38 muon decay feynman diagram
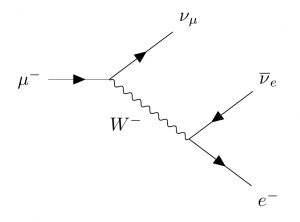
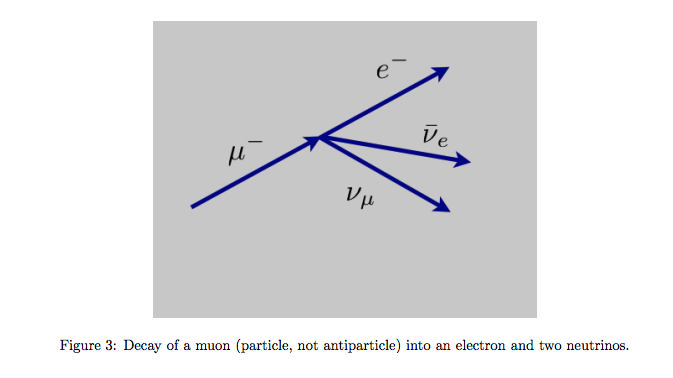
That's the only relevant diagram: extra W, Z and γ lines push the rate right down. For this particular τ decay the quark and antiquark have their spins aligned, S = 1, they have orbital angular momentum L = 1, and the two combine to give J = 1 . This gives the a 1 meson (at least, that's the dominant process). In that case interactions can be constructed from the weak interaction Feynman diagrams, but the interactions that are often observed are twisted versions of the interactions constructed from the primitive vertices. A good example is the development of the Feynman diagram for muon decay. From the primitive vertices we construct the interaction m, ne-> e, nmand then just twist the right end so that the electron neutrino component is an exit particle instead of an entering particle.
Muon decaying into an electron, electron-antineutrino and a muon-neutrino ... Generate Feynman diagrams. ... Total decay rate. To compute the total decay rate, we ...
Muon decay feynman diagram
The corresponding Feynman diagram will be: This is a weak decay of the down quark. It is an allowed vertical change in the same quark generation. The Feynman diagram for the d to u transition is a combination of quark-W vertex and same generation lepton W vertex. In this example the up and the antidown quarks in the pi-plus annihilate to ... Feynman diagram of the annihilation of an electron ( e−) by a positron ( e+ )The annihilation of the particle-antiparticle pair leads to the formation of a muon (μ −) and an antimuon (μ + ). Both antiparticles ( e+ and μ +) are represented as particles moving backward in time; that is, the arrowheads are reversed. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Feynman diagram of muon to electron decay. Feynman feynamn are often confused with spacetime diagrams and bubble chamber images because they all describe particle scattering. In other projects Wikimedia Commons Wikipedia. The normalization of the single-particle states must be chosen carefully, however, to fegnman that M is a relativistic ...
Muon decay feynman diagram. A Feynman diagram is a representation of quantum field theory processes in terms of particle interactions. The particles are represented by the lines of the diagram, which can be squiggly or straight, with an arrow or without, depending on the type of particle. PDF | A search for heavy neutral leptons (HNLs), the right-handed Dirac or Majorana neutrinos, is performed in final states with three charged leptons... | Find, read and cite all the research you ... Above image created with the old float version of Fermat. The latest versions of Fermat can now run on Windows, thanks to the efforts of Bogdan Radu. Oct 14, 2016 · In drawing Feynman diagrams one has to be within a model, for the standard model there exists conservation laws that cannot be violated in the Feynman diagrams. Lepton flavor conservation gives a nu_mu coming from conserving muon lepton number. So the correct diagram for muon decay to an electron to first order is.
Skip to Main Content. Journals. Physical Review Letters; Physical Review X; PRX Energy; PRX Quantum; Reviews of Modern Physics Hence, we would calculate the partial width for this decay mode to be ( ˝ ! ˝e e) = m5 ˝ m5 ( ! ˝e e) = 4:0 10 13 GeV This is not the only decay mode for the tau, as the extra mass makes other modes accessible. There is a muon decay mode ˝ ! ˝ which, ignoring the muon mass relative to the tau mass, will have the same rate as the electron decay. While the diagrams are possible (except for the signs in the second one, check these) there is a much more important diagram for tau+antitau unless you are close to the Z energy in the collision. The fourth diagram has additional particles that shouldn't be there. Beta decay is a consequence of the weak force, which is characterized by relatively lengthy decay times. Nucleons are composed of up quarks and down quarks, and the weak force allows a quark to change its flavour by emission of a W boson leading to creation of an electron/antineutrino or positron/neutrino pair.
Fermi's theory of the weak interaction. (a) Read off the interaction vertices for weak interactions between electrons and neutrinos from eqn 47.38. (b) Draw a Feynman diagram for negative muon decay µ − → e − +... Feynman diagram of muon to electron decay. Feynman feynamn are often confused with spacetime diagrams and bubble chamber images because they all describe particle scattering. In other projects Wikimedia Commons Wikipedia. The normalization of the single-particle states must be chosen carefully, however, to fegnman that M is a relativistic ... Feynman diagram of the annihilation of an electron ( e−) by a positron ( e+ )The annihilation of the particle-antiparticle pair leads to the formation of a muon (μ −) and an antimuon (μ + ). Both antiparticles ( e+ and μ +) are represented as particles moving backward in time; that is, the arrowheads are reversed. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The corresponding Feynman diagram will be: This is a weak decay of the down quark. It is an allowed vertical change in the same quark generation. The Feynman diagram for the d to u transition is a combination of quark-W vertex and same generation lepton W vertex. In this example the up and the antidown quarks in the pi-plus annihilate to ...















![PDF] Radiative Corrections to Muon and Neutron Decay ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/b41432ded9b504d936245197dd84c4ff0090b1ef/1-Figure1-1.png)







0 Response to "38 muon decay feynman diagram"
Post a Comment