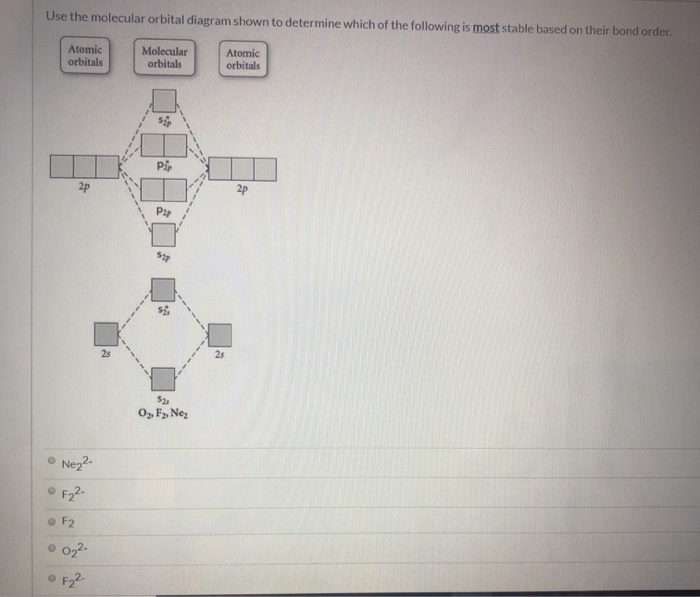
36 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown below to determine which of the following molecules/species is most stable (O2, F2 and Ne2) . Explain their magnetic properties using the same diagram. Calculate the bond order in each of the molecule. The product of a Lewis acid-base reaction, is a neutral, dipolar or charged complex, which may be a stable covalent molecule. As shown at the top of the following drawing, coordinate covalent bonding of a phosphorous Lewis base to a boron Lewis acid creates a complex in which the formal charge of boron is negative and that of phosphorous is ...
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a. F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2 FREE Expert Solution Recall that the bond order t ells us the strength and length of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is stronger and shorter. ...
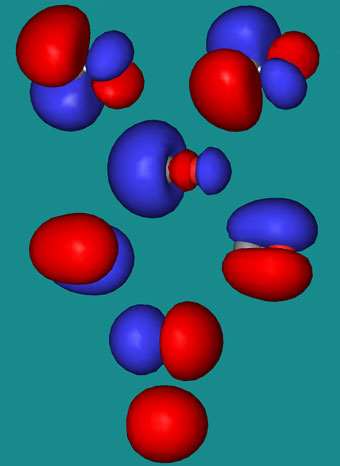
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Electron configuration was first conceived under the Bohr model of the atom, and it is still common to speak of shells and subshells despite the advances in understanding of the quantum-mechanical nature of electrons.. An electron shell is the set of allowed states that share the same principal quantum number, n (the number before the letter in the orbital label), that electrons … A molecular orbital diagram of ethene is created by combining the twelve atomic orbitals associated with four hydrogen atoms and two sp 2 hybridized carbons to give twelve molecular orbitals. Six of these molecular orbitals (five sigma & one pi-orbital) are bonding, and are occupied by the twelve available valence shell electrons.
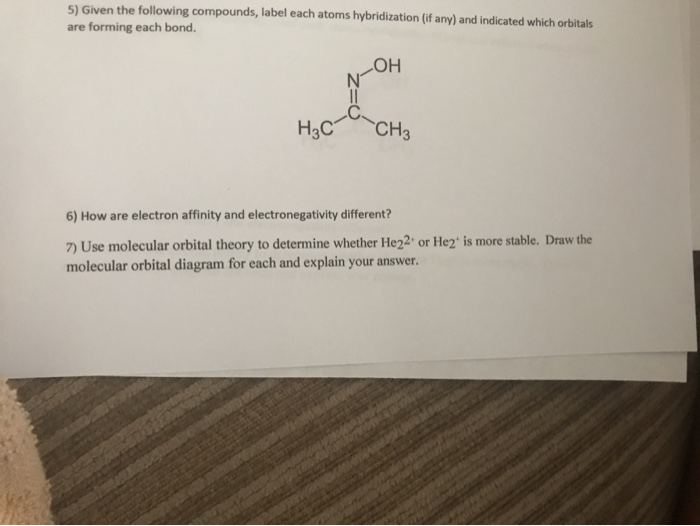
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. 31) Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) C2^2⁺ B) N2^2⁺ C) B2; D) C2^2⁻ E) B2^2⁺ 32) How many moles of oxygen are formed when 58.6 g of KNO3 decomposes according to the following reaction? The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.11 g/mol. 4 KNO3(s) → 2 K2O(s) + 2 N2(g) + 5 O2(g) Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ... The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) C2^2+ B) N2^2+ C) B2; D) C2^2-E) B2^2+ 5) Which statement regarding stable heteronuclear diatomic ...
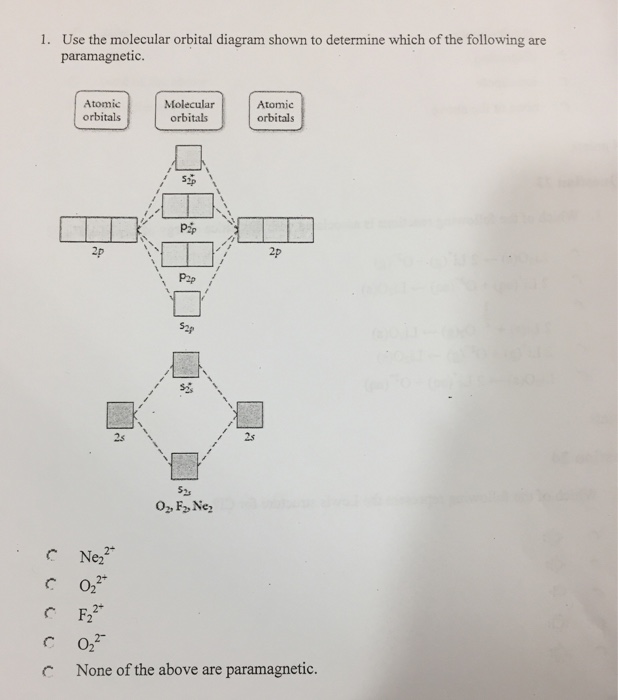
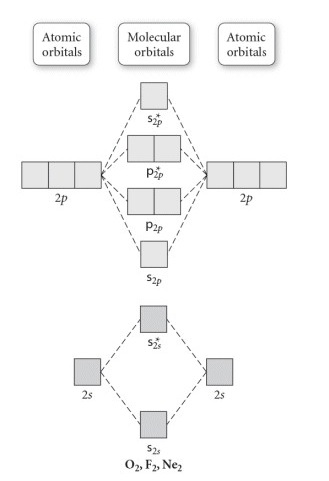
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures. Use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which is most stable a o22 bf2 c f22 d f22 e ne22 a. A asdfasdf b asdfasdf c asdf d f2 2 e none of the above are paramagnetic. Label each and each and every molecular orbital with its call sigma pi and position the accessible electrons interior the perfect atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Molecular Orbitals Of The Allyl Cation Allyl Radical And Allyl Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. 38 ... Chemistry questions and answers. Part A Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals TE 2p 2p 22 Tap 25 BCN NA? 82 MacBoo Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals ...
4.9.2021 · Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, … b. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in energy than the separate atomic orbitals. c. Electrons placed in anti-bonding orbitals stabilize the ion/molecule. d. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ B) F2^2⁺ C) F2^2⁻ D) F2 E) O2^2⁺ E). O2^2⁺ Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2 2⁺ B) Ne2 2⁺ C) F2 2⁺ D) O2 2⁻ E) None of the above are paramagnetic. C). F2^2⁺ Identify the characteristics of a liquid A ... Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
In Molecular orbital diagram, we just need to calculate the number of electrons in anti-bonding orbital and bonding orbital, then we can use the formula in order to calculate bond order is: Bond order = (No. of electrons in anti-bonding MO) - (No. of electrons in bonding MO) / 2. Hope this helps!
Start studying Module Two Chem 101 Problems. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. D c 2 2. Start studying exam 3. Inorganic Chemistry Why Do Compounds Like Sf6 And Sf4 Exist But What Is The Molecular Orbital Diagram For O2 And O2 Ions Quora
Solution: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) N22+ B) B2 C) B22+ D) C E) C22+. Sketch the molecular orbital energy level diagram for the ion. How many net σ and π bonds does the ion have? What is the carbon-carbon bond order? How has the bond order changed on adding electrons to C 2 ...
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. The three 3 component mixture shown below was spotted to a tlc plate and developed using the solvent system listed. 1 draw the molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following is most stable.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Identify the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons in water. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals one molecular ...
Draw the Molecular orbital Diagram Shown to Determine which Of the Following is Most Stable. use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable 38 a b2 b c22 use the molecular orbital question draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to answer to draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to ...
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.A) N22+ B) B2C) B22+D) C22-E) C22+ FREE Expert Solution Show answer Answer:
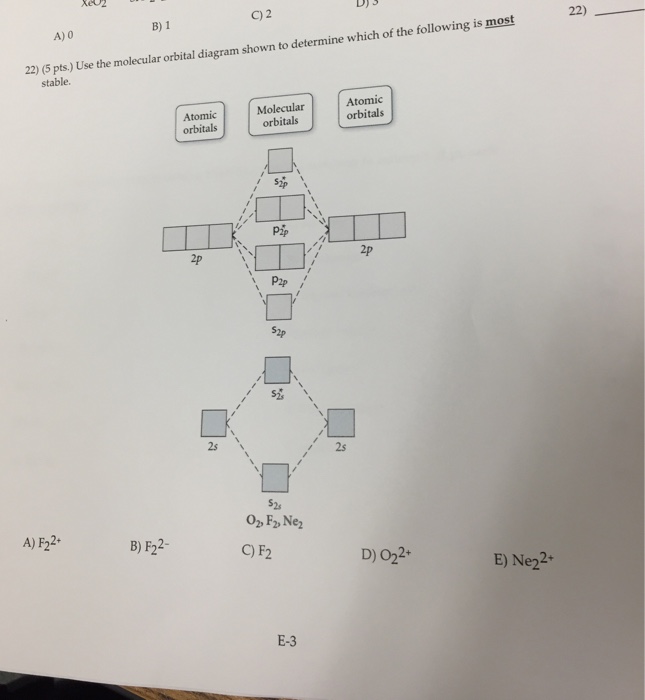
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F, Ne Ne22 F₂2. F2 . 022- • F22. Question: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order.
The most stable geometry is an arrangement that keeps the atoms or electrons bonded to the central atom as far apart as possible. ... the 𝜋2𝑝 orbitals are higher in energy than the 𝜎2𝑝 orbital as shown in diagram B. ... Use the molecular orbital theory to determine the ground state electron configuration of F2 and F+2.
Which of the following is the correct orbital diagram for a nitrogen (n) atom_ In the ground state, they are arranged in the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1 x 2p 1 y 2p 1 z. Write the complete orbital diagram. Nitrogen molecule (N 2)Energy Levels, Orbital Diagrams, Electron Config, Noble Gas - Google Slides.
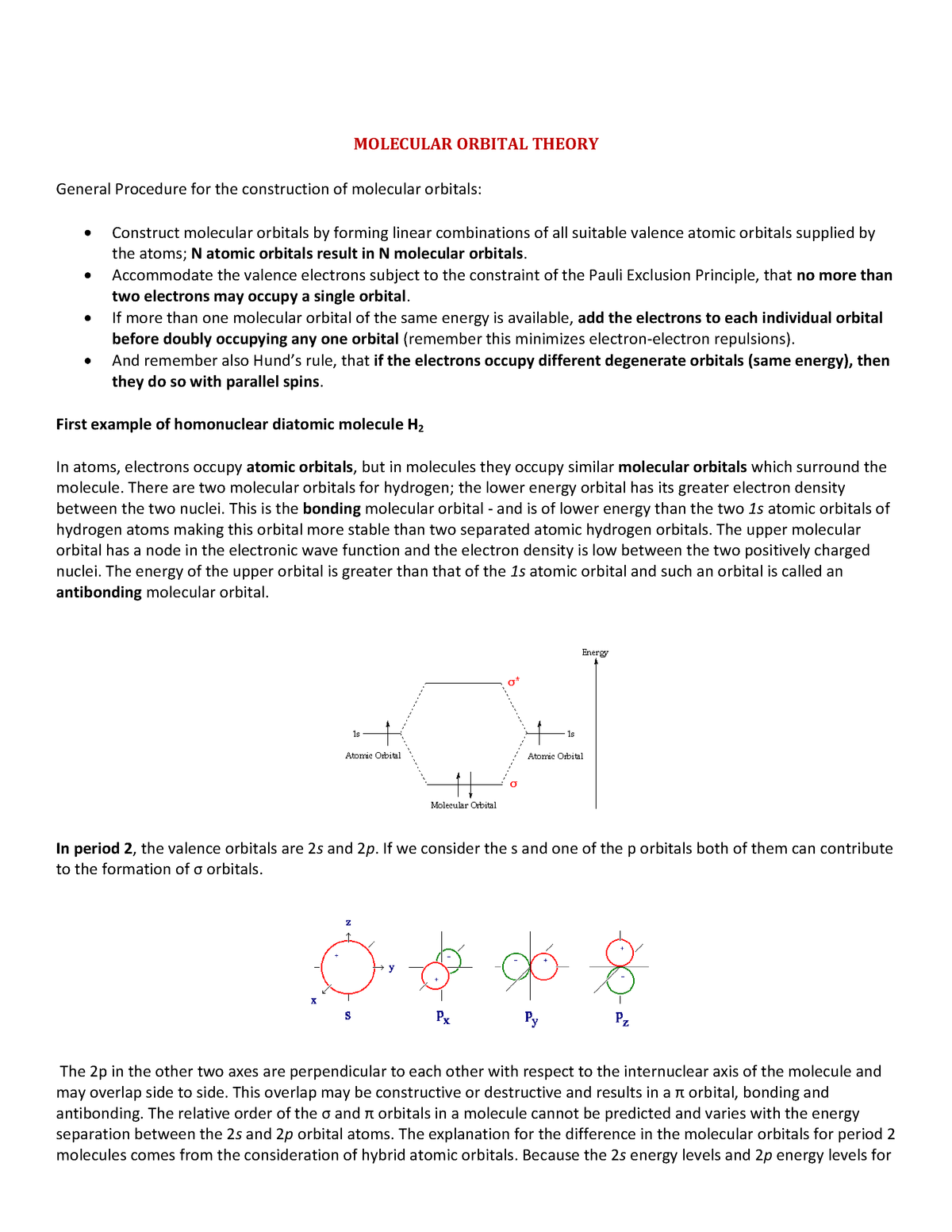
Eg: H + H two 1s orbitals mix to form sigma and sigma*. Two electrons total, both occupy the sigma orbital, two more electrons in bonding than antibonding orbitals, the compound is stable. Eg: He + He; same mixing as above. Four electrons, two in the sigma, two in the sigma*. Since there are as many bonding electrons as as antibonding, there is ...
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. asked Jul 15, 2019 in Chemistry by brittanyr9777. general-chemistry; Refer to the information provided in Figure 16.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) is ...
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. asked Aug 5, 2019 in Chemistry by z1stxfile. general-chemistry; Long, thin lava flows are typically produced by. asked Aug 27, 2019 in Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences by Schmubby. introductory-courses ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
🔴 Answer: 1 🔴 on a question Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. a. f22+ b. ne22+ c. f22- d. o22+ e. f2 - the answers to answer-helper.com
According to Merriam-Webster and the Online Etymology Dictionary, the word "molecule" derives from the Latin "moles" or small unit of mass.. Molecule (1794) – "extremely minute particle", from French molécule (1678), from New Latin molecula, diminutive of Latin moles "mass, barrier". A vague meaning at first; the vogue for the word (used until the late 18th century only in Latin …
The theory uses Molecular Orbital (MO) diagram to explain the bonding between atoms. For example, to determine the stability of an atom, bond order is calculated. Bond order is calculated to determine the strength and length of the bond. The high value of the bond order means the bond is shorter, stronger, and have high bond strength.
Mar 09, 2018 · Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. 38 a b2 b c22. C o22 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. 3 draw the molecular orbital diagram needed and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A n 2 2. D c 2 2. C b 2 2.
Dec 16, 2021 · Chemistry questions and answers. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F2, Nez • Nez2 • F₂2. • F2 022 • F22. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
A molecular orbital diagram of ethene is created by combining the twelve atomic orbitals associated with four hydrogen atoms and two sp 2 hybridized carbons to give twelve molecular orbitals. Six of these molecular orbitals (five sigma & one pi-orbital) are bonding, and are occupied by the twelve available valence shell electrons.
Electron configuration was first conceived under the Bohr model of the atom, and it is still common to speak of shells and subshells despite the advances in understanding of the quantum-mechanical nature of electrons.. An electron shell is the set of allowed states that share the same principal quantum number, n (the number before the letter in the orbital label), that electrons …
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.


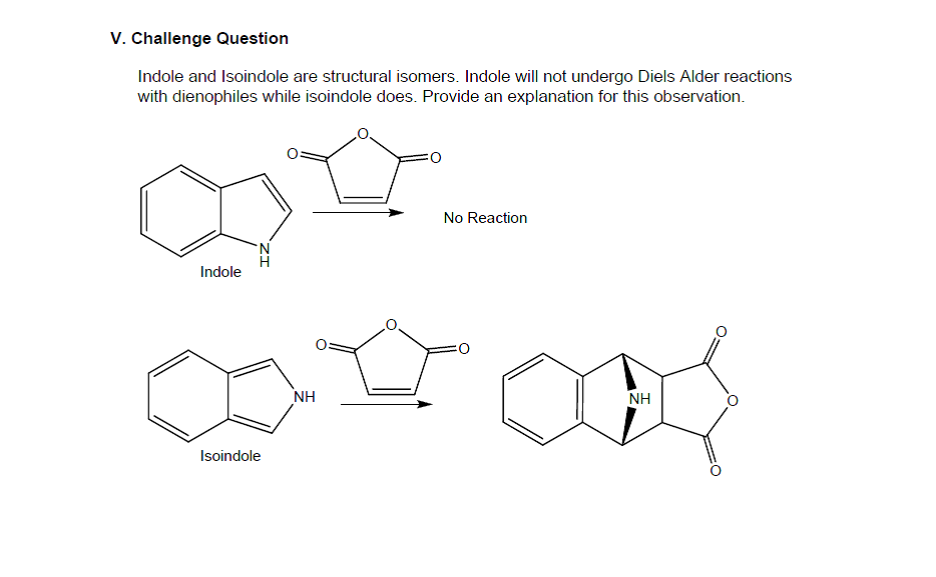
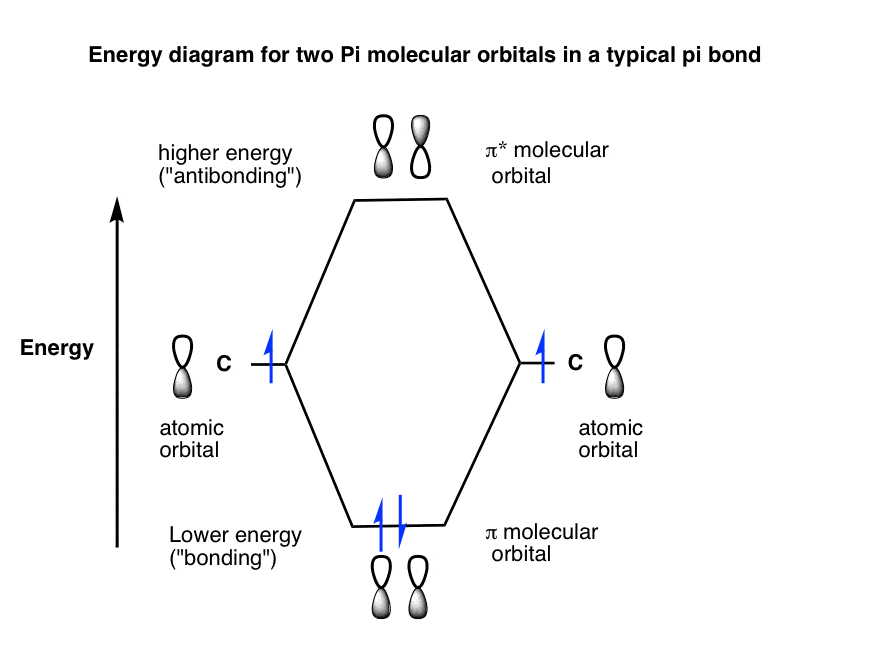

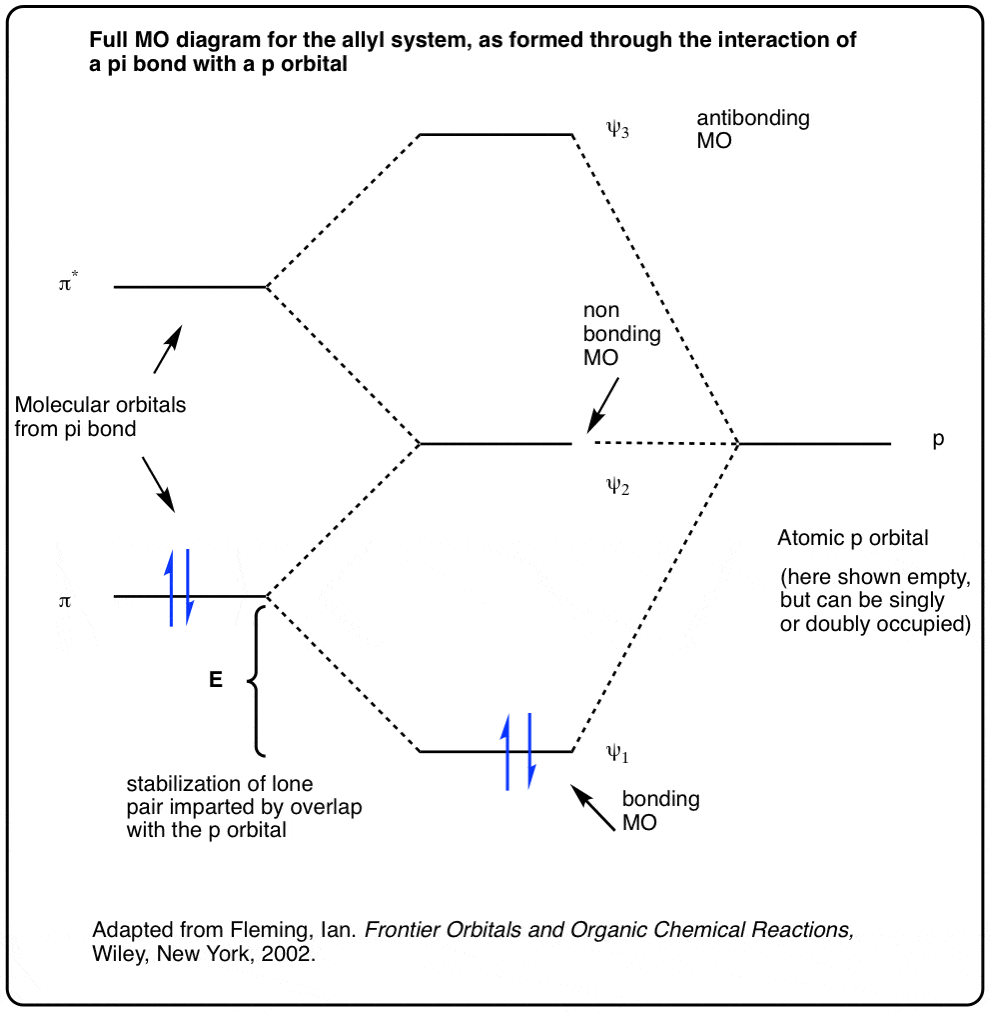








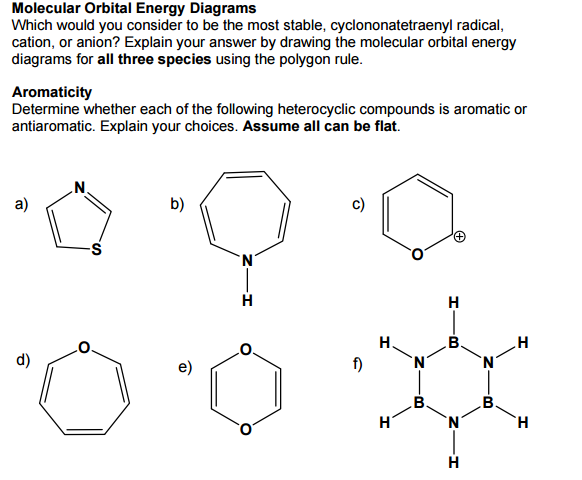

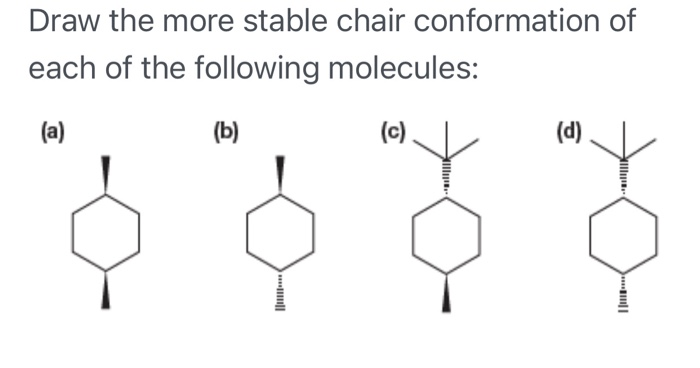



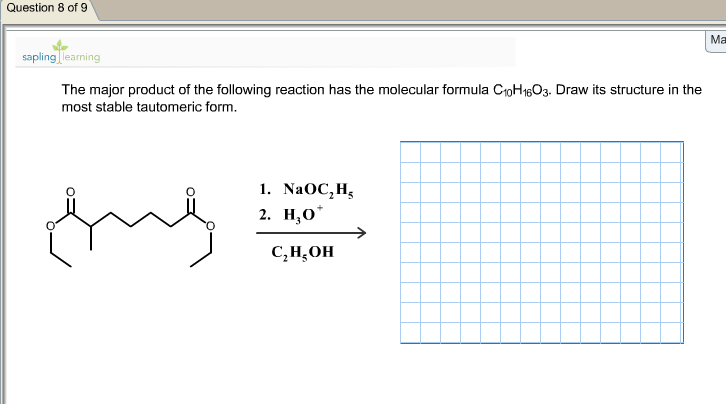

0 Response to "36 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable"
Post a Comment