38 co molecular orbital diagram
In the molecular orbital diagram for `O_(2)^(+)` ion the highest occupied orbital is . Total number of molecular orbitals containing electrons present in . O_(2)^(+) ion is . 74445608. ... H.O.M.O(Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital ) of CO molecular is : 135904495. 1.1 k+. 22.3 k+. 04:19. H.O.M.O(Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital ) of CO ...
1 Answer. 1. Electronic configuration of N atom is 1s2 2s2 2p3. 2. Electronic configuration of O atom is 1s2 2s2 2p4. 3. Electronic configuration of NO molecule is σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2px2 π2py2 π2pz2 π*2px1. 4. Bond order = N b−N a 2 N b − N a 2 = 10−5 2 10 − 5 2 = 2.5.
b) A molecular orbital is singly occupied. c) An example is oxygen molecule. d) Repelled by the magnetic field. Answer: Repelled by the magnetic field. 48. Combination of two atomic orbitals results in the formation of two molecular orbitals namely. a) one bonding and one non-bonding orbital. b) two bonding orbitals. c) two non-bonding orbitals
Co molecular orbital diagram
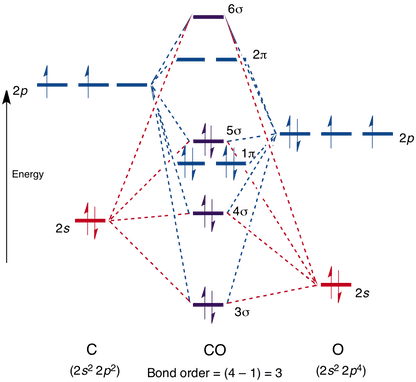
Why is the bond order of CO 3? In molecular orbital theory, we define bond order as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. First we should write the molecular orbital electronic configuration of CO molecules. So, from the above calculation the bond order of carbon monoxide molecules is 3.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. Chemistry: Molecular orbital diagrams.
The calculations were carried out using two equivalent Au surfaces and considering that the observed spin-filter effects arise from the mixing of the Au surface levels with the spin-polarized molecular orbitals in the paramagnetic metal center. 20, 21, 23, 24 The Ni tip is not included in the calculation since it just controls the final device ...
Co molecular orbital diagram.
In the molecular orbital description of CO (assuming it has the same MO energy levels as N2): a) The highest energy electrons occupy antibonding orbitals. b) Six molecular orbitals contain electrons. c) There are two unpaired electrons. d) The bond order is 3. e) All of the above are false.
Resulting energy level diagram of the molecular orbitals for the Co-O bond, arising from our model calculation. Left: The 5 3 d orbitals of Co with the tetrahedral crystal-field splitting. Right: The 3 2 p orbitals of O, with the x axis located along the Co-O bond direction. Middle: Energy level diagram for the Co-O bond molecular orbitals at J ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining . However, experimental and computational results for homonuclear diatomics from Li2 to N2 and certain heteronuclear combinations such as CO and NO. Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2: Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6. Li2 = σ1s2,σ*1s2,σ2s2.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Monoxide (CO) The above image shows energy levels for the molecular orbitals of the carbon monoxide (CO) The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of showing how chemical bonding is taking place within a molecule.
Molecular orbital theory Features of Molecular orbital theory 1) The atomic orbitals overlap to form new orbitals called molecular orbitals. When two atomic orbitals overlap or combine ,they lose their identity and form new orbitals. The new orbitals thus formed are called molecular orbitals. 2) Molecular orbitals are the energy states of a molecule in […]
Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. From the molecular orbital diagram, we observe that oxygen has two unpaired electrons which is consist with the paramagnetic nature of oxygen. Transcribed Image Text from this Question.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B_2^2+, B2, C_2^2-, B_2^2- and N_2^2+ b. Draw the Lewis structures and molecular orbital diagrams for
The mo diagram for the diatomic carbon monoxide, co, shows it to be isoelectronic with nitrogen, n2 They provide the highest level of service, including product training, presales services, and ongoing support. 14+ N2 Mo Diagram. Mo diagram of homonuclear diatomic molecules.
For examplea molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao molecular orbital method in particular. Beh2 molecular orbital diagram. Molecular orbitals diagram for beh 2.
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air.Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl.It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.
A schematic molecular orbital diagram for a co molecule. All about chemistry july 2 2020. Controls click on the co molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. So again its drawn in the familiar pattern. Molecular orbitals for co.
Draw MO diagram of CO and calculate its bond order. chemical bonding; class-11; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. 1 Answer +1 vote . answered Dec 17, 2020 by Maisa (45.7k points) selected Dec 18, 2020 by Panna01 . Best answer. 1. Electronic configuration of C atom: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2. ...
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni) 29: Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu) 30: Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn) 31: Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga) 32: Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge) 33: Orbital diagram of Arsenic (As) 34: Orbital diagram of Selenium (Se) 35:
We can now fill the molecular orbital diagram: The two electrons occupy the lowest-energy molecular orbital, which is the bonding (σ 1s) orbital, giving a (σ 1s) 2 electron configuration. To avoid violating the Pauli principle, the electron spins must be paired. C So the bond order is (9.7.8) 2 − 0 2 = 1
CO2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. To understand the bonding in metal carbonyls, we need to first learn the Molecular Orbital \(\left( {{\rm{MO}}} \right)\) diagram of carbon monoxide. There are ten electrons in the carbon monoxide ligand. The order of energy of the molecular orbitals and the accommodation of ten electrons of the carbon monoxide ...
Co molecular orbital diagram bond order. 3) Sketch the molecular orbital diagram for CO.Calculate the bond order.Identify the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). Does the structure predicted by molecular orbital theory match the Lewis Dot Structure? Question: 3) Sketch the molecular orbital diagram for CO. ...
Carbon monoxide molecular orbital diagram explanation. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining mo diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. Generic s p valence mo diagram for carbon monoxide co chain one can reasonably explain that the homo of carbon monoxide must be of.
In carbon monoxide (CO, isoelectronic with dinitrogen) the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the carbon 2s orbital and therefore the degree of ...
Molecular orbitals diagrams of [Co (NH3)6]3+. 1. M. O. diagram for [Co (NH3)6]3+ Dr. Mithil Fal Desai Shree Mallikarjun and Shri Chetan Manju Desai College Canacona Goa. 2. t* 1u a1g t2g, eg a1g, t1u, eg a1g t1u a* 1g e* g eg t1u Δo t2g Metal (Ti3+)orbitals Co3+→ [Ar] 3d6, 4s0 6e- Ligand group (NH3) orbitals 6 x 2 = 12 e- σ [Co (NH3)6]3 ...
Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Monoxide (CO) The above image shows energy levels for the molecular orbitals of the carbon monoxide (CO) The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of showing how chemical bonding is taking place within a molecule.
The Molecule · CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN]– and with N2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than ...
Co orbital diagram. Cobalt has a total of 27 electrons which are contained in 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s and 3d sub. Controls click on the co molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. So you have the carbon two s orbital and you have the carbon two p orbitals. Molecular orbitals in carbon monoxide.
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram For Co - Drivenheisenberg from www.researchgate.net. 9 molecular orbital diagram for co analysis done by bond order if value of bond order is positive it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero it means that the molecule is unstable. Carbon monoxide lumo lowest unoccupied molecular orbital.
Mar 19, 2021 — Carbon monoxide MO diagram ... Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The ...Molecular orbital diagrams for... · Carbon monoxide MO diagram

0 Response to "38 co molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment