38 veins of the head and neck diagram
It is mainly intended to be used by residents or students as an introduction to the vascular anatomy of the brain. Neurointerventional radiology requires such a diverse anatomical knowledge that its anatomy cannot be combined into a single module. Atlas of normal neurovascular anatomy of arteries of the brain on a cerebral angiogaphy. Body System ( T022 ) SnomedCT. 281232002. English. Vascular structure head & neck, Vascular structure of head and neck, Vascular structure of head and neck (body structure) Spanish. estructura vascular de cabeza y cuello (estructura corporal), estructura vascular de cabeza y cuello. Derived from the NIH UMLS ( Unified Medical Language System )
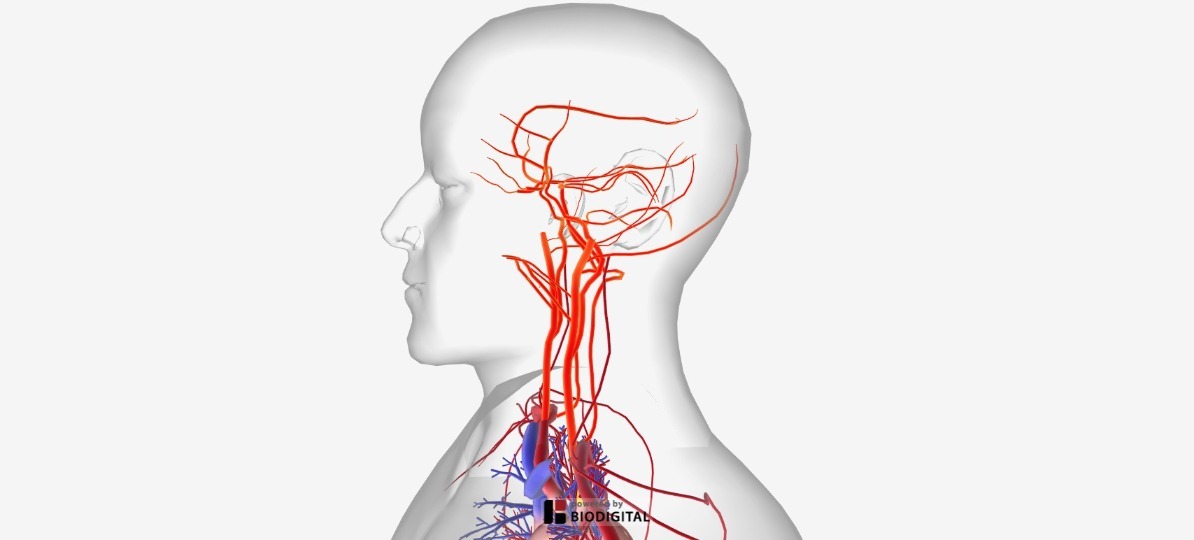
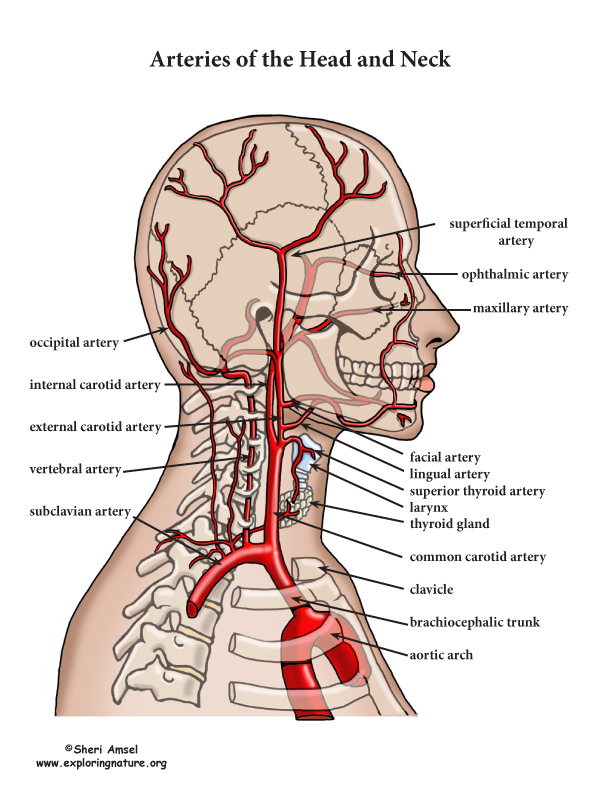
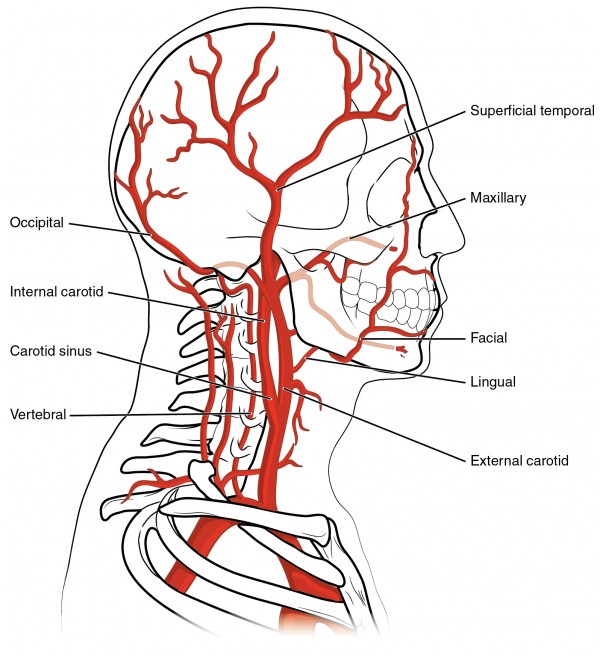
The head and neck region obtain the majority of its blood supply via the carotid and also vertebral arteries. This activity primarily focuses on the in-depth orientation of the carotid arteries, including their anatomical course, branches and also the area of distribution. The carotid arteries are the primary vessels supplying blood to the brain and face.[1][2] The right common carotid artery ...

Veins of the head and neck diagram
Niki Foster Date: October 16, 2021 A diagram of the human head and neck, including the blood vessels in red.. Blood vessels are part of the circulatory system, which passes nutrients, blood, hormones, and other important substances to and from body cells in order to maintain homeostasis.The blood vessels are responsible for transporting blood throughout the body. The vagus nerve extends farther than any other cranial nerve. It exits the cranial cavity via the jugular foramen, where it initially travels alongside the internal jugular vein and descends through the carotid sheath. During its course through the neck, it gives off branches such as the superior laryngeal nerve and the pharyngeal branch. The neck is supplied by arteries other than the carotids. The right and left subclavian arteries give rise to the thyrocervical trunk. From this trunk, several vessels arise, which go on to supply the neck. The first branch of the thyrocervical trunk is the inferior thyroid artery.
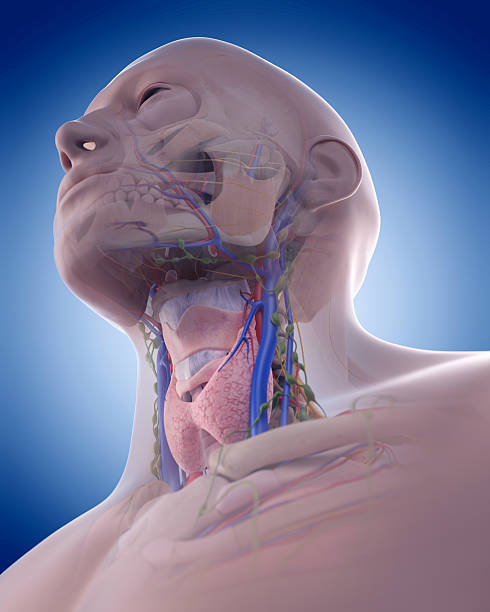
Veins of the head and neck diagram. Arteries In Neck. The internal carotid artery (latin: Blocked arteries in neck, produce symptoms only when the blockage is severe. Coronary arteries, the carotid arteries in the neck, and renal (kidney) or biliary (gall bladder) when a person has a stroke it can be from blockage in 1 or both of the carotid arteries in the neck. However, the head and neck, right upper limb, and hemithorax all drain lymphatics into the right lymphatic duct and then into the right internal jugular and subclavian veins. Nerves Many important nerves in this region innervate local structures and other structures in the head and neck. The veins of the head and neck collect deoxygenated blood and return it to the heart. Anatomically, the venous drainage can be divided into three parts: Venous drainage of the brain and meninges: Supplied by the dural venous sinuses. Venous drainage of the scalp and face: Drained by veins synonymous with the arteries of the face and scalp. MRI Atlas of the Brain. This page presents a comprehensive series of labeled axial, sagittal and coronal images from a normal human brain magnetic resonance imaging exam. This MRI brain cross-sectional anatomy tool serves as a reference atlas to guide radiologists and researchers in the accurate identification of the brain structures.
15 Systemic Circulation Flow Chart. While humans, as well as other vertebrates, have a closed cardiovascular system (meaning that the blood never leaves the network of arteries, veins and capillaries), some. Blood must always circulate to sustain life. 20.5 Circulatory Pathways - Anatomy and Physiology from opentextbc.ca Body fluid is… Figure 0562: [] The fascia and middle thyroid veins Figure 0602: [] Superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of head and neck Figure 0672: [] Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord The dural venous sinuses (i.e., superior sagittal, straight, and transverse sinuses) and superficial and deep veins of the head (i.e., cerebral veins, great vein of Galen, cerebellar, and facial veins) drain into the internal and external jugular veins bilaterally and ultimately to the superior vena cava and right atrium of the heart. 15 Inferior Vena Cava Diagram. The inferior vena cava is the common convergence of venous drainage from all structures below the diaphragm. The inferior vena cava (ivc) drains venous blood from the lower trunk, abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs to the right atrium of the heart. In this image, you will find hepatic veins, inferior phrenic vein ...
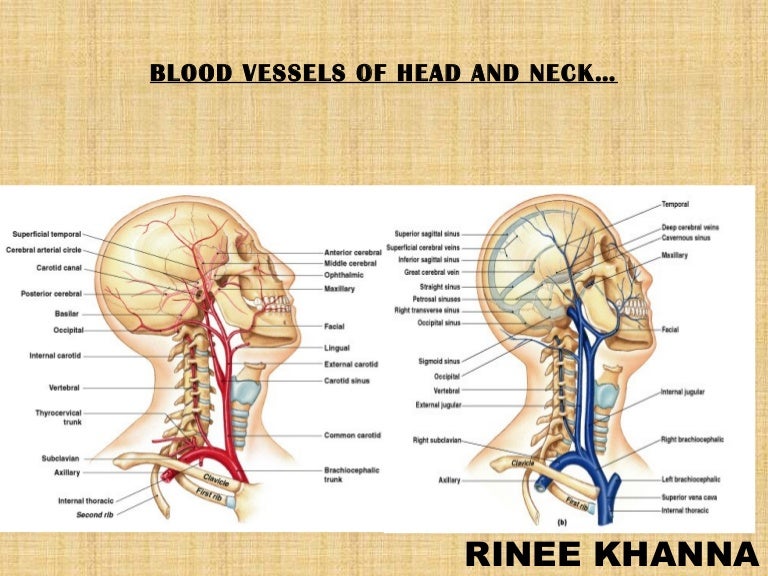
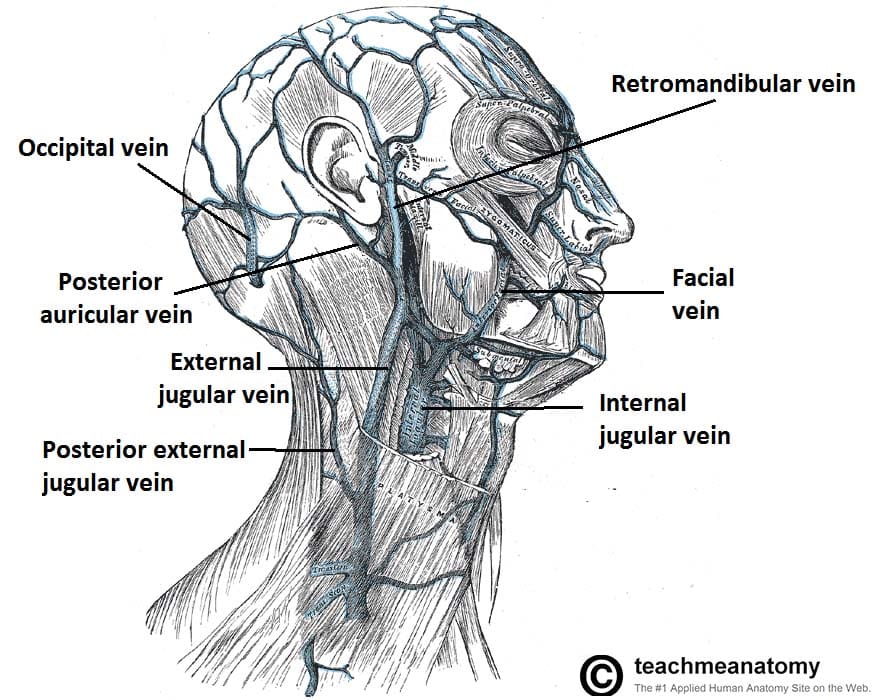
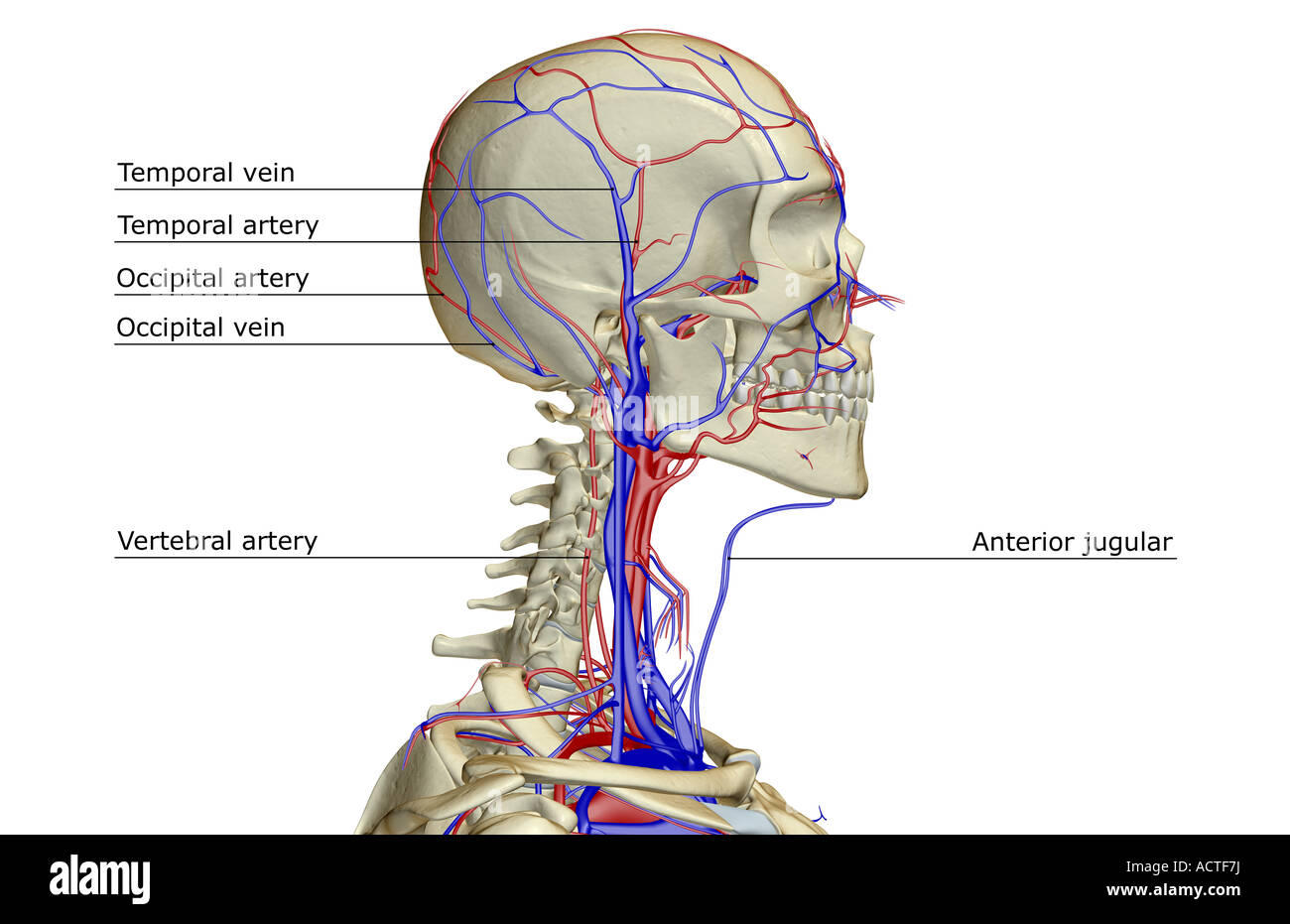
The content of the neck is grouped into 4 neck spaces, called the compartments. Vertebral compartment: contains cervical vertebrae and postural muscles. Visceral compartment: contains glands ( thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus ), the larynx, pharynx and trachea. Two vascular compartments: contain the common carotid artery, internal jugular vein ... Circulatory Pathways | Anatomy and Physiology II. This diagram shows the veins present in the head and neck. The neck is the bridge between the head and the rest of the body. It is located in between the mandible and the clavicle, connecting the head directly to the torso, and contains numerous vital structures. It contains some of the most complex and intricate anatomy in the body and is comprised of numerous organs and tissues with essential structure and function for normal physiology. Veins of head and neck Now that we have covered the arteries, we will complete the picture of the vasculature of the head and neck by learning about the veins. The main ones draining these two regions are the: Facial vein; Inferior, middle, and superior thyroid veins; Vertebral veins; External and internal jugular veins
However, the head and neck, right upper limb, and hemithorax all drain lymphatics into the right lymphatic duct and then into the right internal jugular and subclavian veins. Nerves Many important nerves in this region innervate local structures and other structures in the head and neck.
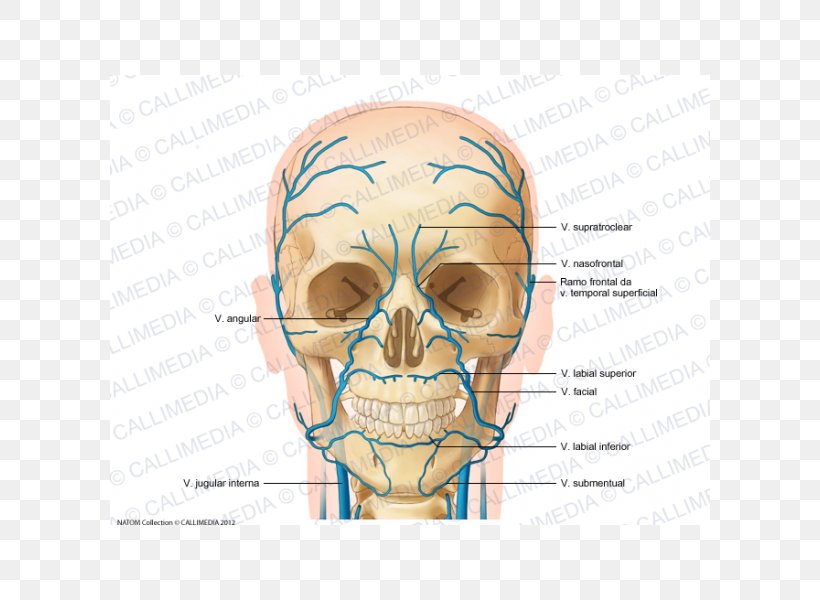
Anterior Jugular Vein Head And Neck Anatomy Supratrochlear Artery Png 600x600px Watercolor Cartoon Flower Frame Heart
The arteries of the upper extremity. 13+ Human Body Veins And Arteries Diagram. The capillaries connect the two types of blood vessel and molecules are exchanged between the blood and the cells across their walls. Arteries and veins are main blood vessels. The arteries of the head and neck.
by AB Rivard · 2020 · Cited by 4 — The internal jugular vein is a paired venous structure that collects blood from the brain, superficial regions of the face, and neck, ...
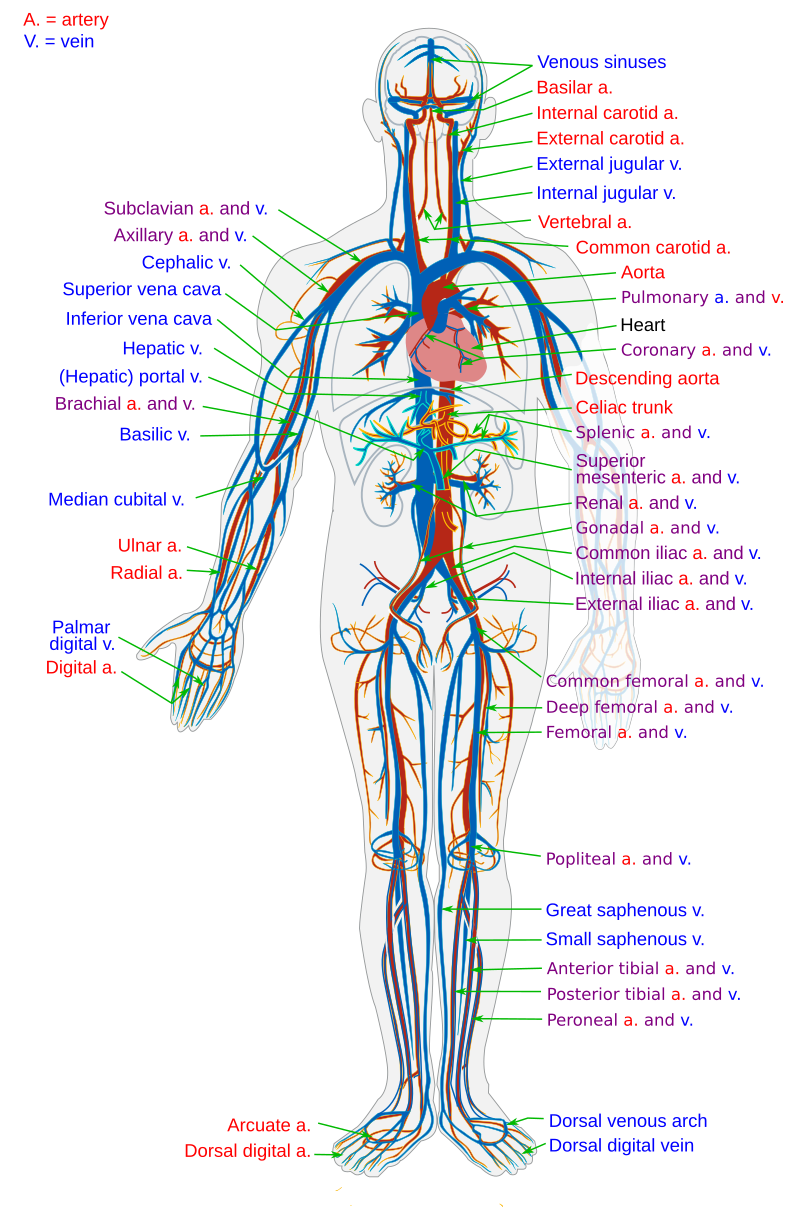
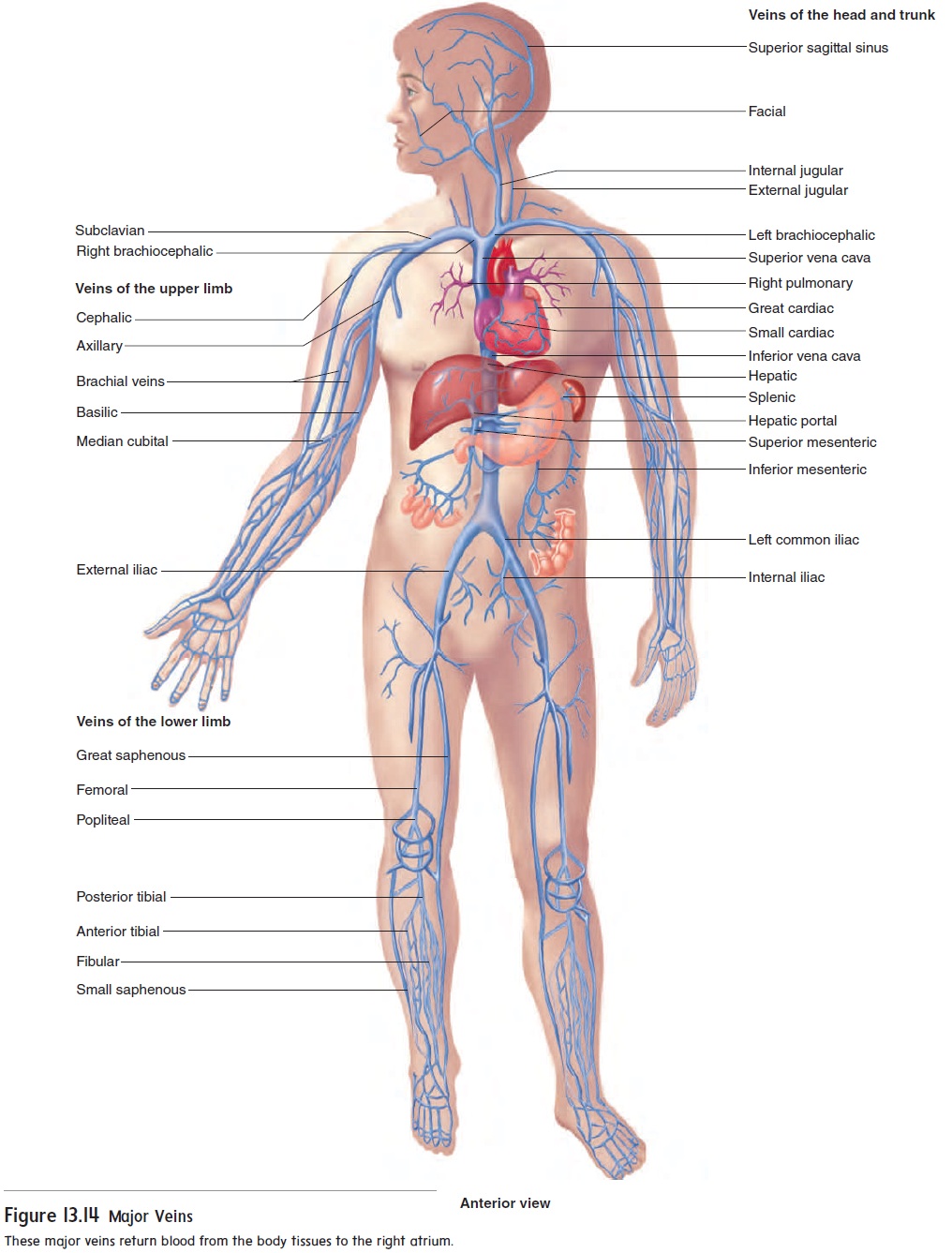
The veins of the head and neck the veins of the exterior of the head and face. Major veins of the body. The veins of the upper extremity. The veins of the heart. Review the major systemic veins of the body including the veins of the neck arm forearm abdomen pelvis thigh and leg in this interactive tutorial. Start studying major veins of the body.
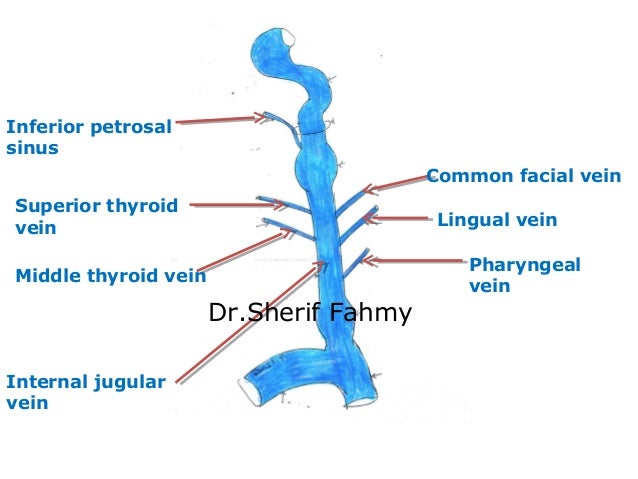
The external jugular veins descend on either side of the neck, passing over the sternomastoid muscles and beneath the platysma. They empty into the right and left subclavian veins in the base of the neck. The internal jugular veins form the major venous drainage of the head and neck and are deep veins that parallel the common carotid artery.
The veins of the brain are thin-walled, valveless and pierce the arachnoid mater and meningeal layer of dura mater (of meninges) to empty poorly oxygenated blood into the dural venous sinuses. The dural venous sinuses drain into the sigmoid sinus which becomes continuous with the internal jugular veins (IJVs).
The occipital cervical nodes are located where the back of the head meets the neck and drain lymph from the surrounding areas. Superficial cervical nodes are located along the jugular vein and ...
Head and neck (anterior view) The head and neck are two examples of the perfect anatomical marriage between form and function, mixed with a dash of complexity. The neck is resilient enough to sustain a five kilogram weight 24/7, yet sufficiently mobile to move it in several directions.
The internal jugular vein is the largest vein in the neck and is the main source of venous drainage, or blood flow, down from the brain, returning deoxygenated blood back from the head and neck to the heart, where it will be pumped to the lungs to become oxygenated again. 1 . The internal jugular vein also serves as the main channel to ...
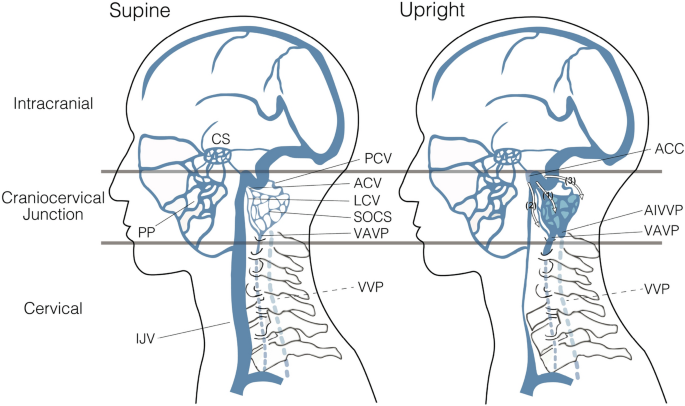
Posture Induced Changes In The Vessels Of The Head And Neck Evaluation Using Conventional Supine Ct And Upright Ct Scientific Reports
The study of the arterial supply of blood to the brain is facilitated by a diagram showing the cerebral arterial vascular areas in lateral and medial views and axial and coronal section and by diagrams of arteries forming the Willis' circle (internal and vertebral carotid arteries, basilar artery, anterior and posterior communicating arteries ...
IMAIOS and selected third parties, use cookies or similar technologies, in particular for audience measurement. Cookies allow us to analyze and store information such as the characteristics of your device as well as certain personal data (e.g., IP addresses, navigation, usage or geolocation data, unique identifiers).
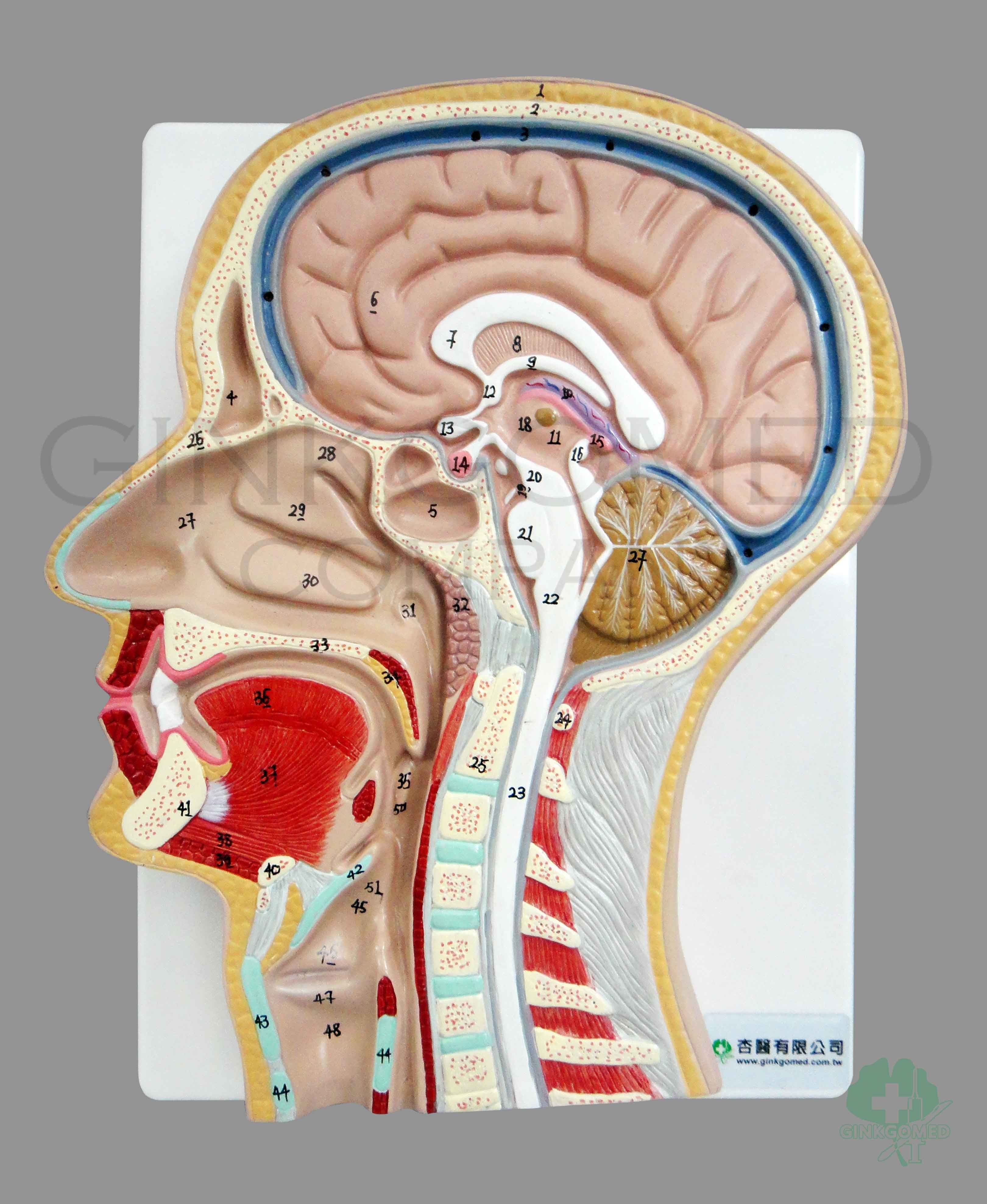
Cross-sectional anatomy: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the head and neck. An MRI of the face and neck was performed on a healthy patient, using T2 weighting, (image size: 320 * 320 pixels) (600 images). We did not select the T1 weighting because it provided a lower contrast.
Labeled diagram showing the structure of a blood vessel . Observe the blood vessels diagrams above, where you can see the structures of arteries and veins clearly labeled. Spend a while piecing these diagrams together in your mind, trying to link the labeled names with the functions you learned about in the video. Worksheets to label
The neck is supplied by arteries other than the carotids. The right and left subclavian arteries give rise to the thyrocervical trunk. From this trunk, several vessels arise, which go on to supply the neck. The first branch of the thyrocervical trunk is the inferior thyroid artery.
The vagus nerve extends farther than any other cranial nerve. It exits the cranial cavity via the jugular foramen, where it initially travels alongside the internal jugular vein and descends through the carotid sheath. During its course through the neck, it gives off branches such as the superior laryngeal nerve and the pharyngeal branch.
Niki Foster Date: October 16, 2021 A diagram of the human head and neck, including the blood vessels in red.. Blood vessels are part of the circulatory system, which passes nutrients, blood, hormones, and other important substances to and from body cells in order to maintain homeostasis.The blood vessels are responsible for transporting blood throughout the body.

It S Not A Cervical Lymph Node It S A Vein Ct And Mr Imaging Findings In The Veins Of The Head And Neck Radiographics
Head And Neck Muscles Labeled Anatomical Diagram Facial Vector Illustration With Female Face Health Care Educational Information Stock Vector Illustration Of Movement Adult 118338016

Dural Venous Sinuses And Veins Of Head And Neck Labeled Eccles Health Sciences Library J Willard Marriott Digital Library
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12652/Introduction.png)
















0 Response to "38 veins of the head and neck diagram"
Post a Comment