38 d orbital energy level diagram
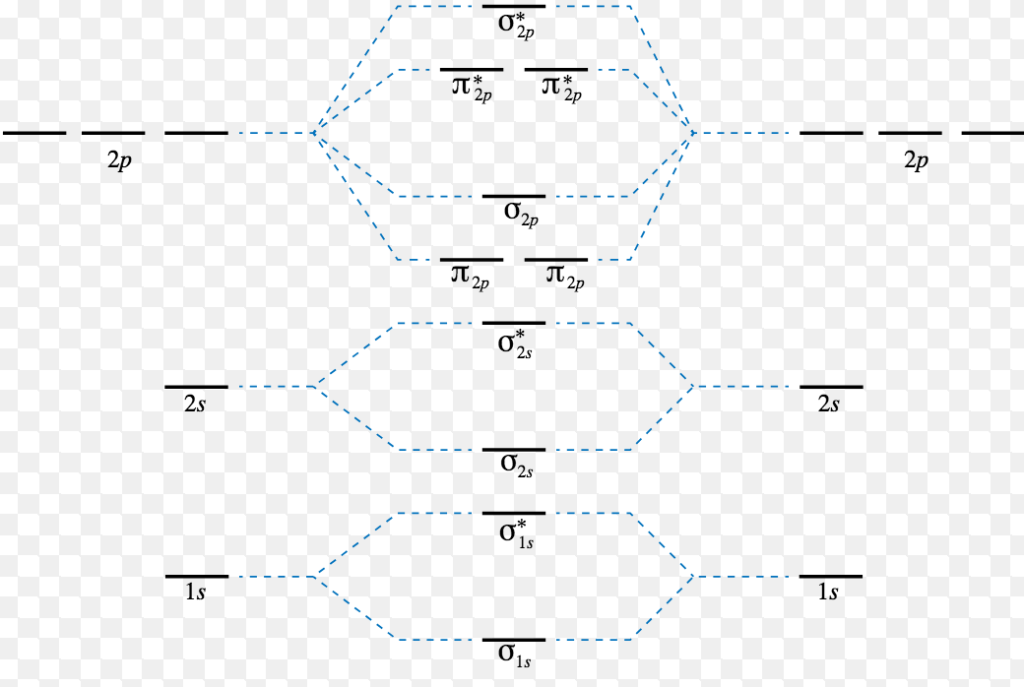
Oct 11, 2021 · 1 answer(a) The complex ion, [Ni(en)3]2+ is octahedral. Since en is a strong ligand there is pairing of electrons. Number of unpaired electrons = n ... Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
The CFT diagram for tetrahedral complexes has d x 2 −y 2 and d z 2 orbitals equally low in energy because they are between the ligand axis and experience little repulsion. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane.
D orbital energy level diagram
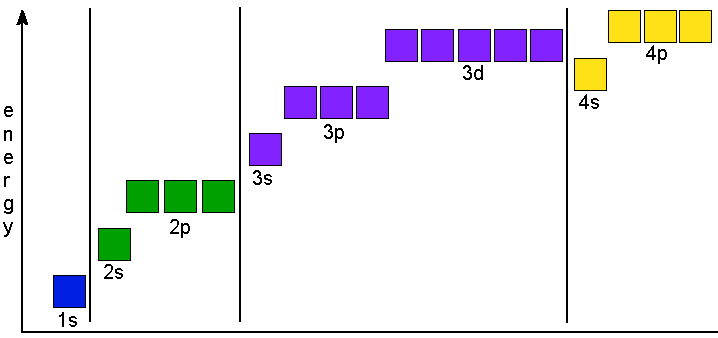
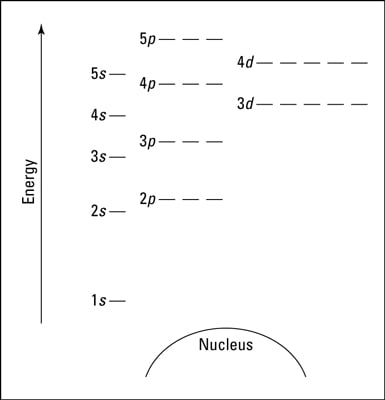
The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals. For example, the orbital 1s (pronounced as the individual numbers and letters: "'one' 'ess'") is the lowest energy level (n = 1) and has an angular quantum number of ℓ = 0, denoted as s. Orbitals with ℓ = 1, 2 and 3 are denoted as p, d and f respectively. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron in each orbital. Question: Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbital on the cobalt atom in a [CoBr_6]^3- complex. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron ...
D orbital energy level diagram. The energy of an orbital depends on the shape and size of the orbital. In a multiple-electron system, the shielding effect also influences the orbital's energy. Energies of orbitals are quantized as per quantum mechanics. Thus, there are only selected energy levels available, which an electron can occupy. An electron residing in a particular ... The molecular, sp 3 orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedron, with bond angles of 109.5 o. Each of the 1s orbitals of H will overlap with one of these hybrid orbitals to give the predicted tetrahedral geometry and shape of methane, CH 4. Hybridization also changes the energy levels of the orbitals. The 2s orbital of carbon is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals, since it is more penetrating. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Figure 46. The splitting pattern of d-orbital energy levels of d3-metal complexes in tetragonal distortion. 2. Rhombic distortion: The unequal amount of elongation or compression along two four-fold axes of rotation in octahedral complexes produces rhombic distortions. The common examples of rhombic distortion are high-
energy level, d. block, 7th. column, this means that the electron configuration will end. 3d8. with the. d. orbital being one level lower than the energy level it is on. orbital diagram for arsenic see more ideas approximately from diagram electron configuration gallery & create your house design images related to pictures as well help you in locating the solution are seeking about … A P-Orbital in the second energy level is a 2p orbital ( 2p(x), 2p(y), 2p(z) ) A P-Orbital in the third energy level is a 3p orbital ( 3p(x), 3p(y), 3p(z) ) etc. In addition, the third and subsequent energy levels each contain five D-Orbitals, the fourth and subsequent energy levels contain seven F-Orbitals and so on. Dec 16, 2021 · Energy level diagrams are diagrams that show the arrangement of orbitals in order of increasing energy. The principal quantum number alone can indicate the energy of an electron in a single atom. In multi-electron atoms, an electron's energy is determined by both its principal quantum number (n) and its azimuthal quantum number (l). The d orbitals also split into two different energy levels. The top three consist of the dxy, ...May 6, 2021 · Uploaded by Chuck WightCrystal Field Stabilization Energy · Introduction to Crystal Field...
Sketch the d-orbital energy level diagrams for [Fe(OH 2) 6] 3+ and [Fe(CN) 6] 3-. Use your diagrams to answer the questions. Use your diagrams to answer the questions. 1 a). Electron configuration of sodium atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f. Before moving on to show the energy level diagram for A. 2 . molecules - we need to be clear about the labels for. M.O.’s Two types of . M.O. - in terms of symmetry to rotation about molecular axis. s/s, p. z /p z. s/p z - completely symmetrical to such rotation. All such given Greek symbol : σ ("sigma") p x /p x, p y /p y - change sign every 180 o rotation - these are given symbol : π ... Electron configuration of fluorine(F) atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
OOPS!! "Where an atom's ELECTRONS go" is what the heading should read.Electron orbital diagrams showing energy levels (n), subshells or sublevels(s, p, d, f...
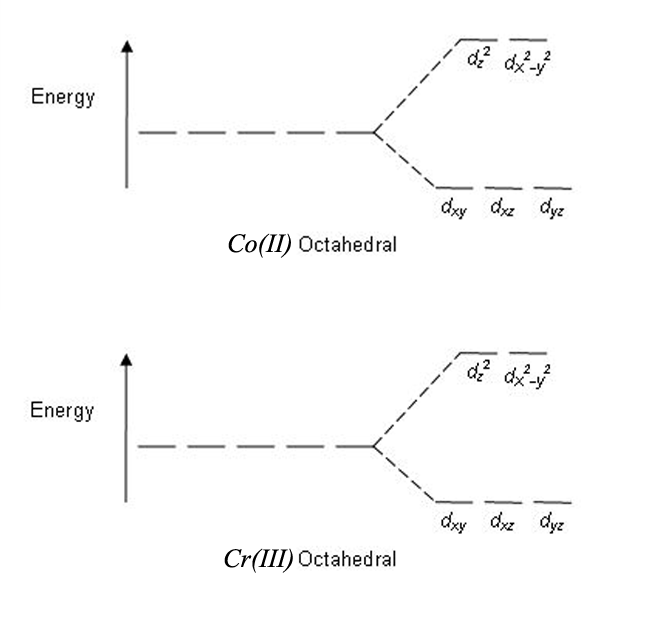
Metal d orbitals in an O h ... • A low‐spin configuration avoids occupying the higher energy e g level by pairing electrons in the t 2g level. • The o energy gap in octahedral complexes of transition metals is relatively small and is comparableto typicalpairingenergies. • For a given first‐row transition metal ion, i.e. of a fixed oxidation state, the magnitude of o …
one d orbital to another (small energy gap) ... molecular orbital diagram for a coordination complex? ... Electronic Structure of Transition Metal Complexes.31 pages
Stable electronic configurations: MO Energy Level Diagrams Reviewed ... Ligand (σ- and π*) orbitals and metal d-orbitals are shown.) Simplified MO energy ...37 pages
by RJ Deeth · 2020 · Cited by 1 — Qualitative MO theory predicts degenerate dπ orbitals for planar coordination complexes with formally σ-only ligands and the splitting energy, ...
All levels except the first have p orbitals. d ORBITALS. In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3px, 3py, 3pz). At the third level there are a total of nine orbitals altogether. The five 3d orbitals are called
The CFT diagram for tetrahedral complexes has d x 2 −y 2 and d z 2 orbitals equally low in energy because they are between the ligand axis and experience little repulsion. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane.
Figure 6.27 "Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom" shows that the energy levels become closer and closer together as the value of n increases, as expected because of the 1/n 2 dependence of orbital energies. Figure 6.27 Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom.
another twice-degenerate energy level consisting of $\mathrm{d}_{xy}$ and $\mathrm{d}_{x^2-y^2}$ The first two should be immediately obvious, the third maybe not. ... What is the correct molecular orbital diagram for the d orbitals in platinum for the tetraammineplatinum(II) complex?
Draw a qualitatively energy-level diagram showing d-orbital splitting in the octahedral environment. Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the complex ...
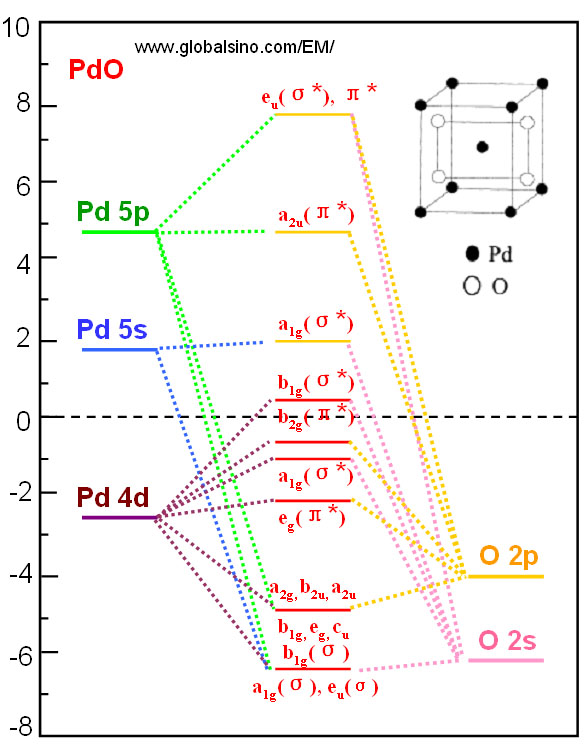
Similarly if the energy of σ-orbital is closer to ... The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 10. The formation of σ-molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding and non-bonding) in octahedral complexes of transition metals. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, high resolution images and no …
This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes. It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. n represents the energy leve...
The electron shell is known as an energy level present on the outside part of an atom around the atomic nucleus. Inside the shell we have subshells. These Sub-Shells of an atom are subdivisions of electron shells (energy levels) represented by s, p, d, f.
• that raises the energy of the d-orbitals! • The d-orbitals are anti-bonding or at best non-bonding. • The stability of the bonding comes from the ligand
The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting the molecular orbitals in order of increasing number of internuclear nodal planes, the orbital with no such nodal plane lying at lowest energy and the orbital with nodal planes between all the atoms lying at highest energy.
Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals.
The s-orbital has the azimuthal quantum number value of 0, the p-orbital has a value of 1, and the d-orbital has two and f-orbital 3. The orbital energy levels of these are varied, s-orbital having the lowest energy level and f-orbital being the highest, summed up as s < p <; d < f.
So here we're essentially given to different complexes. We have F E tho the following. Then we have a cyanide uh complex. So irons normal electron configuration involves the nearest noble gas for us to then 36. And we can see that in both cases we have iron in the FE three plus form, which means that after ionization completely occurs, we're going to have three D five, so we have five …
But two of the d orbitals have lobes pointing along those axes - the 3d x 2 - y 2 and 3d z 2 orbitals. Those will feel more repulsion than the other three, which have lobes in between the axes. That means that two of the d orbitals will now have a higher energy than the other three - which is exactly what the diagram we have been using shows.
Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron in each orbital. Question: Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbital on the cobalt atom in a [CoBr_6]^3- complex. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron ...
For example, the orbital 1s (pronounced as the individual numbers and letters: "'one' 'ess'") is the lowest energy level (n = 1) and has an angular quantum number of ℓ = 0, denoted as s. Orbitals with ℓ = 1, 2 and 3 are denoted as p, d and f respectively.
The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals.




















0 Response to "38 d orbital energy level diagram"
Post a Comment