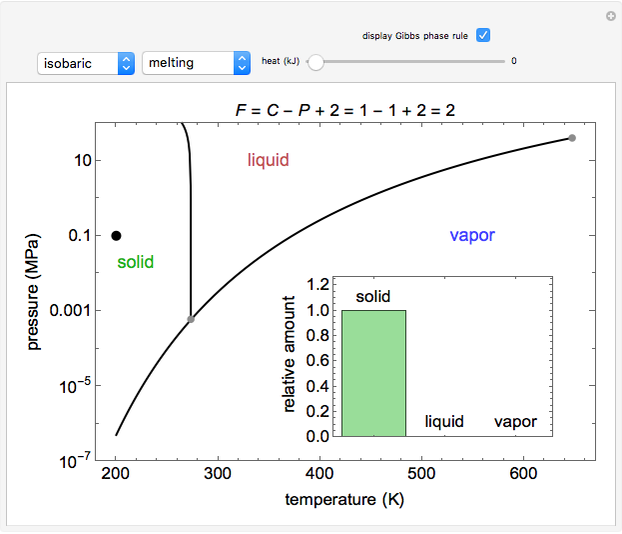
Gibbs Phase Rule -example Phase Diagram of Water C = 1 N = 1 (fixed pressure or fixed temperature) P = 2 1 atm. boiling sublimation melting fixed pressure (1atm) solid liquid vapor 0 0C 100 C fixed pressure (0.0060373atm=611.73 Pa) Ice Ih vapor 0.01 0C fixed temperature (0.01 oC) Terminology of Phase Diagrams Critical Temperature and Critical Pressure This is the point on the phase diagram above which a liquid is unable to form. It cannot form because the particles have TOO much kinetic energy to form intermolecular bonds needed for liquids. Phase diagram or equilibrium diagram which has controllable parameter which affect phase structure, it has many types dependent on number of components and number of phases. Most phase diagrams at 1 atm Reading: West 11-12 Chem 253, UC, Berkeley Phases Homogeneous portion of the system with uniform physical and chemical characteristics Salt - water Salt NaCl A difference in either physical or chemical properties constitutes a phase Water and ice FCC and BCC polymorphic forms of an element
Use the following phase diagram for problems (16) - (22) (16) List the phase changes a sample of ice would go through if heated to its critical temperature at one atmosphere pressure. _____ (17) At what range of pressure will water be a liquid at temperatures above its normal boiling point? _____ (18) In what phase does water exist at its ... Phase diagram of water Note: for H2O melting point decreases with increasing pressure, for CO2 melting point increases with increasing pressure. WATER Covers ~ 70% of the earth's surface Life on earth depends on water Water is a "universal" solvent Easily polluted; hard to purify. MSE 2090: Introduction to Materials Science Chapter 9, Phase Diagrams 2 Component - chemically recognizable species (Fe and C in carbon steel, H2O and Sucrose in sugar solution in water). A binary alloy contains two components, a ternary Equilibrium phase diagram A diagram that depicts existence of different phases of a system under equilibrium is termed as phase diagram. It is actually a collection of solubility limit curves. It is also known as equilibrium or constitutional diagram. Equilibrium phase diagrams represent the relationships
(ice) melting into liquid H2O (water) is an example of a phase transition. ... Here are some example phase diagrams for carbon dioxide, argon and water.17 pages
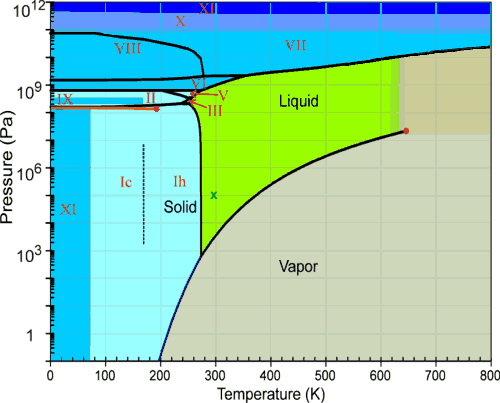
8.1 Phase Diagram of Water • Field - 1 phase • Line - phase coexistence, 2 phases • Triple point - 3 phases 3 phases: solid, liquid, vapour Triple point: 4.579 Torr (~603Pa), 0.0098oC. Chapter 8 4 8.2 Gibbs Phase Rule F + P = C + 2 F is # of degrees of freedom or variance P is # of phases C is # of components H
PHASE DIAGRAMS This is a phase-change diagram for water. 1. Along LEG 'A' water exists as a solid (ice), and the temperature increases as HEAT energy is absorbed. 2. At 0 °C a phase change begins: a) Moving from left to right along LEG 'B', ice is melting to form liquid water
3. The degree of freedom at triple point in unary diagram for water _____. (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 4. Above the following line, liquid phase exist for all compositions in a phase diagram. (a) Tie-line (b) Solvus (c) Solidus (d) Liquidus 5. Following is wrong about a phase diagram. (a) It gives information on transformation rates.
Solid ↔ Liquid. Here. P= 2. C= 1. Here. P= 2, C= 1. Therefore, F= C- P+ 2= 1. Hence the system is univariant. Curve OA': It represents the liquid water- p q.21 pages
We will consider a phase change of 1 kg of liquid water contained within a piston-cycinder assembly as shown in Figure 3.2-1a. The water is at 20oC and 1.014 bar (or 1 atm) as indicated by point (1) on Figure 3.2-2. Figure 3.2-1 Phase change at constant pressure for water3 Figure 3.2-2 Sketch of T-v diagram for water4
A phase is a form of matter that is uniform throughout ... A phase transition is the spontaneous conversion of one ... Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram.21 pages
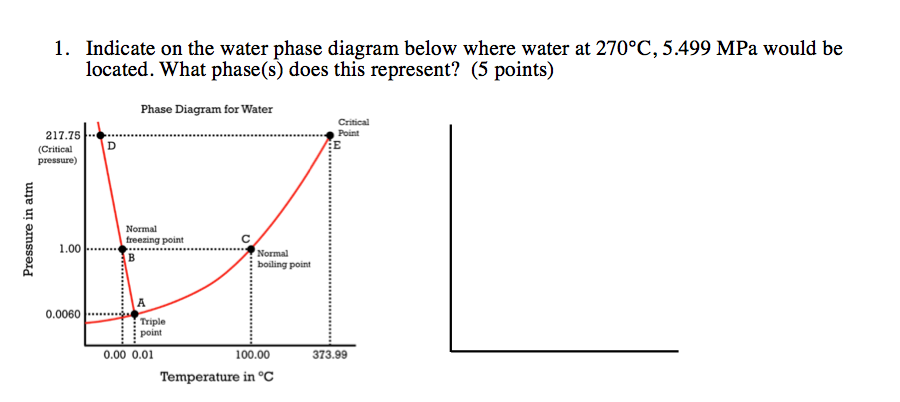
View PHASE DIAGRAM-ASSESSMENT .pdf from STEM 11 at University of the Cordilleras (formerly Baguio Colleges Foundation). Part 1: Using the phase diagram for Water below, determine the STATE of Water
Phase Diagrams Revised: 1/27/16 2 a liquid are still closely packed, but are not organized, allowing them to conform to the shape of the container in which held. A gas has no definite shape or volume, but occupies the entire container in which it is confined. Figure 2: Physical states The lines on the phase diagram represent combinations of pressures and temperatures at
diagram in which pressure is treated as independent variable and is plotted along y - axis whereas temperature is plotted along x-axis. The phase diagram for the water system is shown in Fig 6.1. The phase diagram consists of 1.Curves: There are three curves OA, OB and OC. 2.Areas: Three curves OA , OB and OC divide the diagram into
This has a consequence for the phase diagram of water. The slope of the melting line for water is the opposite of everything else. When you increase the pressure, the melting point of water decreases rather than increases. However, increasing the pressure still moves you to the more dense phase. In this case it is liquid that is most dense.
Phase Diagram of Water Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. LN-10 The number of degrees of freedom of a system is the number of variables that may be changed independently without causing the appearance of a new phase or disappearance of an existing phase. The number of chemical constituents that must be
Phase Diagram for Carbon Dioxide • In contrast to the phase diagram of water, the phase diagram of CO2 has a more typical melting curve, sloping up and to the right. • The triple point is − 56.6°C and 5.11 atm, which means that liquid CO2 cannot exist at pressures lower than 5.11 atm. At 1 atm, therefore, solid CO2 sublimes directly to the vapor while maintaining a temperature of − 78 ...
The present phase diagram equations may be rearranged to give expressions for composition variables such as water content, salt concentration, unfrozen fraction of the solution, etc., which may be employed in the analysis of the relationship between solution composition and solution effects injury.
Phase diagram questions. 14:440:407 ch9 Question 9.1 Consider the sugar-water phase diagram of Figure 9.1. (a) How much sugar will dissolve in 1500 g water at 90°C (194°F)? (b) If the saturated liquid solution in part (a) is cooled to 20°C (68°F), some of the sugar will precipitate out as a solid. What will be the composition of the ...
The phase diagram for the water-surfactant (A-C) binary solution is more complex and is characterized by a UCST behavior at low temperatures and a closed loop immiscibility island at high temperatures; i.e., it phase separates both upon cooling and upon heating. The closed loop is due to the breaking of hydrogen bonds upon heating and
The phase diagram of water is complex,b ,f having a number of triple points and one, or possibly two, critical points. Many of the crystalline forms may remain metastable in much of the low-temperature phase space at lower pressures. A thermodynamic model of water and




![98materials Phase Diagrams - [PDF Document]](https://demo.vdocument.in/img/378x509/reader023/reader/2020111721/55cf9a68550346d033a19301/r-1.jpg)















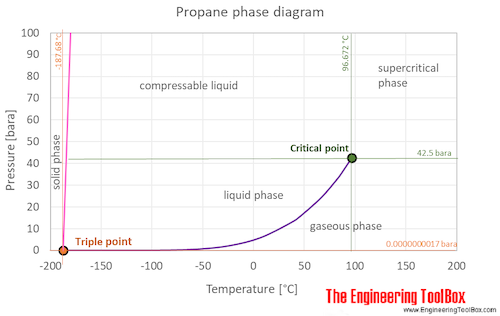
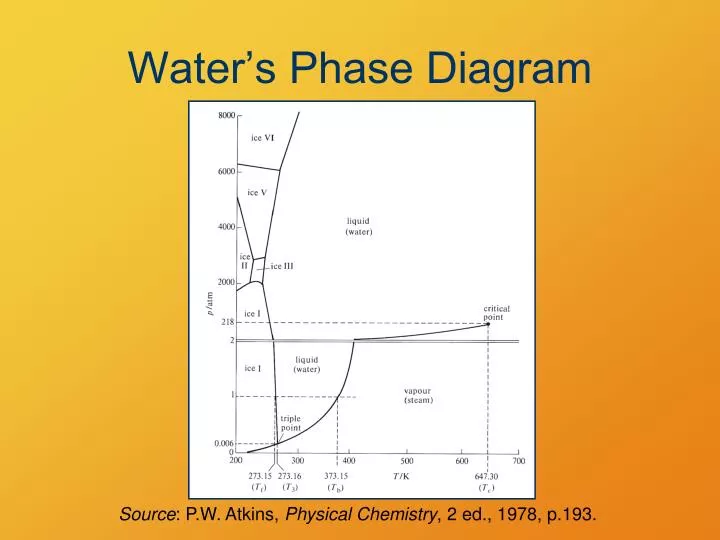

0 Response to "41 phase diagram of water pdf"
Post a Comment