37 rough endoplasmic reticulum diagram
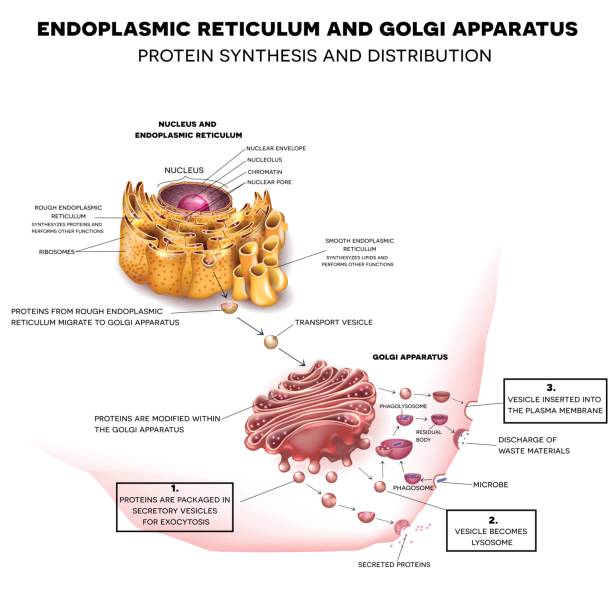
The endoplasmic reticulum, also known as the ER, has two parts; rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is so named because of the ribosomes embedded into the membrane wall of the rough ER. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes found within almost all eukaryotic cells. The membranes are connected to the membrane of the cell's nucleus and are important for many cellular processes such as protein production and the metabolism of lipids and carbohydrates.
The cell was first discovered in 1665 by an English scientist named Robert Hooke. While looking through a microscope, he observed tiny box-like objects in a slice of cork (bark from an oak tree) and named these boxescells.Cells are the basic units of life, which make up all living things.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum diagram
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. [1] [2] Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Granular (Rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER)—Ergastoplasm ... Endoplasmic Reticulum structure-Biology - Stock My Story; Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure, Types and Functions ... Cell organelles (2) Golgi Apparatus Stock Photos & Golgi Apparatus Stock ... Ultrastructural micrograph of mammary glandular epithelial ... The rough ER is studded with ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) The main difference between the rough ER and the smooth ER is that the smooth ER does not have ribosomes attached to its surface. The smooth ER is not involved in protein synthesis; instead, it is the site of lipid and steroid production in the cell. Golgi Apparatus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum diagram. endoplasmic reticulum (ER), in biology, a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions, being important particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins . All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum (ER). D - Rough endoplasmic reticulum . E - Vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum. F- Golgi apparatus. G - Secretory vesicle/granule. H - Mature secretory vesicle/granule/lysosome (b) Functions of part A, C, D and H. A - Supplies energy in the form of ATP. C - Makes ribosome. D - Making protein through incorporating amino acid. At this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. Organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time. Before discussing the functions of organelles within a eukaryotic cell, let us first examine two important components of the cell: the plasma membrane and ... Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Separate from the nuclear membrane, but continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and does not contain ribosomes; site of lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism and detoxification; helps transport materials within the cell. Vesicles
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. The surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is studded with protein-manufacturing ribosomes giving it a 'rough' appearance (hence its name). However, the ribosomes bound to the RER at any one time are not a stable part of this organelle's structure as ribosomes are constantly being bound and released ... The HFL-1 cell model induced by TGF-β1 was used to detect the corresponding indices through intervention with drug-containing serum. The best intervention time for drug-containing serum was detected by the CCK-8 method. Changes in apoptosis, cytoskeleton and rough endoplasmic reticulum structure were detected. An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job. Organelles are involved in many vital cell functions. Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and vacuoles. Of Plant and Animal Cells 7L12 - Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells including major organelles cell membrane cell wall nucleus chloroplasts mitochondria and vacuoles. 5 Rough endoplasmic reticulum RER. Separates the cell from its environment. Plant cells only Cell Parts Functions. Nucleus controls the cells.
Cell Structure and Function Class 8 Science Chapter 8 as per NCERT Book used in CBSE and other Schools. The lesson covers the complete explanation of class 8 Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Function.Topics covered are cells, discovery of cells, cell shape and size, cell numbers, basic structure of cell, cell organelles and the differences between plant and animal cells. Model for chloroplast biogenesis in transgenic petals. (a ... The cell. 6. Non vesicular. Plastids. endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes; Golgi apparatus; Nucleus: the cell's headquarters Diagram of a nucleus with endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes. The nucleus is a relatively big membrane organelle. It is located in the centre of the cell. It looks like a hollow ball made from double membranes. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of flattened membranes called cisternae (mainpoint: I spelt it wrong in the diagram, sorry). It's a continuous single membrane which is also the nuclear outer-membrane. When ribosomes are found on its surface it's known as a rough ER and it transports any proteins made by the ribosomes.
Nucleolus: The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus and take positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protein synthesis.
Microfilaments are long, thin, and stringy proteins. When first produced by the cell, the actin monomers join together to form two parallel polymers of globular-(G)-actin.Once they are joined, the elongated strands twist around each other into a helical orientation having a diameter of about 6-7 nm and are called filamentous-(F)-actin.. Diagram 2 (Heading: Structure and Assembly of ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of flattened membranes called cisternae (mainpoint: I spelt it wrong in the diagram, sorry). It's a continuous single membrane which is also the nuclear outer-membrane. When ribosomes are found on its surface it's known as a rough ER and it transports any proteins made by the ribosomes.
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. [1] Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination.
Nucleolus: The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus and take positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protein synthesis.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum - These are made up of cisternae and tubules and vesicles that are present throughout the cell and involved in protein production. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - These are the storage organelles, which are associated with the production and use of steroids, lipids, and detoxification.
Nucleolus: The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus and take positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protein synthesis.
The structure of the plant cell is also aided by microfilaments. These are rods of actin, a globular protein, that act as structural components of the cytoskeleton, helping to keep the cell's shape. Besides providing the structure, strength, and rigidity of the cell, the cell walls are also porous and allow the movement of materials into and ...
Nucleolus: The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus and take positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protein synthesis.
What are the 13 parts of a plant cell? Each plant cell will have a cell wall, cell membrane, a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, plastids, mitochondria, vacuoles, and various vesicles like peroxisomes. What are the 7 parts of a plant cell? Plant Cell Structure . Cell Wall.
(i) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Inside the cell, there exists a membranous network enclosing a fluid-filled lumen that almost filled the intracellular cavity. It is of two types: It is of two types: (a) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): with ribosomes attached on its surface for synthesising proteins.
The rough ER is studded with ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) The main difference between the rough ER and the smooth ER is that the smooth ER does not have ribosomes attached to its surface. The smooth ER is not involved in protein synthesis; instead, it is the site of lipid and steroid production in the cell. Golgi Apparatus
Granular (Rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER)—Ergastoplasm ... Endoplasmic Reticulum structure-Biology - Stock My Story; Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure, Types and Functions ... Cell organelles (2) Golgi Apparatus Stock Photos & Golgi Apparatus Stock ... Ultrastructural micrograph of mammary glandular epithelial ...
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. [1] [2] Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed.



0 Response to "37 rough endoplasmic reticulum diagram"
Post a Comment