39 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c.
Electron Configurations and Bond Orders Just as with atoms, we can write a molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O-O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons.
The F₂ molecule is obtained by the linear combination of two F atomic orbitals. When two electrons are supplemented to the antibonding orbitals of the molecule F₂⁻⁻ molecule will be produced. It is identical to Ne. The molecular orbital energy level diagram is given in the attachment. Bond order = 1/2 (Bonding electrons - Antibonding ...
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 Order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as CO. Mar 26, · This video shows the MO diagrams of the C2, N2, O2 and F2 molecules.A molecular orbital (MO) energy level diagram - Parkway C-2Use the molecular orbital ...
what is the bond order for a molecule with 10 electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and 5 electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals. 2.5. ... molecular orbital diagram for F2. number of elections in the sigma*2p molecular orbital is. 0.
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ...
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order.
Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b - Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero. 3) Relative stability of molecule in terms of ...
Match. Gravity. place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of O2, F2, and Ne2. start with the highest energy molecular orbital at the top of the list. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 1.) o*2p. 2.) pie*2p. 3.) pie2p. 4.) o2p.
• The bond order of a diatomic molecule is defined as one-half the difference between the number of electrons in bonding orbitals, nb, and the number of electrons in antibonding orbitals, na. bond order = 21 (nb - na) Figure 9.29: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2-ion. Bond order = ½ (2 - 1) = 0.5
- Bond order: In simple words, It can be stated that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and antibonds. Bond number also gives an indication of the stability of a bond. Lets calculate the bond order for ${N_2}$ : The total number of electrons present in the ${N_2}$ molecule is 14. Number of electrons in bonding orbitals : 8
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond.
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F 2 with the atomic orbitals labeled and find the bond order. Q12.16 Comparing benezene and cyclopentadiene, which one has a lesser degree of \(\pi\)-electron delocalization?
Chemistry questions and answers. Part A Arrange the following in order of decreasing bond energy. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them. View Available Hint (s) Reset Help F2 F2 Lowest bond energy ...
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
In this example problem, we show how to fill a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule and use molecular bond theory to compare bond order, bond st...
Molecular orbital Diagram F2. molecular orbital theory build f2 for the ion f2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist d write the electron molecular orbital theory c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules this video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules
Solved Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2. | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2. What is the bond order of F2? Oo 0.5 1.5 O O Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2. What is the bond order of F2? 1.5 O 0.5.
Albr3 hybridization [email protected] [email protected] I would like to ask if anyone knew the orbital box hybridization diagram for ClF3. AlBr. Example 10. First, it is found that of the 6 valence electrons that atomic sulfur has (two 3s and four 3p), in SF6 a total of 3. With this result, the Br 3d 3/2 and Br 3d 5/2 binding energies of Br ...
Free PDF download of Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure prepared by expert Chemistry teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register online for Chemistry tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination.
For the ion f2. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. The lumo lowest unoccupied molecular orbital and homo highest occupied molecular orbital of difluorides mo diagram help explain why the molecule is very stable the diagram also tells us that the bond order is 1. The molecular orbital theory mo has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen ...
B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be …
11.8.2021 · In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. For a straightforward answer: use this formula: Bond order = [(Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2.
21.11.2021 · The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be: The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of ethane, we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule.
The molecular orbital bond order is calculated as 1212(x - y), where x is the number of electrons in _____ molecular orbitals and y is the number of electrons in _____ molecular orbitals. In general, the higher the molecular orbital …
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
Answer (1 of 6): O2 2- bond order = 1 O2 - bond order = 1.5 O2 bond order = 2 O2+ bond order = 2.5 O2 2+ bond order =3 I hope it’ll work out :)
17.10.2018 · Molecular orbital diagram of H 2 (Hydrogen molecule). Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the ...
29 Sept 2017 — Bond order is 1 because their formula is total bonding electron - total antibonding electron /2 so lower shell which do not contain asterick(*) ...2 answers · 61 votes: O2 and F2 is an execption so their Z shell is down because of low energy level.but ...
The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen molecules. The same method can be applied to other diatomic molecules, but involving more than the 1s atomic orbitals. For the second period elements, the 2s and 2p orbitals are important for MO considerations. A linear combination of properly oriented atomic orbitals for the formation of sigma s and pi p bonds.
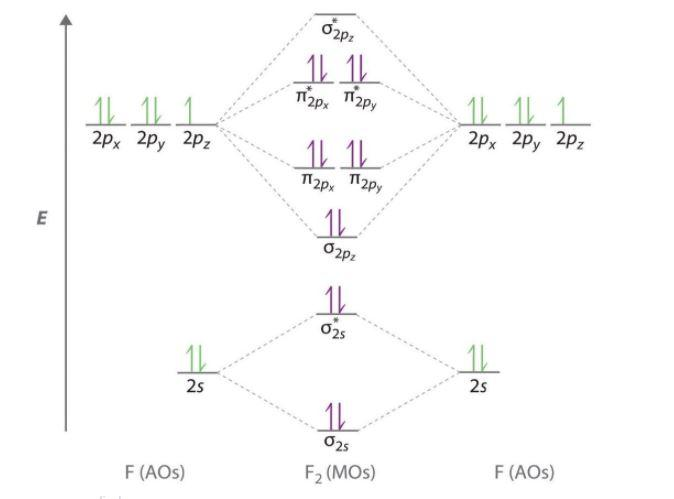
Here, fourteen electrons are filled in the molecular orbitals starting from the least energetic one. As shown, the highest energy antibonding orbital is the only one remaining unoccupied. We have already seen above in the Lewis structure that there is a single sigma bond between two F atoms. Now, from MO theory, let us calculate the bond order in the F2 molecule using the following formula ...
32 F2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram - Wiring Diagram Database from i.ytimg.com Of electrons in bonding orbital is 9. On the atomic level, bond order is the number of bonded electron pairs between two atoms. This table lists the bond types and how many molecules with each bond type are in the cccbdb. The lines represent the number of electrons that ...
Use an mo diagram to find the bond order and predi. By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. How to graph a mo molecular orbital diagram for f2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. The relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals. By drawing ...
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Chemistry >> Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure >> Molecular Orbital Theory >> 37. Draw molecular orbital ... Question . 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its ...
Originally Answered: What is the bond order of F2?In simple terms, since F has 7 valence electrons thus by sharing of electrons with another F it forms a bond to fullfil its octate. You can also find its bond order using advance Molecular orbital theory (MoT). Therefore Bond order of F2 is 1. Mar 26, 2021
21.11.2018 · We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is Figure The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The ...
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
If there are two electrons in the molecular orbitals of an atom, then it’s diamagnetic. However, if there’s a single electron in one or two molecular orbitals of the atom, then it is paramagnetic. The formula to know the bond order is Nb−Na/2. Here, Nb represents the number of bonding orbitals. Na represents the number of antibonding orbitals. Before discussing the bond order first, let ...

0 Response to "39 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment