38 meiosis crossing over diagram
Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. Meiosis is specific to gamete producing cells in the gonads. Meiosis begins with a diploid cell and ends with four haploid cells. These cells eventually differentiate into mature sperm or egg cells. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate, and ... Meiosis (/ m aɪ ˈ oʊ s ɪ s / (); from Ancient Greek μείωσις (meiosis) 'lessening', because it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms used to produce the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells.It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ().
The early stages of meiosis involve pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over followed by condensation.
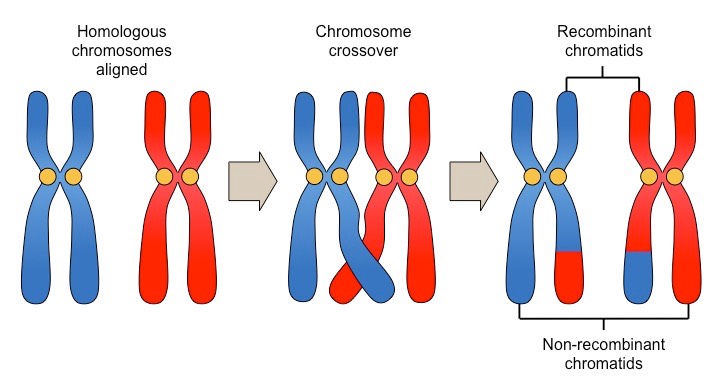
Meiosis crossing over diagram
During meiosis, an event known as chromosomal crossing over sometimes occurs as a part of recombination. In this process, a region of one chromosome is ... Meiosis I (Works Cited See) *1 1. Prophase I Events that occur during prophase of mitosis also occur during prophase I of meiosis. The chromosomes coil up, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, and the centrosomes begin moving apart. The two chromosomes may exchange fragments by a process called crossing over. The crossing over takes place when the chromosomal threads are plectonemically arranged. Although the somatic crossing over is difficult to detect, there is no doubt that it occurs. The exact mechanism is not yet clears (Fig. 16.6). The somatic crossing over may bring several changes in the structure and physiology of the organisms.
Meiosis crossing over diagram. PART B - Crossing over Crossing over plays a critical role in increasing the genetic variation among offspring of sexual reproduction. It is important to understand how crossing over occurs and its consequences in meiosis. Look carefully at the diagrams depicting different stages in meiosis in a cell where 2n = 6. Updated meiosis video. Join the Amoeba Sisters as they explore the meiosis stages with vocabulary including chromosomes, centromeres, centrioles, spindle fib... Crossing Over Definition. Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells.Each diploid cell contains two copies of every chromosome, one derived from the maternal gamete and the other from the paternal gamete. These pairs of chromosomes, each derived from ... Crossing over plays a critical role in increasing the genetic variation among offspring of sexual reproduction. Crossing over is unique to meiosis. Its occurrence depends on specific events early in prophase I, and it has important consequences for the rest of meiosis and beyond. Consider the following statements about crossing over.
Trial 1 - Meiotic Division Beads Diagram. Part 2: Modeling Meiosis with Crossing Over Part 2 - Meiotic Division Beads Diagram: Image of page 3. Info icon This preview has intentionally blurred sections.Lab 4: Meiosis and Vertebrate Reproduction LAB SYNOPSIS: • Meiosis will be modeled using pop-beads. • The genetic diversity of gametes will ... Crossing over occurs during prophase I of meiosis before tetrads are aligned along the equator in metaphase I. By meiosis II, only sister chromatids remain and homologous chromosomes have been moved to separate cells. Recall that the point of crossing over is to increase genetic diversity. Crossing over provides direct proof for the linear arrangement of genes. 2. Through crossing over segments of homologous chromosomes are interchanged and hence provide origin of new characters and genetic variations. 3. Crossing over has led to the construction of linkage map or genetic maps of chromosomes. 4. crossing over. This process of crossing over and the resulting recombination, (exchange of gene alleles across the chromosomes in a pair) enables us to reason about genetic mapping - that is, about the order of genes on a chromosome and the distances among the genes. The next section provides a brief description of crossing over and recombination.
Nov 12, 2018 · How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: crossing over, meiosis I, just the four shown in the diagram, even for a cell with only four chromosomes. Diploid (2n): 2 sets of homologous chromosomes Ploidy = diploid, 2n (4 chromatids); 1 big chromosome, 1 small chromosome in the metaphase cell. See the close-up diagram below. Anaphase I: Instead of chromatids splitting at the centromere, homologous chromosome pairs (now shuffled by crossing over) ... A schematic diagram shows key events in mitosis and meiosis during the ... In human males, the Y chromosome pairs and crosses over with the X chromosome. Diagram 1. Label the side that is mitosis and meiosis. 2. Draw an arrow indicate DNA replication (S-stage). 3. Label the place where crossing over occurs. 4. On mitosis: label metaphase anaphase and cytokinesis. 5. On meiosis: label metaphase1, anaphase1, cytokinesis1. What stages are missing in the mitosis diagram?
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Objective 1, Stages of Meiosis Prophase I: ¾During synapsis, sometimes there is an exchange of homologous parts between non-sister chromatids. This exchange is called crossing over. 8 Objective 1, Stages of Meiosis 9 Objective 1, Stages of Meiosis Prophase I: ¾the spindle apparatus begins to form. ¾the nuclear membrane breaks down: 10
Nov 20, 2018 · There is no crossing over in mitosis. Metaphase. In metaphase II of meiosis, and metaphase of mitosis, chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate due to the action of microtubule spindle fibres emanating from the centrosomes located at opposite cell poles.
10.1.U1 Chromosomes replicate in interphase before meiosis. 10.1.U2 Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister homologous chromads. 10.1.U3 Crossing over produces new combinaons of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells. 10.1.U4 Chiasmata formaon between non-sister chromads can result in an exchange of alleles.
MOVEMENT THROUGH MEIOSIS Cell Cycle Division: Part 1 - Meiotic Bead Diagrams (Without Crossing Over) Prophase I: Nuclear membrane disappears, the centrioles and spindle. fibers appear. Homologous chromosomes pair to form tetrads. Metaphase I: Chromosomes line up at. the metaphase plate between the spindle. fibers. Anaphase I: Tetrads pull ...
Oct 14, 2020 · In meiosis I, a pair of homologous chromosomes separate to produce two diploid daughter cells, each having half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. In contrast, during meiosis II, sister chromatids separate to produce four haploid daughter cells. Also, unlike meiosis I, no genetic recombination by crossing over occurs in meiosis II.
Crossing over is a biological occurrence that happens during meiosis when the paired homologs, or chromosomes of the same type, are lined up. In meiosis, they're lined up on the meiotic plates, [as they're] sometimes called, and those paired chromosomes then have to have some biological mechanism that sort of keeps them together.
How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: crossing over, meiosis I, meiosis II, and genetic variation. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Meiosis and genetic diversity. Fertilization terminology: gametes, zygotes, haploid, diploid. Chromosomal crossover in meiosis I. Phases of meiosis I.
Diagram for Meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which a single cell undergoes division twice to produce four haploid daughter cells. The cells produced are known as the sex cells or gametes (sperms and egg). The diagram of meiosis is beneficial for class 10 and 12 and is frequently asked in the examinations.
By crossing over, the meiosis results in the exchange of the genes and, thus, causes the genetic variations among the species. These variations are the raw materials of the evolutionary process. Read Also: Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram .
Diagram 2. Meiosis without crossing over, but showing the effects of independent assortment. Use colored pens, pencils, etc. to show the series of steps as a cell proceeds through meiosis. Show a different arrangement of the chromosomes in Metaphase I than you did in the previous diagram to illustrate the effects of independent assortment.
Meiosis differs from mitosis primarily because there are two cell divisions in meiosis, resulting in cells with a haploid number of chromosomes. Crossing-over and Recombination During Meiosis. Crossing-over and Recombination During Meiosis. Several different examples of how chromosomes can cross-over during meiosis. Figure Legend: Crossing-over ...
Ex. 2A - Modeling the stages of meiosis Diagram each stage of meiosis as it unfolds for a cell with 1 pair of homologous chromosomes. Be sure to use different colors for maternal and paternal chromosomes and to have one crossover event. MEIOSIS I Important Events Prophase I Tetrad formation and crossing over
Part 2: Modeling Meiosis with Crossing Over Part 2 - Meiotic Division Beads Diagram: Image of page 3. Info icon This preview has intentionally blurred sections. Meiosis, through a process of two nuclear divisions both of which are cell cycle (interphase); Link to diagram of cell in G2 stage of the cell cycle (interphase).
9._____ crossing-over (if any) occurs Short Answer 10. Compare the number and type of cells that result from meiosis vs. mitosis. 11. How do the genetic contents of cells resulting from mitosis and meiosis differ? 12. Comparing and Contrasting Describe a similarity and a difference between meiosis I and meiosis II.
In the diagram, genes B and b are crossed over with each other, making the resulting recombinants after meiosis Ab, AB, ab, and aB.Origins · DNA repair theory · Links to bacterial transformation · Chemistry
♦ Meiosis can be divided in two stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. It is in the prophase of meiosis I that crossing over of the chromosomes takes place, and the homologous chromosomes are separated into two daughter cells. In meiosis II, the sister chromatids are pulled apart from each other to give rise to four haploid daughter cells.
Crossing Over, Genetic recombination, Crossing over during meiosis, Process of genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosome fern life cycle The life cycle of ferns is different from other land plants as both the gametophyte and the sporophyte phases are free living.
Guided Practice. 10 minutes. Display the crossing over diagram. Distribute Crossing over diagrams and markers to students. Instruct students to select two color markers for the assignment and color each of the 2 chromosomes a different color. Allow them to work independently before sharing an example of the color pattern for the 2 chromosomes.
In prophase I of meiosis, the following events occur: Chromosomes condense and attach to the nuclear envelope. Synapsis occurs (a pair of homologous chromosomes lines up closely together) and a tetrad is formed. Each tetrad is composed of four chromatids. Genetic recombination via crossing over may occur.
Meiosis, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each with half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. The process of meiosis is characteristic of organisms that reproduce sexually and have a diploid set of chromosomes in the nucleus.
The crossing over takes place when the chromosomal threads are plectonemically arranged. Although the somatic crossing over is difficult to detect, there is no doubt that it occurs. The exact mechanism is not yet clears (Fig. 16.6). The somatic crossing over may bring several changes in the structure and physiology of the organisms.
Meiosis I (Works Cited See) *1 1. Prophase I Events that occur during prophase of mitosis also occur during prophase I of meiosis. The chromosomes coil up, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, and the centrosomes begin moving apart. The two chromosomes may exchange fragments by a process called crossing over.
During meiosis, an event known as chromosomal crossing over sometimes occurs as a part of recombination. In this process, a region of one chromosome is ...



0 Response to "38 meiosis crossing over diagram"
Post a Comment