41 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q:
Refer to the above data. If the firm decided to increase its output from 6 to 7 units, its total costs would rise by A. $87.14 B. $80.00 C. $6.67 D. $120.00 P MC PA ATC P: AVC P P 18. Refer to the above diagram for a purely compettive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce las coposed to shuting down) АА BP GP DR. 19.
2. Refer to the above figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and S t is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. The total tax collection from this excise tax will be: A. $200 B. $175 C. $120 D. $ 80 3. Refer to the above figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and S t is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed.
The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. In the long run the firm should produce output 0 *B x with a plant of size:
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q:
35) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q1 . A) marginal cost is falling. B) average total cost is falling. C) average variable cost is less than average fixed cost. D) marginal cost is less than average total cost. E) all of the above . Answer: E. Diff: 2. Section: 7.2. 36) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q2 . A) average fixed cost is ...
diagram? 7) A) The firm is making no economic profit and will exit the industry. B) The firm is in long - run equilibrium and is breaking even. C) The firm is suffering an economic loss by producing at Q 0 but will break even if it increases its output to Q 1 . D) The firm achieves productive efficiency by producing at Q 0 . TRUE/FALSE.
If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. 3. earn an economic profit. 4. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. 10. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: 1. neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. 2.
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q:.
3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
22. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of Bare: A. unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B. unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C. attainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D. attainable and imply least-cost production of this level of output.
Exhibit 8-10 Price and cost data for a firm Q P AVC ATC MC 0 $12 − − − 1 12 3 5 5 2 12 5 6 7 3 12 7.3 8 12 4 12 9.5 10 16 In Exhibit 8-10, following the rule regarding MR and MC, the most profitable output level is:
60. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for this firm is J. True False 62. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output M total variable ...
197. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: A) suffer an economic loss. B) earn a normal profit. C) earn an economic profit. D) achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 5 E: 433 MI: 189 198. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q:
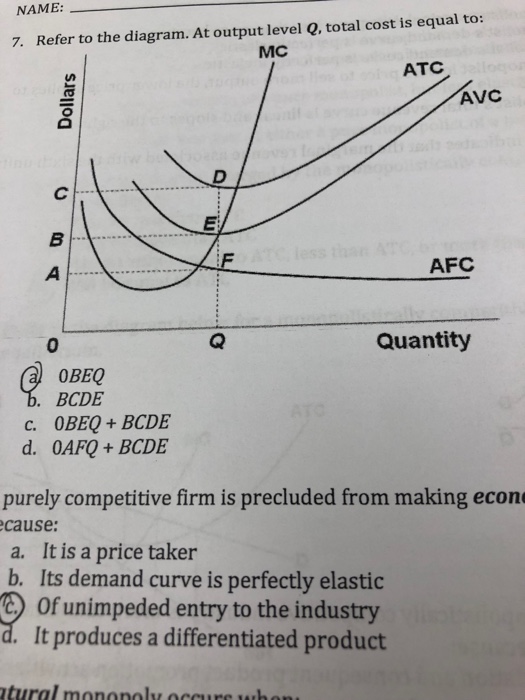
Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total cost is A 0 BEQ B BCDE C 0 from ECON 202 at Old Dominion University
The result will be: Selected Answer: [None Given] Correct Answer: an increase in output, but not in the price, of the product. Question 1 0 out of 1 points Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q : Selected Answer: [None Given] Correct Answer: both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved.
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q 2: A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. B. resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. C. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are underallocated to this product.
Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows:Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2 , where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used.
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect. answer choices . firms to enter the industry, market supply to rise, and product price to fall. ... Refer to the diagram. At output level Q2, answer choices
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved.
Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: A) the law of diminishing returns. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. C) marginal cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale. By definition B is the answer
Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: O A. unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. O B. unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. O C. obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. O D. obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently.
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost. is measured by both QF and ED. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q. ... Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct.
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q, Both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. Accounting profits equal total revenue minus. ... Refer to the diagram. At output level Q2, Resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
Refer to the diagram above. By producing at output level Q: ... Refer to the diagram above. At output level Q1: A. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. 14. Refer to the diagram above. At output level Q2: A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
Economics. Economics questions and answers. MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q O productive efficiency is achieved. but allocative efficiency ls not. D neither productive nor allocetive etficiency s achieved O aflocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not O both productive ...
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved.
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not.

0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q:"
Post a Comment