39 refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
Profit per unit of output=Total profit/Q =P-ATC Look at the graph above, firm should choose to produce output Q to maximize profit since Q is the output level at which point P=MC. The shaded area is total profit for this profit-maximizing firm. The vertical distance between point A and B = (P-ATC), which is profit per unit of output. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is. g, and the profit-maximizing price is d. At the point where 3 units are being sold, the coefficient of price elasticity of demand. ... Refer to the diagrams. Diagram (A) represents. equilibrium price and quantity in a purely competitive industry.
3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
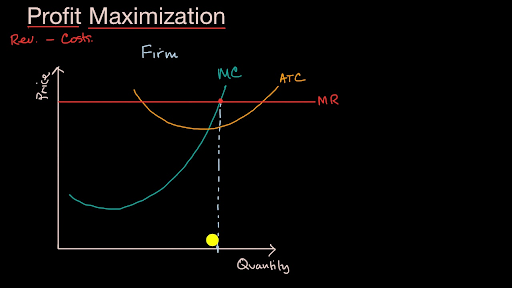
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: A) (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. B) (A) price exceeds marginal cost, resulting in allocative inefficiency. C) (B) price equals marginal cost, resulting in allocative efficiency. In diagram B the profit maximizing quantity is:-g and the profit-maximizing price is d. In which one of the following market models is X-inefficiency most likely to be the greatest? ... Refer to the diagrams. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize:-an economic profit of ABHJ. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h and the profit-maximizing ...
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is. Economics questions and answers. Saved Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit maximizing quantity is Multiple Choice and the profit maximizing price ist and the profit maximizing price is e and the profit maximizing price is e < Prev 6 of 2518 Nexo> MacBook Air Refer to the diagrams. At the profit maximizing level of output total revenue will be. Refer to the above diagram. Refer to the diagram. B refer to the above diagram. Price exceeds marginal revenue. At the profit maximizing output the firm will realize. B 0 aje. Profit Maximizing Output Chapter 10 Proprofs Quiz Econ 2302 Notes Microeconomics Ii .154. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: A) (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. B) (A) price exceeds marginal cost, resulting in allocative inefficiency. C) (B) price equals marginal cost, resulting in allocative efficiency. D) (B) equilibrium price and quantity will be e and h ... Refer to the diagrams. In diagram b the profit maximizing quantity is. B output will be the same as in diagram a. Refer to the above diagram for a noncollusive oligopolist. G and the profit maximizing price is f. C b price equals marginal cost resulting in allocative efficiency. G and the profit maximizing price is d. B output will be the same ...
In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. profit maximizing level of output for the firm is 199.5 units when the price is $400 per unit. Using this information it is easy to find total revenue as the price times the quantity: TR = ($400 per unit)(199.5 units) = $79,800. Total cost is found by substituting q = 199.5 into the TC equation: TC = $40,099.75. Profit is 10. Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is A. g, and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g, and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g, and the profit-maximizing price is d. 3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
Profit maximizing price = $63; Profit maximizing quantity = 4 units. ... producer surplus, represented by triangles B and C in Figure 8-10b, is referred to.5 pagesMissing: diagrams. | Must include: diagrams. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A) g and the profit-maximizing price is e. C) g and the profit-maximizing ... The profit maximizing output is at point where MR = MC. At point g, MR = MC. So, g is profit maximizing output. Then we look at demand curve to know the maximum ...1 answer · 0 votes: Option D ie g and profit maximizing price is d The profit maximizing output is at point where MR = MC. At point g, MR = MC. So, g is profit maximizing ... View Homework Help - ECONHW13Sols41.pdf from ECON 4103 at University of New South Wales. 117. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the prot-maximizing quantity is g, and the
Profit Maximisation Theory: In the neo-classical theory of the firm, the main objective of a business firm is profit maximisation. The firm maximises its profits when it satisfies the two rules. MC = MR and the MC curve cuts the MR curve from below Maximum profits refer to pure profits which are a surplus above the average cost of production.
How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Decides Price. In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve.
Refer to the diagram. at output level q2_. Produce the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. At output level q2. In the long run equilibrium both competitive firms and a monopolistic firms that maximize profits. Answer to 1refer to the diagram above. Refer to the diagram for athletic shoes. Refer to the above graph.
the monopoly to produce that level of output where the firm earns zero economic profit. c) Identify in the graph the equilibrium price and quantity that corresponds to this type of regulation label it with the letter "B". Under this regulatory scheme the equilibrium is when the monopolist gets zero profits. In the picture,
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. ... both diagrams a and c. 8.
An economic profit of abhj. At the profit maximizing level of output the firm will realize. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. A loss of jh per unit. The minimum point on its mc curve. A loss of gh per unit. Refer to the above diagram. Refer to the above diagram. Atthe profit maximizing output the firm will realize.
However, making a final decision about the profit-maximizing quantity to produce and the price to charge will require combining these perspectives on cost with an analysis of sales and revenue, which in turn requires looking at the market structure in which the firm finds itself. Before we turn to the analysis of market structure in other ...
79. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g and the profit-maximizing price is d.
Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms. ... In Figure 2, line B represents the firm's ... In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is.
For a video explanation of a monopolist's profit-maximizing quantity and price using a graph, please watch: Previous Section 2: The Monopolist's Revenue Curves. Next Section 4: Anti-trust legislation in the United States. 2 Comments. may on May 16, 2021 at 1:14 am
The flat shape means that the firm can sell either a low quantity (Ql) or a high quantity (Qh) at exactly the same price (P). (b) A monopolist perceives the ...
D) a single firm operating in a purely competitive industry. 217) Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is A) g, and the profit-maximizing price is e. B) h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. C) g, and the profit-maximizing price is f. D) g, and the profit-maximizing price is d. Version 1 120
B) 0 CFE. C) 0 BGE. D) ABGH. 45. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A) a loss equal to BCFG. B) a loss equal to ACFH. C) an economic profit of ACFH. D) an economic profit of ABGH. D is correct. The area between ATC and AVC at Q=E. TVC = Q x AVC = OE x OC = OCFE, i.e. B is correct.
Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h and the profit-maximizing ...
In diagram B the profit maximizing quantity is:-g and the profit-maximizing price is d. In which one of the following market models is X-inefficiency most likely to be the greatest? ... Refer to the diagrams. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize:-an economic profit of ABHJ.
Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: A) (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. B) (A) price exceeds marginal cost, resulting in allocative inefficiency. C) (B) price equals marginal cost, resulting in allocative efficiency.





0 Response to "39 refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is"
Post a Comment